|
Triphenylcarbinol
Triphenylmethanol (also known as triphenylcarbinol, TrOH) is an organic compound. It is a white crystalline solid that is insoluble in water and petroleum ether, but well soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, and benzene. In strongly acidic solutions, it produces an intensely yellow color, due to the formation of a stable "trityl" carbocation. Many derivatives of triphenylmethanol are important dyes. History After the German chemist August Kekulé and his Belgian student Antoine Paul Nicolas Franchimont (1844–1919) first synthesized triphenylmethane in 1872, the Russian doctoral student Walerius Hemilian (1851–1914) first synthesized triphenylmethanol in 1874 by reacting triphenylmethyl bromide with water as well as by oxidizing triphenylmethane. Structure and properties Triphenylmethanol features three phenyl (Ph) rings and an alcohol group bound to a central tetrahedral carbon atom. All three C–Ph bonds are typical of ''sp''3-''sp''2 carbon-carbon bonds with lengths of appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylmagnesium Bromide
Phenylmagnesium bromide, with the simplified formula , is a magnesium-containing organometallic compound. It is commercially available as a solution in diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran (THF). Phenylmagnesium bromide is a Grignard reagent. It is often used as a synthetic equivalent for the phenyl "Ph−" synthon. Preparation Phenylmagnesium bromide is commercially available as solutions of diethyl ether or THF. Laboratory preparation involves treating bromobenzene with magnesium metal, usually in the form of turnings. A small amount of iodine may be used to activate the magnesium to initiate the reaction. Coordinating solvents such as ether or THF, are required to solvate (complex) the magnesium(II) center. The solvent must be aprotic since alcohols and water contain an acidic proton and thus react with phenylmagnesium bromide to give benzene. Carbonyl-containing solvents, such as acetone and ethyl acetate, are also incompatible with the reagent. Structure Although phenylmagn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triphenylmethane
Triphenylmethane, or triphenyl methane, is the hydrocarbon with the formula (C6H5)3CH. This colorless solid is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents and not in water. Triphenylmethane is the basic skeleton of many synthetic dyes called triarylmethane dyes, many of them are pH indicators, and some display fluorescence. A trityl group in organic chemistry is a triphenylmethyl group Ph3C, e.g. triphenylmethyl chloride (trityl chloride) and the triphenylmethyl radical (trityl radical). Preparation Triphenylmethane was first synthesized in 1872 by the German chemist August Kekulé and his Belgian student Antoine Paul Nicolas Franchimont (1844–1919) by heating diphenylmercury (Hg(C6H5)2, ''Quecksilberdiphenyl'') with benzal chloride (C6H5CHCl2, ''Benzylenchlorid''). Triphenylmethane can be synthesized by Friedel–Crafts reaction from benzene and chloroform with aluminium chloride catalyst: :3 C6H6 + CHCl3 → Ph3CH + 3 HCl Alternatively, benzene may react with carbon tetrachloride us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical and the simplest aliphatic alcohol, with the formula C H3 O H (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is a light, volatile, colourless, flammable liquid with a distinctive alcoholic odour similar to that of ethanol (potable alcohol). A polar solvent, methanol acquired the name wood alcohol because it was once produced chiefly by the destructive distillation of wood. Today, methanol is mainly produced industrially by hydrogenation of carbon monoxide. Methanol consists of a methyl group linked to a polar hydroxyl group. With more than 20 million tons produced annually, it is used as a precursor to other commodity chemicals, including formaldehyde, acetic acid, methyl tert-butyl ether, methyl benzoate, anisole, peroxyacids, as well as a host of more specialised chemicals. Occurrence Small amounts of methanol are present in normal, healthy hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triarylmethane Dye
Triarylmethane dyes are synthetic organic compounds containing triphenylmethane backbones. As dyes, these compounds are intensely colored. They are produced industrially as dyes. Families Triarylmethane dyes can be grouped into families according to the nature of the substituents on the aryl groups. In some cases, the anions associated with the cationic dyes (say crystal violet) vary even though the name of the dye does not. Often it is shown as chloride. Methyl violet dyes Methyl violet dyes have dimethylamino groups at the ''p''-positions of two aryl groups. Image:Methyl Violet 2B.png, Methyl violet 2B Image:Methyl Violet 6B.png, Methyl violet 6B Image:Methyl Violet 10B.png, Methyl violet 10B Fuchsine dyes Fuchsine dyes have primary or secondary amines (NH2 or NHMe) functional groups at the ''p''-positions of each aryl group. File:Pararosaniline.png, Pararosaniline File:Rosaniline hydrochloride.svg, Fuchsine (hydrochloride salt) Neofuchsin.svg, New fuchsine (As chlorid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthesis Of Triphenylmethanol
Synthesis or synthesize may refer to: Science Chemistry and biochemistry *Chemical synthesis, the execution of chemical reactions to form a more complex molecule from chemical precursors ** Organic synthesis, the chemical synthesis of organic compounds ***Total synthesis, the complete organic synthesis of complex organic compounds, usually without the aid of biological processes ***Convergent synthesis or linear synthesis, a strategy to improve the efficiency of multi-step chemical syntheses **Dehydration synthesis, a chemical synthesis resulting in the loss of a water molecule * Biosynthesis, the creation of an organic compound in a living organism, usually aided by enzymes **Photosynthesis, a biochemical reaction using a carbon molecule to produce an organic molecule, using sunlight as a catalyst **Chemosynthesis, the synthesis of biological compounds into organic waste, using methane or an oxidized molecule as a catalyst **Amino acid synthesis, the synthesis of an amino ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diethyl Carbonate
Diethyl carbonate (sometimes abbreviated DEC) is an ester of carbonic acid and ethanol with the formula OC(OCH2CH3)2. At room temperature (25 °C) diethyl carbonate is a colorless liquid with a low flash point. Diethyl carbonate is used as a solvent such as in erythromycin intramuscular injections. It can be used as a component of electrolytes in lithium batteries. It has been proposed as a fuel additive to support cleaner diesel fuel combustion because its high boiling point might reduce blended fuels' volatility, minimizing vapor buildup in warm weather that can block fuel lines. As a fuel additive, it can reduce emissions such as volatile organic compounds, CO2, and particulates.{{cite journal , last1=Shukla , first1=Kartikeya , last2=Srivastava , first2=Vimal Chandra , date=2016 , title=Diethyl carbonate: critical review of synthesis routes, catalysts used and engineering aspects , url=https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/pdf/article/2016/ra/c6ra02518h , journal=RSC Advance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grignard Reaction
The Grignard reaction () is an organometallic chemical reaction in which alkyl, allyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides ( Grignard reagent) is added to a carbonyl group in an aldehyde or ketone. This reaction is important for the formation of carbon–carbon bonds. The reaction of an organic halide with magnesium is ''not'' a Grignard reaction, but provides a Grignard reagent. : Grignard reactions and reagents were discovered by and are named after the French chemist François Auguste Victor Grignard (University of Nancy, France), who published it in 1900 and was awarded the 1912 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work. Reaction mechanism Because carbon is more electronegative than magnesium, the carbon attached to magnesium functions as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon atom that is present within the polar bond of a carbonyl group. The addition of the Grignard reagent to the carbonyl typically proceeds through a six-membered ring transition state. Based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzophenone
Benzophenone is the organic compound with the formula (C6H5)2CO, generally abbreviated Ph2CO. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. Benzophenone is a widely used building block in organic chemistry, being the parent diarylketone. Uses Benzophenone can be used as a photo initiator in UV(Ultra-violet)-curing applications such as inks, imaging, and clear coatings in the printing industry. Benzophenone prevents ultraviolet ( UV) light from damaging scents and colors in products such as perfumes and soaps. Benzophenone can also be added to plastic packaging as a UV blocker to prevent photo-degradation of the packaging polymers or its contents. Its use allows manufacturers to package the product in clear glass or plastic (such as a PETE water bottle). Without it, opaque or dark packaging would be required. In biological applications, benzophenones have been used extensively as photophysical probes to identify and map peptide–protein interactions. Benzophenone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Benzoate
Methyl benzoate is an organic compound. It is an ester with the chemical formula C6H5CO2CH3. It is a colorless liquid that is poorly soluble in water, but miscible with organic solvents. Methyl benzoate has a pleasant smell, strongly reminiscent of the fruit of the feijoa tree, and it is used in perfumery. It also finds use as a solvent and as a pesticide used to attract insects such as orchid bees. Synthesis and reactions Methyl benzoate is formed by the condensation of methanol and benzoic acid, in presence of a strong acid.. Methyl benzoate reacts at both the ring and the ester, depending on the substrate. Electrophiles attack the ring, illustrated by acid-catalysed nitration with nitric acid to give methyl 3-nitrobenzoate. Nucleophiles attack the carbonyl center, illustrated by hydrolysis with addition of aqueous NaOH to give methanol and sodium benzoate. Occurrence Methyl benzoate can be isolated from the freshwater fern ''Salvinia molesta''. It is one of many com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
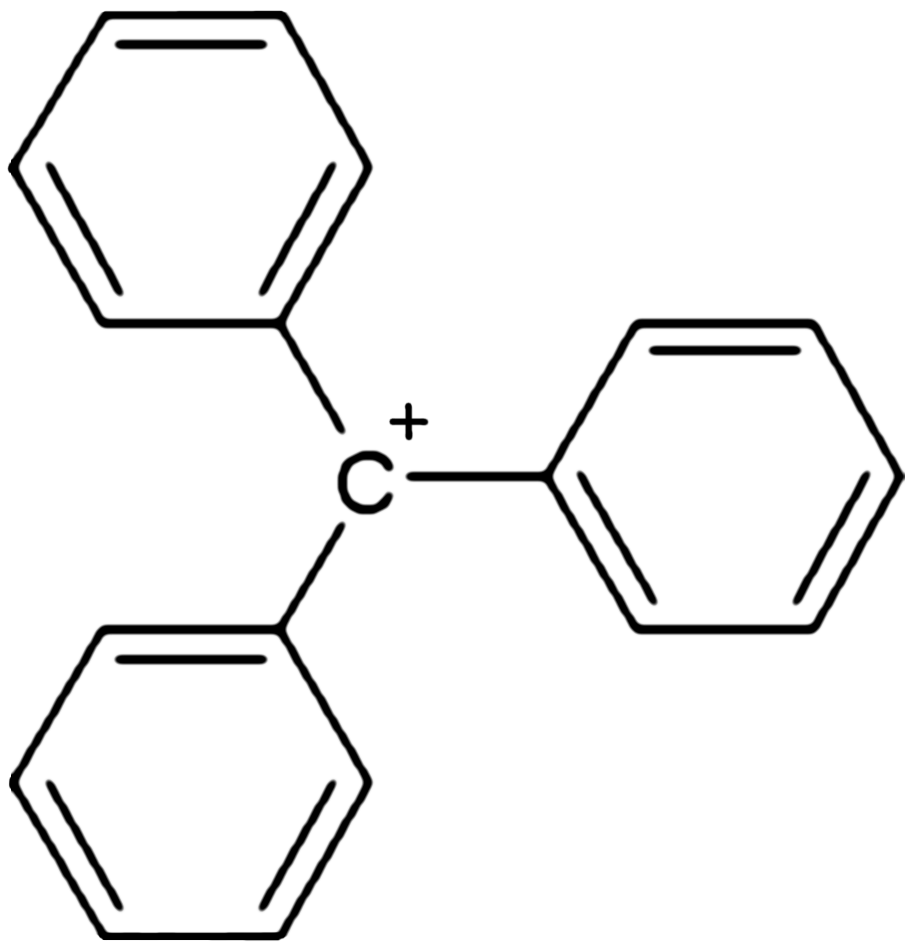
Trityl Cation
In chemistry, triphenylcarbenium, triphenylmethyl cation, tritylium , or trityl cation is an ion with formula or , consisting of a carbon atom with a positive charge connected to three phenyl groups. It is a charged version of the triphenylmethyl radical •. The name is often abbreviated to triphenylmethyl or trityl in salts, although these names also denote the chemical group in compounds like triphenylmethyl chloride that do not contain the cation. Triphenylcarbenium is a relatively stable carbenium ion, because the positive charge is partially distributed among 10 of the carbon atoms (the 3 carbon atoms in the ''ortho'' and ''para'' positions of each of the three phenyl groups, plus the central carbon atom). Derivatives The cation exists in important chemical reagents and catalysts such as triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate . Related salts are known with diverse anions including (), hexachloroantimonate (), and perchlorate (). This and other similar cations can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (chemistry)
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula . Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (), secondary () and tertiary () alcohols. The suffix ''-ol'' appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority. When a higher priority group is present in the compound, the prefix ''hydroxy-'' is used in its IUPAC name. The suffix ''-ol'' in non-IUPAC names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance is an alcohol. However, some compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroperoxide
Hydroperoxides or peroxols are Chemical compound, compounds containing the hydroperoxide functional group (ROOH). If the R is organic, the compounds are called organic hydroperoxides. Such compounds are a subset of organic peroxides, which have the formula ROOR. Organic hydroperoxides can either intentionally or unintentionally initiate explosive polymerisation in materials with Unsaturated bond, unsaturated chemical bonds. Properties The O−O bond length in peroxides is about 1.45 Ångström, Å, and the R−O−O angles (R = H, C) are about 110° (water-like). Characteristically, the C−O−O−H dihedral angles are about 120°. The O−O bond is relatively weak, with a bond dissociation energy of , less than half the strengths of C−C, C−H, and C−O bonds. Hydroperoxides are typically more volatile than the corresponding alcohols: * tert-Butyl hydroperoxide, ''tert''-BuOOH (b.p. 36°C) vs tert-Butyl alcohol, ''tert''-BuOH (b.p. 82-83°C) * Methyl hydroperoxide, CH3O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |