|
Tungsten Nitride
Tungsten nitride (W2N, WN, WN2) is an inorganic compound, a nitride of tungsten. It is a hard, solid, brown-colored ceramic material that is electrically conductive and decomposes in water. It is used in microelectronics as a contact material, for conductive layers, and barrier layers between silicon and other metals, e.g. tungsten or copper. It is less commonly used than titanium nitride or tungsten films. Tungsten nitride forms together with tungsten dioxide, tungsten trioxide, and tungsten pentoxide when an incandescent light bulb breaks while the filament is heated. Tungsten silicide Tungsten silicide (WSi2) is an inorganic compound, a silicide of tungsten. It is an electrically conductive ceramic material. Chemistry Tungsten silicide can react violently with substances such as strong acids, fluorine, oxidizers, and interh ... is another material with similar use. References Tungsten compounds Nitrides Ceramic materials {{material-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitride
In chemistry, a nitride is an inorganic compound of nitrogen. The "nitride" anion, N3- ion, is very elusive but compounds of nitride are numerous, although rarely naturally occuring. Some nitrides have a find applications, such as wear-resistant coatings (e.g., titanium nitride, TiN), hard ceramic materials (e.g., silicon nitride, Si3N4), and semiconductors (e.g., gallium nitride, GaN). The development of GaN-based light emitting diodes was recognized by the 2014 Nobel Prize in Physics. Metal nitrido complexes are also common. Synthesis of inorganic metal nitrides is challenging because nitrogen gas (N2) is not very reactive at low temperatures, but it becomes more reactive at higher temperatures. Therefore, a balance must be achieved between the low reactivity of nitrogen gas at low temperatures and the entropy driven formation of N2 at high temperatures. However, synthetic methods for nitrides are growing more sophisticated and the materials are of increasing technological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isolated as a metal in 1783. Its important ores include scheelite and wolframite, the latter lending the element its alternate name. The free element is remarkable for its robustness, especially the fact that it has the highest melting point of all known elements barring carbon (which sublimes at normal pressure), melting at . It also has the highest boiling point, at . Its density is , comparable with that of uranium and gold, and much higher (about 1.7 times) than that of lead. Polycrystalline tungsten is an intrinsically brittle and hard material (under standard conditions, when uncombined), making it difficult to work. However, pure single-crystalline tungsten is more ductile and can be cut with a hard-steel hacksaw. Tungsten occ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain, and brick. The earliest ceramics made by humans were pottery objects (''pots,'' ''vessels or vases'') or figurines made from clay, either by itself or mixed with other materials like silica, hardened and sintered in fire. Later, ceramics were glazed and fired to create smooth, colored surfaces, decreasing porosity through the use of glassy, amorphous ceramic coatings on top of the crystalline ceramic substrates. Ceramics now include domestic, industrial and building products, as well as a wide range of materials developed for use in advanced ceramic engineering, such as in semiconductors. The word "'' ceramic''" comes from the Greek word (), "of pottery" or "for pottery", from (), "potter's clay, tile, pottery". The earliest kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
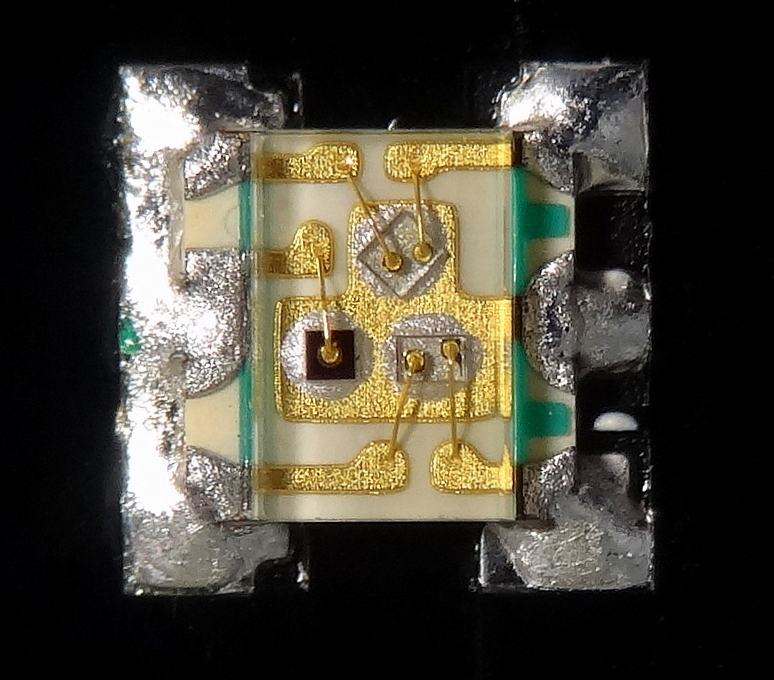
Microelectronics
Microelectronics is a subfield of electronics. As the name suggests, microelectronics relates to the study and manufacture (or microfabrication) of very small electronic designs and components. Usually, but not always, this means micrometre-scale or smaller. These devices are typically made from semiconductor materials. Many components of normal electronic design are available in a microelectronic equivalent. These include transistors, capacitors, inductors, resistors, diodes and (naturally) insulators and conductors can all be found in microelectronic devices. Unique wiring techniques such as wire bonding are also often used in microelectronics because of the unusually small size of the components, leads and pads. This technique requires specialized equipment and is expensive. Digital integrated circuits (ICs) consist of billions of transistors, resistors, diodes, and capacitors. Analog circuits commonly contain resistors and capacitors as well. Inductors are used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wire Bonding
Wire bonding is the method of making interconnections between an integrated circuit (IC) or other semiconductor device and its packaging during semiconductor device fabrication. Although less common, wire bonding can be used to connect an IC to other electronics or to connect from one printed circuit board (PCB) to another. Wire bonding is generally considered the most cost-effective and flexible interconnect technology and is used to assemble the vast majority of semiconductor packages. Wire bonding can be used at frequencies above 100 GHz. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barrier Layer
A diffusion barrier is a thin layer (usually micrometres thick) of metal usually placed between two other metals. It is done to act as a barrier to protect either one of the metals from corrupting the other.. Adhesion of a plated metal layer to its substrate requires a physical interlocking, inter-diffusion of the deposit or a chemical bonding between plate and substrate in order to work. The role of a diffusion barrier is to prevent or to retard the inter-diffusion of the two superposed metals. Therefore, to be effective, a good diffusion barrier requires inertness with respect to adjacent materials. To obtain good adhesion and a diffusion barrier simultaneously, the bonding between layers needs to come from a chemical reaction of limited range at both boundaries. Materials providing good adhesion are not necessarily good diffusion barriers and vice versa. Consequently, there are cases where two or more separate layers must be used to provide a proper interface between substrates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic table: carbon is above it; and germanium, tin, lead, and flerovium are below it. It is relatively unreactive. Because of its high chemical affinity for oxygen, it was not until 1823 that Jöns Jakob Berzelius was first able to prepare it and characterize it in pure form. Its oxides form a family of anions known as silicates. Its melting and boiling points of 1414 °C and 3265 °C, respectively, are the second highest among all the metalloids and nonmetals, being surpassed only by boron. Silicon is the eighth most common element in the universe by mass, but very rarely occurs as the pure element in the Earth's crust. It is widely distributed in space in cosmic dusts, planetoids, and planets as various forms of silicon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable metallic form ( native metals). This led to very early human use in several regions, from circa 8000 BC. Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, circa 5000 BC; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, c. 4000 BC; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium Nitride
Titanium nitride (TiN; sometimes known as Tinite) is an extremely hard ceramic material, often used as a physical vapor deposition (PVD) coating on titanium alloys, steel, carbide, and aluminium components to improve the substrate's surface properties. Applied as a thin coating, TiN is used to harden and protect cutting and sliding surfaces, for decorative purposes (due to its golden appearance), and as a non-toxic exterior for medical implants. In most applications a coating of less than is applied. Characteristics TiN has a Vickers hardness of 1800–2100, a modulus of elasticity of 251 GPa, a thermal expansion coefficient of 9.35 K−1, and a superconducting transition temperature of 5.6 K. TiN will oxidize at 800 °C in a normal atmosphere. TiN has a brown color, and appears gold when applied as a coating. It is chemically stable at 20 °C, according to laboratory tests, but can be slowly attacked by concentrated acid solutions with rising temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungsten Dioxide
Tungsten(IV) oxide is the chemical compound with the formula W O2. The bronze-colored solid crystallizes in a monoclinic cell. The rutile Rutile is an oxide mineral composed of titanium dioxide (TiO2), the most common natural form of TiO2. Rarer polymorphs of TiO2 are known, including anatase, akaogiite, and brookite. Rutile has one of the highest refractive indices at visib ...-like structure features distorted octahedral WO6 centers with alternate short W–W bonds (248 pm). Each tungsten center has the d2 configuration, which gives the material a high electrical conductivity. WO2 is prepared by reduction of WO3 with tungsten powder over the course of 40 hours at 900 °C. An intermediate in this reaction is the partially reduced, mixed valence species W18O49. :2 WO3 + W → 3 WO2 The molybdenum analogue MoO2 is prepared similarly. Single crystals are obtained by chemical transport technique using iodine. Iodine transports the WO2 in the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungsten Trioxide
Tungsten(VI) oxide, also known as tungsten trioxide is a chemical compound of oxygen and the transition metal tungsten, with formula WO3. The compound is also called tungstic anhydride, reflecting its relation to tungstic acid . It is a light yellow crystalline solid. Tungsten(VI) oxide occurs naturally in the form of hydrates, which include minerals: tungstite WO3·H2O, meymacite WO3·2H2O and hydrotungstite (of the same composition as meymacite, however sometimes written as H2WO4). These minerals are rare to very rare secondary tungsten minerals. History In 1841, a chemist named Robert Oxland gave the first procedures for preparing tungsten trioxide and sodium tungstate. He was granted patents for his work soon after, and is considered to be the founder of systematic tungsten chemistry. Structure and properties The crystal structure of tungsten trioxide is temperature dependent. It is tetragonal at temperatures above 740 °C, orthorhombic from 330 to 740 °C, monoclini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungsten Pentoxide
Tungsten pentoxide () was reported in early literature but proved to have the stoichiometry W18O49.Wells A.F. (1984) ''Structural Inorganic Chemistry'' 5th edition Oxford Science Publications Sometimes called mineral blue, it is a blue solid formed by the reaction of tungsten trioxide, WO3, and tungsten metal at 700 °C. Intermediate oxides of tungsten There are a number of these unusual intermediate oxides formed from reacting metal and trioxide namely, W20O58, W24O70. W18O49 contains both octahedral and pentagonal bipyramidal co-ordination of the metal atoms by oxygen. See also * Tungsten(III) oxide * Tungsten(IV) oxide *Tungsten(VI) oxide Tungsten(VI) oxide, also known as tungsten trioxide is a chemical compound of oxygen and the transition metal tungsten, with formula WO3. The compound is also called tungstic anhydride, reflecting its relation to tungstic acid . It is a light ... References Tungsten compounds Transition metal oxides {{inorganic-compound-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |