|
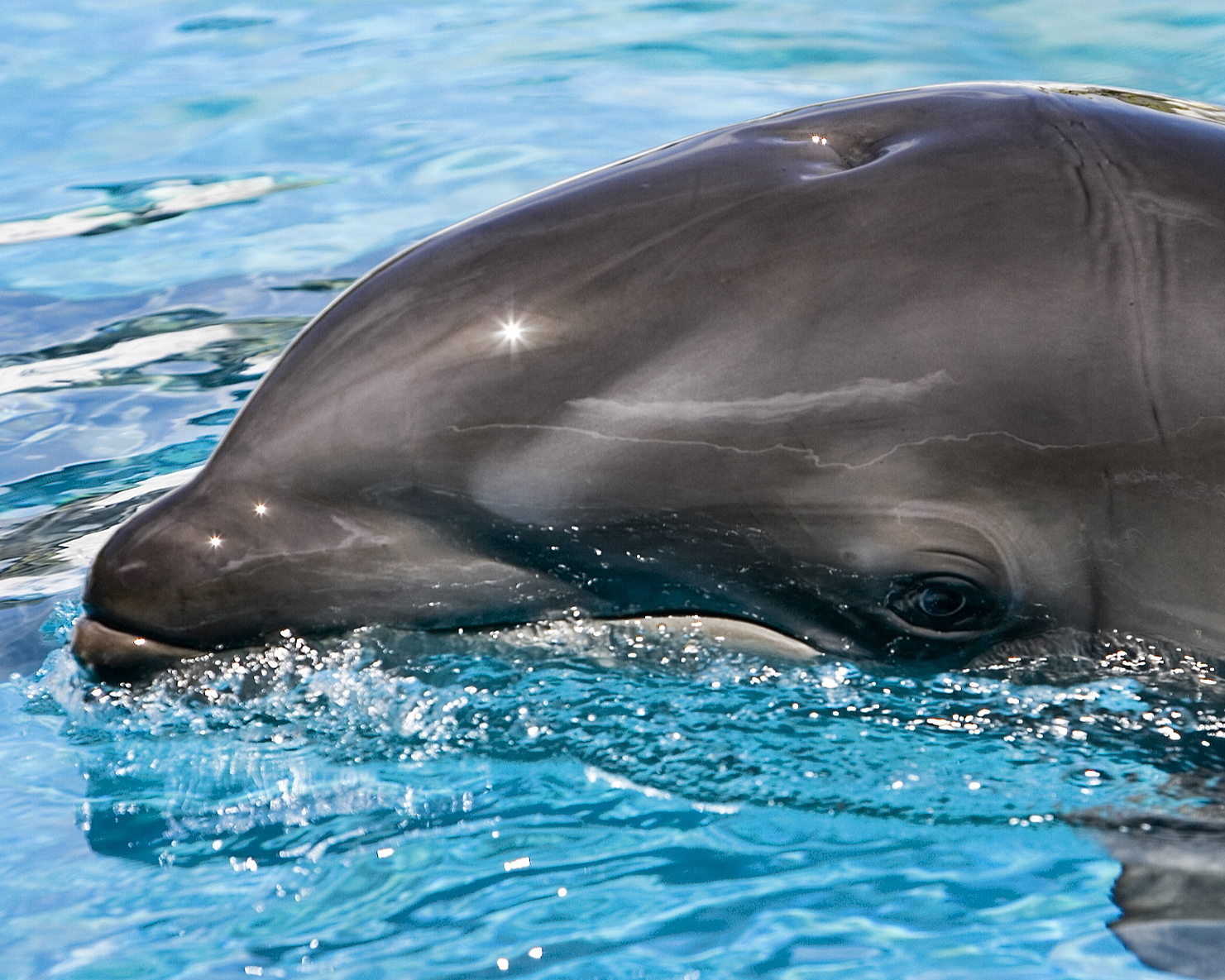
Tursiops Truncatus
Bottlenose dolphins are aquatic mammals in the genus ''Tursiops.'' They are common, cosmopolitan members of the family Delphinidae, the family of oceanic dolphins. Molecular studies show the genus definitively contains two species: the common bottlenose dolphin (''Tursiops truncatus'') and the Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphin (''Tursiops aduncus''). Others, like the Burrunan dolphin (''Tursiops (aduncus) australis''), may be alternately considered their own species or be subspecies of ''T. aduncus''. Bottlenose dolphins inhabit warm and temperate seas worldwide, being found everywhere except for the Arctic and Antarctic Circle regions. Their name derives from the Latin ''tursio'' (dolphin) and ''truncatus'' for their characteristic truncated teeth. Numerous investigations of bottlenose dolphin intelligence have been conducted, examining mimicry, use of artificial language, object categorization, and self-recognition. They can use tools (sponging; using marine sponges to fora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Bottlenose Dolphin
The common bottlenose dolphin or Atlantic bottlenose dolphin (''Tursiops truncatus'') is a wide-ranging marine mammal of the family Delphinidae. The common bottlenose dolphin is a very familiar dolphin due to the wide exposure it gets in captivity in marine parks and dolphinariums, and in movies and television programs.Leatherwood, S., & Reeves, R. (1990). ''The Bottlenose Dolphin''. San Diego: Academic Press, Inc., It is the largest species of the beaked dolphins. It inhabits temperate and tropical oceans throughout the world, and is absent only from polar waters.Klinowska, M. (1991). ''Dolphins, Porpoises and Whales of the World: The IUCN Red Data Book''. Gland, Switzerland, U.K.: IUCN, While formerly known simply as the bottlenose dolphin, this term is now applied to the genus ''Tursiops'' as a whole. As considerable genetic variation has been described within this species, even between neighboring populations, many experts think additional species may be recognized. Taxo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Bottlenose Dolphin
The common bottlenose dolphin or Atlantic bottlenose dolphin (''Tursiops truncatus'') is a wide-ranging marine mammal of the family Delphinidae. The common bottlenose dolphin is a very familiar dolphin due to the wide exposure it gets in captivity in marine parks and dolphinariums, and in movies and television programs.Leatherwood, S., & Reeves, R. (1990). ''The Bottlenose Dolphin''. San Diego: Academic Press, Inc., It is the largest species of the beaked dolphins. It inhabits temperate and tropical oceans throughout the world, and is absent only from polar waters.Klinowska, M. (1991). ''Dolphins, Porpoises and Whales of the World: The IUCN Red Data Book''. Gland, Switzerland, U.K.: IUCN, While formerly known simply as the bottlenose dolphin, this term is now applied to the genus ''Tursiops'' as a whole. As considerable genetic variation has been described within this species, even between neighboring populations, many experts think additional species may be recognized. Taxo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tursiops Truncatus
Bottlenose dolphins are aquatic mammals in the genus ''Tursiops.'' They are common, cosmopolitan members of the family Delphinidae, the family of oceanic dolphins. Molecular studies show the genus definitively contains two species: the common bottlenose dolphin (''Tursiops truncatus'') and the Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphin (''Tursiops aduncus''). Others, like the Burrunan dolphin (''Tursiops (aduncus) australis''), may be alternately considered their own species or be subspecies of ''T. aduncus''. Bottlenose dolphins inhabit warm and temperate seas worldwide, being found everywhere except for the Arctic and Antarctic Circle regions. Their name derives from the Latin ''tursio'' (dolphin) and ''truncatus'' for their characteristic truncated teeth. Numerous investigations of bottlenose dolphin intelligence have been conducted, examining mimicry, use of artificial language, object categorization, and self-recognition. They can use tools (sponging; using marine sponges to fora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquarium
An aquarium (plural: ''aquariums'' or ''aquaria'') is a vivarium of any size having at least one transparent side in which aquatic plants or animals are kept and displayed. Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, aquatic reptiles, such as turtles, and aquatic plants. The term ''aquarium'', coined by English naturalist Philip Henry Gosse, combines the Latin root , meaning 'water', with the suffix , meaning 'a place for relating to'. The aquarium principle was fully developed in 1850 by the chemist Robert Warington, who explained that plants added to water in a container would give off enough oxygen to support animals, so long as the numbers of animals did not grow too large. The aquarium craze was launched in early Victorian England by Gosse, who created and stocked the first public aquarium at the London Zoo in 1853, and published the first manual, ''The Aquarium: An Unveiling of the Wonders of the Deep Sea'' in 1854.Katherine C. Grier (2008) "Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimicry
In evolutionary biology, mimicry is an evolved resemblance between an organism and another object, often an organism of another species. Mimicry may evolve between different species, or between individuals of the same species. Often, mimicry functions to protect a species from predators, making it an anti-predator adaptation. Mimicry evolves if a receiver (such as a predator) perceives the similarity between a mimic (the organism that has a resemblance) and a model (the organism it resembles) and as a result changes its behaviour in a way that provides a selective advantage to the mimic. The resemblances that evolve in mimicry can be visual, acoustic, chemical, tactile, or electric, or combinations of these sensory modalities. Mimicry may be to the advantage of both organisms that share a resemblance, in which case it is a form of mutualism; or mimicry can be to the detriment of one, making it parasitic or competitive. The evolutionary convergence between groups is driven by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Language
Artificial languages are languages of a typically very limited size which emerge either in computer simulations between artificial agents, robot interactions or controlled psychological experiments with humans. They are different from both constructed languages and formal languages in that they have been consciously devised by an individual or group but are the result of (distributed) conventionalisation processes, much like natural languages. Opposed to the idea of a central ''designer'', the field of artificial language evolution in which artificial languages are studied can be regarded as a sub-part of the more general cultural evolution studies. Origin The idea of creation of artificial language arose in 17th and 18th century as a result of gradually decreasing international role of Latin. The initial schemes were mainly aimed at the development of a rational language free from inconsistence of living language and based on classification of concepts. The material of living la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-recognition
In philosophy of self, self-awareness is the experience of one's own personality or individuality. It is not to be confused with consciousness in the sense of qualia. While consciousness is being aware of one's environment and body and lifestyle, self-awareness is the recognition of that awareness. Self-awareness is how an individual consciously knows and understands their own character, feelings, motives, and desires. Neurobiological basis Introduction There are questions regarding what part of the brain allows us to be self-aware and how we are biologically programmed to be self-aware. V.S. Ramachandran has speculated that mirror neurons may provide the neurological basis of human self-awareness. In an essay written for the Edge Foundation in 2009, Ramachandran gave the following explanation of his theory: "... I also speculated that these neurons can not only help simulate other people's behavior but can be turned 'inward'—as it were—to create second-order represen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proceedings Of The Royal Society
''Proceedings of the Royal Society'' is the main research journal of the Royal Society. The journal began in 1831 and was split into two series in 1905: * Series A: for papers in physical sciences and mathematics. * Series B: for papers in life sciences. Many landmark scientific discoveries are published in the Proceedings, making it one of the most historically significant science journals. The journal contains several articles written by the most celebrated names in science, such as Paul Dirac, Werner Heisenberg, Ernest Rutherford, Erwin Schrödinger, William Lawrence Bragg, Lord Kelvin, J.J. Thomson, James Clerk Maxwell, Dorothy Hodgkin and Stephen Hawking. In 2004, the Royal Society began ''The Journal of the Royal Society Interface'' for papers at the interface of physical sciences and life sciences. History The journal began in 1831 as a compilation of abstracts of papers in the ''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society'', the older Royal Society publication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Mine
A naval mine is a self-contained explosive device placed in water to damage or destroy surface ships or submarines. Unlike depth charges, mines are deposited and left to wait until they are triggered by the approach of, or contact with, any vessel or a particular vessel type, akin to anti-infantry vs. anti-vehicle mines. Naval mines can be used offensively, to hamper enemy shipping movements or lock vessels into a harbour; or defensively, to protect friendly vessels and create "safe" zones. Mines allow the minelaying force commander to concentrate warships or defensive assets in mine-free areas giving the adversary three choices: undertake an expensive and time-consuming minesweeping effort, accept the casualties of challenging the minefield, or use the unmined waters where the greatest concentration of enemy firepower will be encountered. Although international law requires signatory nations to declare mined areas, precise locations remain secret; and non-complying individual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flipper (1964 TV Series)
''Flipper'' is an American television program broadcast on NBC from September 19, 1964, until April 15, 1967. Flipper, a bottlenose dolphin, is the pet of Porter Ricks, chief warden at Coral Key Park and Marine Preserve (a fictional version of John Pennekamp Coral Reef State Park in Key Largo, Florida), and his two young sons, Sandy and Bud. The show has been dubbed an "aquatic ''Lassie''", and a considerable amount of children's merchandise inspired by the show was produced during its first run. Production The television show is an extension of the 1963 film '' Flipper'' starring Chuck Connors and Luke Halpin as Porter and Sandy Ricks, and of its 1964 sequel, '' Flipper's New Adventure''. For the second film, the producers scripted that Mrs. Ricks had died, making Porter now a single parent, with Brian Kelly taking over the role as Porter Ricks, but now as a trainee park ranger rather than a fisherman. In adapting the films to a television series, the producers gave Porter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic Circle
The Arctic Circle is one of the two polar circles, and the most northerly of the five major circles of latitude as shown on maps of Earth. Its southern equivalent is the Antarctic Circle. The Arctic Circle marks the southernmost latitude at which, on the December solstice, the shortest day of the year in the northern hemisphere, the sun will not rise all day, and on the June solstice, the longest day of the year in the northern hemisphere, the sun will not set. These phenomena are referred to as polar night and midnight sun respectively, and the further north one progresses, the more pronounced these effects become. For example, in the Russian port city of Murmansk, three degrees above the Arctic Circle, the sun does not rise for 40 successive days in midwinter. The position of the Arctic Circle is not fixed and currently runs north of the Equator. Its latitude depends on the Earth's axial tilt, which fluctuates within a margin of more than 2° over a 41,000-year per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(3).jpg)