|
U-69,593
U-69,593 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective κ1-opioid receptor agonist. In animal studies it has been shown to produce antinociception, anti-inflammation, anxiolysis (at low doses), respiratory depression, and diuresis, while having little effect on gastrointestinal motility. It also inhibits the peripheral, though not central secretion of oxytocin and vasopressin in rats. See also * U-50,488 *The dichloro analog is called spiradoline Spiradoline (U-62066) is a drug which acts as a highly selective κ-opioid agonist. It has analgesic, diuretic, and antitussive effects, and produces subjective effects in animals similar to those of ketazocine and alazocine. The main effect .... References Acetamides Opioids 1-Pyrrolidinyl compounds Kappa-opioid receptor agonists Tetrahydrofurans Spiro compounds {{Analgesic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U-50,488
U-50488 is a drug which acts as a highly selective κ-opioid agonist, but without any μ-opioid antagonist effects. It has analgesic, diuretic and antitussive effects, and reverses the memory impairment produced by anticholinergic Anticholinergics (anticholinergic agents) are substances that block the action of the acetylcholine (ACh) neurotransmitter at synapses in the central nervous system, central and peripheral nervous system. These agents inhibit the parasympatheti ... drugs. U-50488 was one of the first selective kappa agonists invented and research on its derivatives has led to the development of a large family of related compounds. This compound has never received FDA approval and there are no reported human cases in the literature involving an U-50488 overdose. See also * LPK-26 * U-47700 * U-69,593 References Chlorobenzene derivatives Acetamides 1-Pyrrolidinyl compounds Kappa-opioid receptor agonists {{Analgesic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug
A drug is any chemical substance other than a nutrient or an essential dietary ingredient, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. Consumption of drugs can be via insufflation (medicine), inhalation, drug injection, injection, smoking, ingestion, absorption (skin), absorption via a dermal patch, patch on the skin, suppository, or sublingual administration, dissolution under the tongue. In pharmacology, a drug is a chemical substance, typically of known structure, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. A pharmaceutical drug, also called a medication or medicine, is a chemical substance used to pharmacotherapy, treat, cure, preventive healthcare, prevent, or medical diagnosis, diagnose a disease or to promote well-being. Traditionally drugs were obtained through extraction from medicinal plants, but more recently also by organic synthesis. Pharmaceutical drugs may be used for a limited duration, or on a re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilateria, bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and Coelenterata, diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the Anatomical_terms_of_location#Rostral,_cranial,_and_caudal, rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain, though precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets. The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opioids
Opioids are a class of Drug, drugs that derive from, or mimic, natural substances found in the Papaver somniferum, opium poppy plant. Opioids work on opioid receptors in the brain and other organs to produce a variety of morphine-like effects, including analgesic, pain relief. The terms "opioid" and "opiate" are sometimes used interchangeably, but the term "opioid" is used to designate all substances, both natural and synthetic, that bind to opioid receptors in the brain. Opiates are alkaloid compounds naturally found in the opium poppy plant ''Papaver somniferum''. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid use disorder, and Cold medicine, suppressing cough. The opioid receptor antagonist naloxone is used to reverse opioid overdose. Extremely potent opioids such as carfentanil are approved only for Veterinary medicine, veterinary use. Opioids are also frequently use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetamides
Acetamide (systematic name: ethanamide) is an organic compound with the formula CH3CONH2. It is an amide derived from ammonia and acetic acid. It finds some use as a plasticizer and as an industrial solvent. The related compound ''N'',''N''-dimethylacetamide (DMA) is more widely used, but it is not prepared from acetamide. Acetamide can be considered an intermediate between acetone, which has two methyl (CH3) groups either side of the carbonyl (CO), and urea which has two amide (NH2) groups in those locations. Acetamide is also a naturally occurring mineral with the IMA symbol: Ace. Production Laboratory scale Acetamide can be produced in the laboratory from ammonium acetate by dehydration: : H4CH3CO2] → CH3C(O)NH2 + H2O Alternatively acetamide can be obtained in excellent yield via ammonolysis of acetylacetone under conditions commonly used in reductive amination. It can also be made from anhydrous acetic acid, acetonitrile and very well dried hydrogen chloride gas, u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiradoline
Spiradoline (U-62066) is a drug which acts as a highly selective κ-opioid agonist. It has analgesic, diuretic, and antitussive effects, and produces subjective effects in animals similar to those of ketazocine and alazocine. The main effect in humans is sedation, along with analgesic and diuretic effects, but significant side effects such as dysphoria and hallucinations A hallucination is a perception in the absence of an external stimulus that has the compelling sense of reality. They are distinguishable from several related phenomena, such as dreaming ( REM sleep), which does not involve wakefulness; pse ... have stopped it from being used clinically. See also * Enadoline References Dissociative drugs Chloroarenes Acetamides 1-Pyrrolidinyl compounds Kappa-opioid receptor agonists {{hallucinogen-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasopressin
Mammalian vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized from the ''AVP'' gene as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then travels down the axon terminating in the posterior pituitary, and is released from vesicles into the circulation in response to extracellular fluid hypertonicity ( hyperosmolality). AVP has two primary functions. First, it increases the amount of solute-free water reabsorbed back into the circulation from the filtrate in the kidney tubules of the nephrons. Second, AVP constricts arterioles, which increases peripheral vascular resistance and raises arterial blood pressure. A third function is possible. Some AVP may be released directly into the brain from the hypothalamus, and may play an important role in social behavior, sexual motivation and pair bonding, and maternal responses to stress. Vasopressin induces differentiation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxytocin
Oxytocin is a peptide hormone and neuropeptide normally produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary. Present in animals since early stages of evolution, in humans it plays roles in behavior that include Human bonding, social bonding, love, reproduction, childbirth, and the Postpartum period, period after childbirth. Oxytocin is released into the bloodstream as a hormone in response to Human sexual activity, sexual activity and during childbirth. It is also available in Oxytocin (medication), pharmaceutical form. In either form, oxytocin stimulates uterine contractions to speed up the process of childbirth. In its natural form, it also plays a role in maternal bonding and lactation, milk production. Production and secretion of oxytocin is controlled by a positive feedback mechanism, where its initial release stimulates production and release of further oxytocin. For example, when oxytocin is released during a contraction of the uterus at the start of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
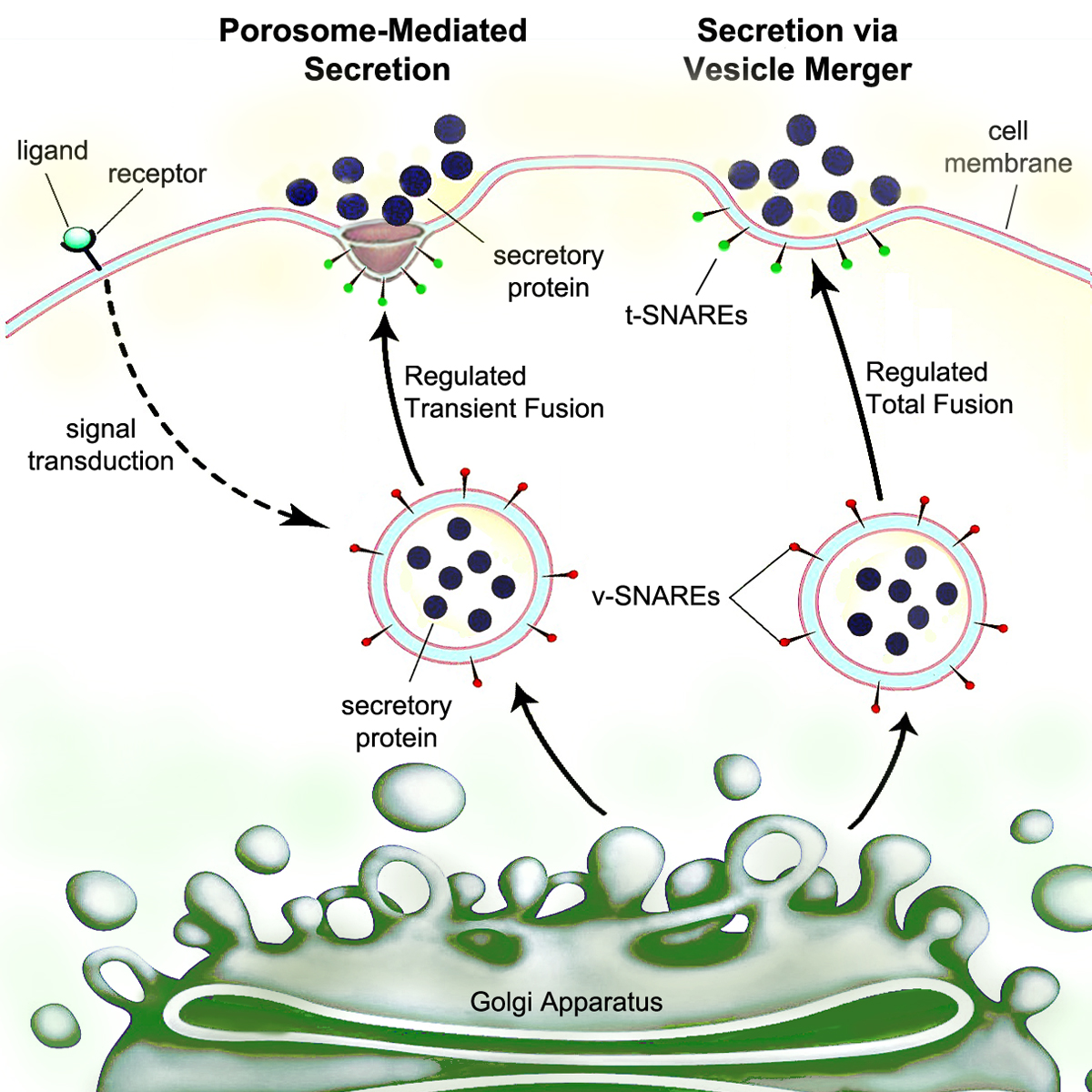
Secretion
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structures embedded in the cell membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell. Secretion in bacterial species means the transport or translocation of effector molecules. For example: proteins, enzymes or toxins (such as cholera toxin in pathogenic bacteria e.g. '' Vibrio cholerae'') from across the interior (cytoplasm or cytosol) of a bacterial cell to its exterior. Secretion is a very important mechanism in bacterial functioning and operation in their natural surrounding environment for adaptation and survival. In eukaryotic cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of Bilateria, bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brain and the spinal cord. The main function of the PNS is to connect the CNS to the Limb (anatomy), limbs and Organ (anatomy), organs, essentially serving as a relay between the brain and spinal cord and the rest of the body. Unlike the CNS, the PNS is not protected by the vertebral column and skull, or by the blood–brain barrier, which leaves it exposed to toxins. The peripheral nervous system can be divided into a somatic nervous system, somatic division and an autonomic nervous system, autonomic division. Each of these can further be differentiated into a sensory and a motor sector. In the somatic nervous system, the cranial nerves are part of the PNS with the exceptions of the olfactory nerve and epithelia and the optic nerve (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |