|
UIC Country Code
The UIC Country Code is a two digit-number identifying countries in which members of the International Union of Railways (UIC) are active. The UIC has issued numbering systems for rolling stock ( UIC wagon numbers) and stations that include the country code. The values are defined in UIC leaflet 920-14. The country code had originally been designed as a company code but mainly as a consequence of the reorganisation of the rail sector in Europe changes were necessary. When the former UIC vehicle number became a vehicle register number (European Vehicle Number, EVN) issued by governmental organisations, the code was attributed to the countries. Vehicle numbering is now governed by the Intergovernmental Organisation for International Carriage by Railsee: UTP Marking 2015, Uniform Technical Prescription Applicable to Vehicle Numbers and linked alphabetical marking on the bodywork: THE RAILWAY VEHICLE MARKING, Applicable from 1.1.2015, retrieved fromOTIF page Prescriptions and Other R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union Of Railways
The International Union of Railways (, UIC) is an international rail transport industry body based in Paris. History The railways of Europe had originated during the nineteenth century as many separate concerns across numerous nations; this led to disparate and conflicting standards emerging and thus onto incompatibility. One prominent example was the British Gauge War, during which different rail transport, railway companies were laying different track gauges across Great Britain, causing inefficiency wherever a break of gauge occurred, prior to an Regulating the Gauge of Railways Act 1846, Act of Parliament the issue in 1846 by establishing one standard gauge of . The early effort towards standardisation somewhat influenced railways aboard as well, however various other track gauges persisted and developed across the world; even through to the twenty first century, incompatible track gauges, let alone other issues, persisted to hinder interoperability efforts. Several key eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In Estonia
The rail transport system in Estonia consists of about of railway lines, of which are currently in public use. The infrastructure of the railway network is mostly owned by the state and is regulated and surveyed by the Estonian Technical Surveillance Authority (). All public railways in Estonia are (Russian gauge), the same as in Russia, Belarus, Latvia, and Lithuania. The gauge used in Estonia is also compatible with Finland's gauge. Sometimes it is defined to be (see Rail gauge in Estonia), for example when buying track maintenance or vehicles from Finland. Railways in Estonia today are used mostly for freight transport, but also for passenger traffic, with 8.3 million passengers reported in 2019. Passenger transport is most frequent near Tallinn, centred on the main Tallinn Baltic Station. The Tallinn to Tartu railway is due to be electrified by 2024, with electrification of the remaining network expected to be completed by 2028. 16 new electric trains manufactured b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In Poland
The Polish railways network consists of around of track as of 2023, of which is electrified. The national electrification system runs at 3 kV DC. Poland is a member of the International Union of Railways (UIC), its UIC Country Code is 51. Rail services are operated by a range of public and private rail operators. The state-owned PKP Group operates the majority of rail services. In addition to PKP owned companies, there are a number of private cargo operators, as well as a number of independent passenger operators, with the latter owned predominantly by Voivodeship provincial governments. Overview The vast majority of the network was built before World War II by various railway companies, including by the German Deutsche Reichsbahn and by the Russian Imperial State Railways, and a minor component was built from 1946 onwards by the Communist authorities of the Polish People's Republic. During the invasion of Poland at the beginning of World War II the Polish railwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In Bosnia And Herzegovina
Railway operations in Bosnia and Herzegovina are successors of the Yugoslav Railways within the country boundaries following independence from Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavia in March 1992. Overview The two companies operating services (in their respective divisions following the Dayton Agreement) are: *Railways of Republika Srpska (ŽRS), which operates in Republika Srpska *Railways of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (ŽFBH), which operates in the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Railways of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Railways of Republika Srpska have been members of International Union of Railways (UIC) since 1992 and 1998, respectively. They were assigned separate UIC Country Code, 44 for the Republika Srpska and 50 for the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. The new code for Bosnia and Herzegovina is 49. History The railway system in Bosnia and Herzegovina during the Austro-Hungarian period was shaped by military, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In Japan
Rail transport in Japan is a major means of passenger public transport, transport, especially for mass and high-speed rail, high-speed travel between major cities of Japan, cities and for commuter rail, commuter transport in urban areas. It is used relatively little for rail freight transport, freight transport, accounting for just 0.84% of goods movement. The privatised network is highly efficient, requiring few railway subsidy, subsidies and running with extreme punctuality, though since privatisation several unprofitable but socially valuable lines have been closed by private operators. Overview Rail transport services in Japan are provided by more than 100 private companies, including * Six Japan Railways Group (JR) regional companies (state owned until 1987) which provide passenger services to most parts of Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu; * The nationwide JR freight company; and * 16 major regional companies which provide railway services as part of their corpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In Albania
Railways in Albania are administered by the national railway company ''Hekurudha Shqiptare'' (HSH) (). It operates a standard-gauge railway gauge () rail system in Albania. All trains are, currently, hauled by Czechoslovakia, Czechoslovak-built ČKD diesel-electric locomotives. The small system, now mostly dysfunctional, was considered by many travel guides as a tourist attraction and de facto a panoramic train journey, however the railway from Elbasan to Pogradec, often considered to be the most scenic part of the railway, was closed in 2012 due to the poor condition of the line and the structures along it. The Section of the Shkodër - Vora line south of Laç is closed. The tracks on the Tirana - Durrës line have been removed as it is currently undergoing rehabilitation works. The Durrës - Elbasan service had its Durrës-bound terminus moved up the line to Plazhi due to rehabilitation works at the Durrës station. This is, currently, the only operating passenger rail service ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
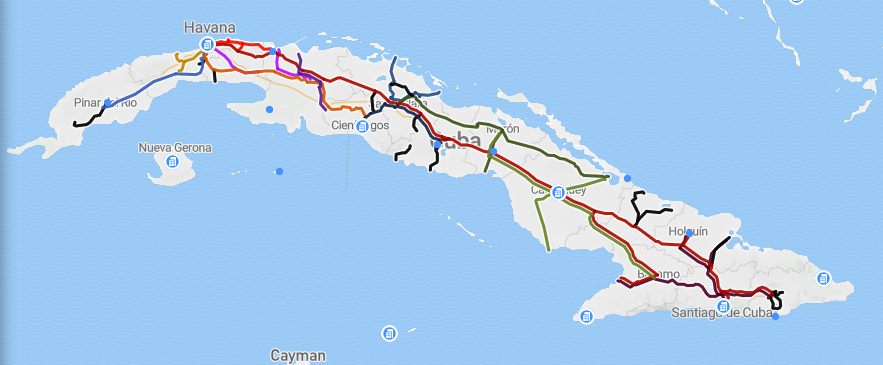
Rail Transport In Cuba
Ferrocarriles de Cuba (FCC) or Ferrocarriles Nacionales de Cuba (English: National Railway Company of Cuba), provides passenger and freight services for Cuba. Route network Ferrocarriles de Cuba uses that extends from Guane, Pinar del Río province, in the westernmost part of the island up to Guantánamo bay in the eastern part. The Central railway runs from Havana to Santiago de Cuba in the eastern region. Most of the system is diesel-powered with electrified. The flagship Train Number 1 travels between Havana and Baracoa. Other long-distance passenger services link Havana to Pinar del Río (western railway), Cienfuegos (South branch), Sancti Spíritus, Bayamo-Manzanillo and Guantánamo. The network connects the six first-level ports in Cuba: Havana, Mariel, Matanzas, Cienfuegos, Nuevitas and Santiago de Cuba, as well as all provincial capital cities. The Hershey Electric Railway is an electrified railway from Havana to Matanzas that was built by the Hershey Company in ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In Laos
Laos has of standard gauge railways, primarily consisting of the Boten–Vientiane railway, which opened in December 2021. It also has a metre gauge railway with two stations in Vientiane, Khamsavath railway station, Khamsavath and Thanaleng railway station, Thanaleng, both of which are connected to Northeastern Line (Thailand), Thailand's railway system. There are a total of 22 stations in Laos - 20 on the Boten–Vientiane railway, and 2 linking to the State Railway of Thailand. History Due to the mountainous geography of Laos, the country had no substantial railway infrastructure, thus traditionally rail transport has not played a significant part in Laos's transport sector. A short portage railway, the Don Det–Don Khon railway, Don Det–Don Khon narrow gauge railway, was built by the French while Laos was a part of French Indochina. The railway crossed over the islands of Don Det and Don Khon, enabling vessels, freight and passengers to travel along the Mekong, Mek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
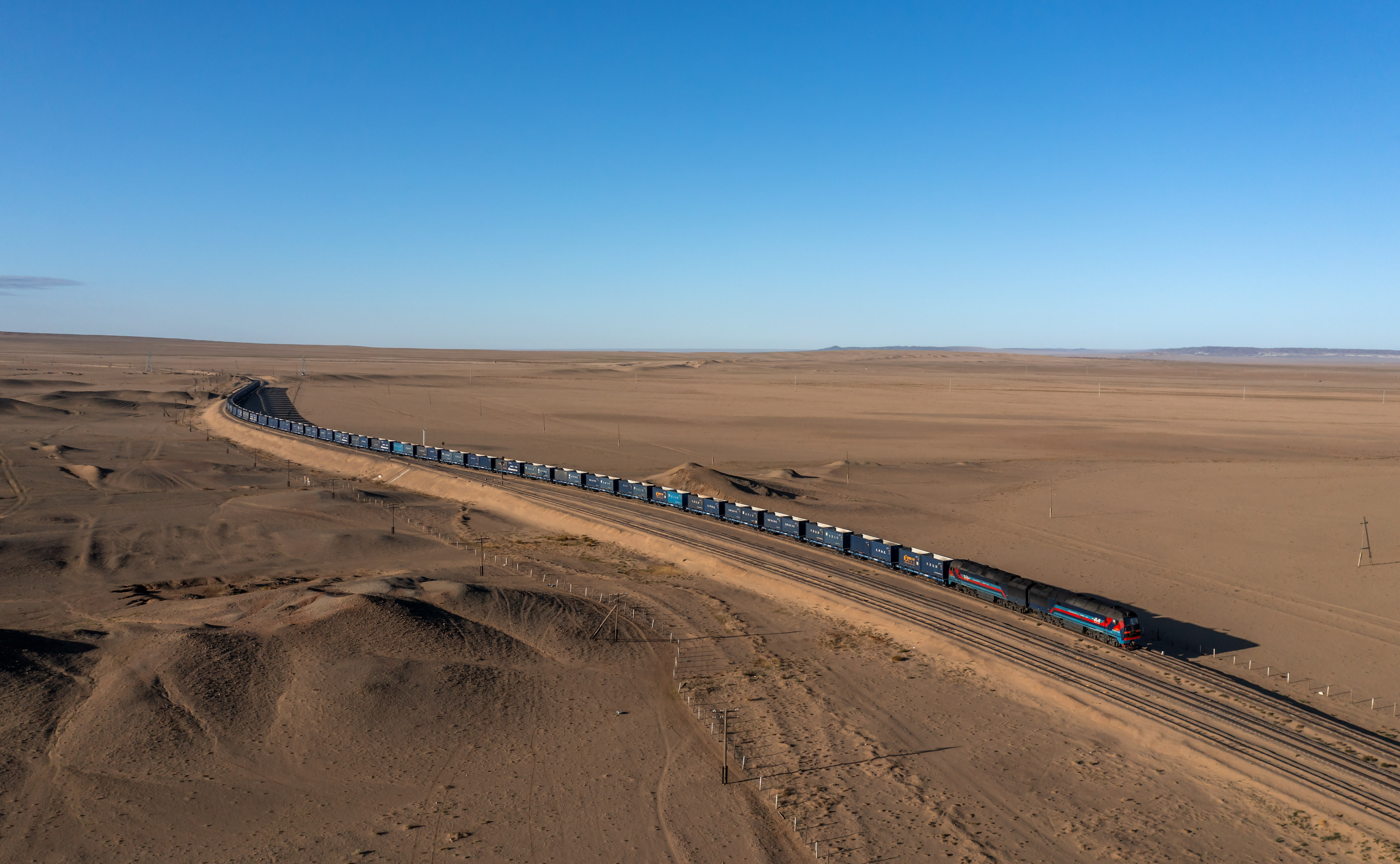
Rail Transport In China
Rail transport is an important mode of long-distance transportation in China. As of 2024, the country had more than of railways, the 2nd longest network in the world. By the end of 2023, China had more than of high-speed rail (HSR), the longest HSR network in the world. The railway sector in China is essentially operated by the central government. Almost all rail operations are handled by the China State Railway Group Company, Limited, a state-owned company created in March 2013 (as China Railway Corporation) after the dissolution of the Ministry of Railways. It was converted into a joint-stock company and placed under the control of the Ministry of Finance in June 2019. China's railways are the busiest in the world. In 2019, railways in China delivered 3.660 billion passenger trips, generating 1,470.66 billion passenger-kilometres and carried 4.389 billion tonnes of freight, generating 3,018 billion cargo tonne-kilometres. Freight traffic turnov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In Vietnam
The railway system in Vietnam is owned and operated by the state-owned Vietnam Railways (). The principal route, the single track North-South Railway running between Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City, accounts for of the network's total length of . The national railway network uses mainly metre gauge, although there are several standard gauge and mixed gauge lines in the north of the country. The first railways in Vietnam were established in the 1880s, with construction beginning in 1888; these included a tram running between the ports of Saigon and Cholon, and a regional rail line connecting Saigon with Mỹ Tho. Railway construction flourished soon afterwards, during the administration of Paul Doumer as Governor-General of French Indochina from 1897 to 1902. It was during this time that construction of the Yunnan–Vietnam and North–South railways began. Construction of the north–south line took over thirty years, finally ending in 1936, during which time other branch line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In Mongolia
Ulaanbaatar Railway (, , , ) is the national railway operator of Mongolia. It was established in 1949 as a joint venture between the Mongolian People’s Republic and the Soviet Union. The company is jointly owned by the Mongolian and Russian government through Russian Railways, with each having a 50% stake. Rail transport is an important means of travel in the landlocked country of Mongolia, which has relatively few paved roads. According to official statistics, rail transport carried 93% of Mongolian freight and 43% of passenger turnover in 2007. The Mongolian rail system employs 12,500 people. The national operator is UBTZ (Ulaanbataar Railway, traditionally also known as Mongolian Railway (MTZ, ). This can be a source of confusion, since MTZ is a distinct company established in 2008 to maintain UBTZ infrastructure. The Mongolian Railway College is located in Ulaanbaatar. The infrastructure of UBTZ consists of 1,815 km of broad gauge lines. UBTZ employs 14,046 people, owns 11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In North Korea
Rail transport in North Korea is provided by Korean State Railway (조선 민주주의 인민 공화국 철도성, ''Chosŏn Minjujuŭi Inmin Konghwaguk Ch'ŏldosŏng'') which is the only rail operator in North Korea. It has a network of over 6,000 km of track, of which the vast majority is Standard-gauge_railway, standard gauge; there is, however, nearly 400 km of Narrow-gauge_railway, narrow gauge lines (762 mm) in various locations around the country.Hayato, Kokubu, 将軍様の鉄道 (Shōgun-sama no Tetsudō), Routes In many cases, the name of the line is a portmanteau of the original termini. However, because of the division of Korea, some lines now terminate short of their original destinations. The following lists the main standard-gauge trunk lines: * Hambuk Line: Chongjin, Ch'ŏngjin Ch'ŏngnyŏn - Rajin-guyok, Rajin, 331.1 km, * Kangwŏn Line: Kowon, Kowŏn - Pyonggang, P'yŏnggang, 145.8 km, * Manp'o Line: Sunchon, North Korea, Sunch'ŏn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |