|
Trichloromethyl Compounds
The trichloromethyl group is a functional group that has the formula –CCl3. The naming of is group is derived from the methyl group (which has the formula –CH3), by replacing each hydrogen atom by a chlorine atom. Compounds with this group are a subclass of the organochlorines. Some notable examples of compounds with this group are trichloromethane H–, 1,1,1-trichloroethane –, and chloral –. The trichloromethyl group has a significant electronegativity. For this reason, trichloromethyl-substituted acids, such as trichloromethanesulfonic acid, are often stronger than the original. For example, the acidity constant (pKa) of trichloroacetic acid – is 0.77, whereas that of acetic acid is 4.76. By the same principle, the trichloromethyl group generally lowers the basicity of organic compounds, e.g. trichloroethanol. See also * Trifluoromethyl group The trifluoromethyl group is a functional group that has the formula -CF3. The naming of is group is derived from the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichloromethyl Group
The trichloromethyl group is a functional group that has the formula –CCl3. The naming of is group is derived from the methyl group (which has the formula –CH3), by replacing each hydrogen atom by a chlorine atom. Compounds with this group are a subclass of the organochlorines. Some notable examples of compounds with this group are trichloromethane H–, 1,1,1-trichloroethane –, and chloral –. The trichloromethyl group has a significant electronegativity. For this reason, trichloromethyl-substituted acids, such as trichloromethanesulfonic acid, are often stronger than the original. For example, the acidity constant (pKa) of trichloroacetic acid – is 0.77, whereas that of acetic acid is 4.76. By the same principle, the trichloromethyl group generally lowers the basicity of organic compounds, e.g. trichloroethanol. See also * Trifluoromethyl group The trifluoromethyl group is a functional group that has the formula -CF3. The naming of is group is derived from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
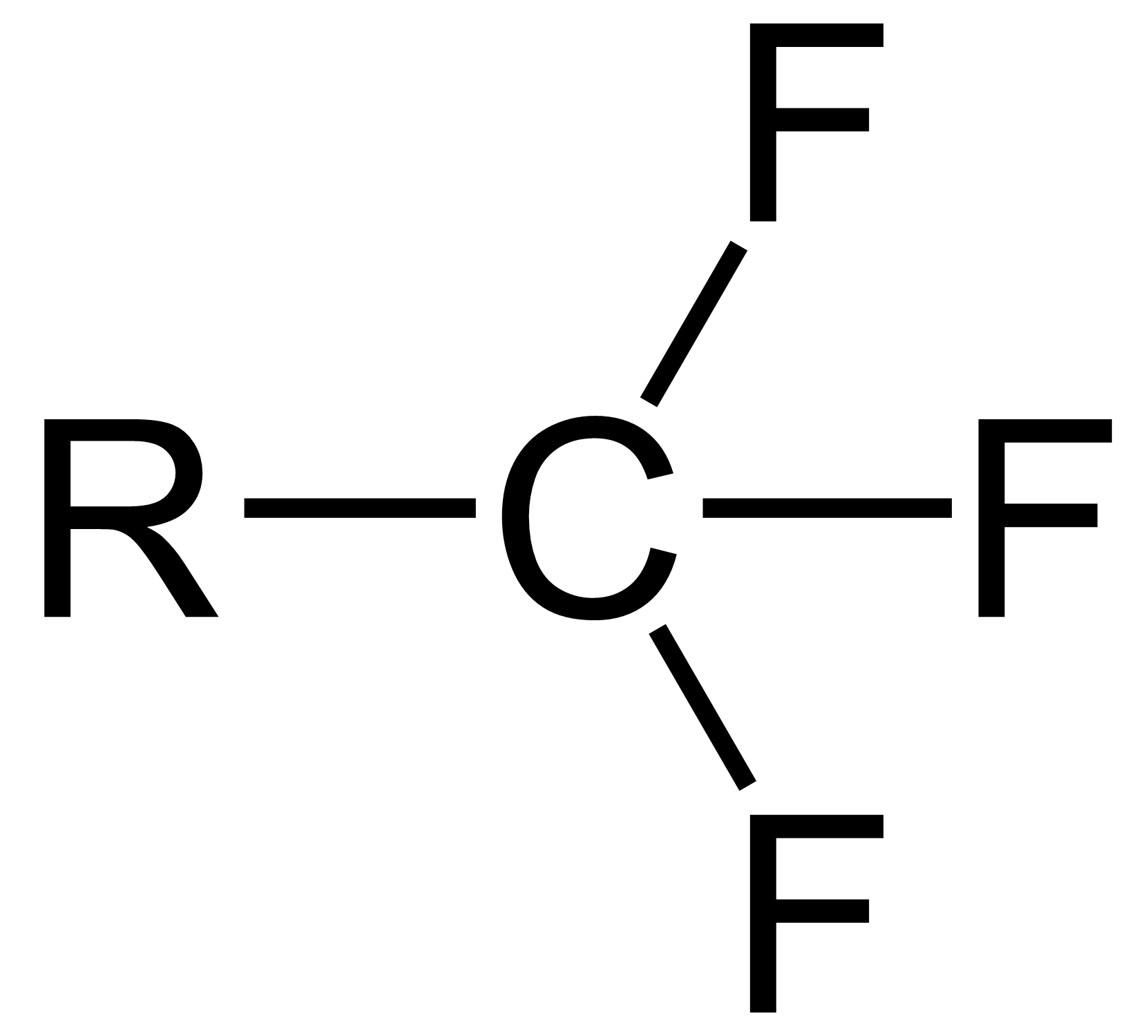
Trifluoromethyl Group
The trifluoromethyl group is a functional group that has the formula -CF3. The naming of is group is derived from the methyl group (which has the formula -CH3), by replacing each hydrogen atom by a fluorine atom. Some common examples are trifluoromethane H–, 1,1,1-trifluoroethane –, and hexafluoroacetone –CO–. Compounds with this group are a subclass of the organofluorines. Properties The trifluoromethyl group has a significant electronegativity that is often described as being intermediate between the electronegativities of fluorine and chlorine. For this reason, trifluoromethyl-substituted compounds are often strong acids, such as trifluoromethanesulfonic acid and trifluoroacetic acid. Conversely, the trifluoromethyl group lowers the basicity of compounds like trifluoroethanol. Uses The trifluoromethyl group occurs in certain pharmaceuticals, drugs, and abiotically synthesized natural fluorocarbon based compounds. The medicinal use of the trifloromethyl group dates from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
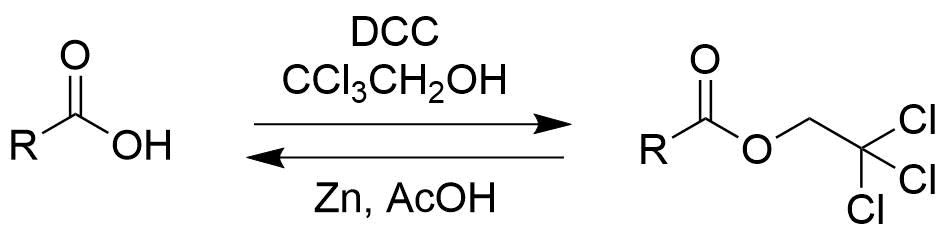
Trichloroethanol
2,2,2-Trichloroethanol is the chemical compound with formula . Its molecule can be described as that of ethanol, with the three hydrogen atoms at position 2 (the methyl group) replaced by chlorine atoms. It is a clear flammable liquid at room temperature, colorless when pure but often with a light yellow color.2,2,2-Trichloroethanol ≥99% . Online product catalog page at Merck website. Accessed on 2020-07-11. The pharmacological effects of this compound in humans are similar to those of its , and of |
Acetic Acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water and other trace elements. Acetic acid is the second simplest carboxylic acid (after formic acid). It is an important chemical reagent and industrial chemical, used primarily in the production of cellulose acetate for photographic film, polyvinyl acetate for wood glue, and synthetic fibres and fabrics. In households, diluted acetic acid is often used in descaling agents. In the food industry, acetic acid is controlled by the food additive code E260 as an acidity regulator and as a condiment. In biochemistry, the acetyl group, derived from acetic acid, is fundamental to all forms of life. When bound to coenzyme A, it is central to the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats. The global demand for acetic aci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichloroacetic Acid
Trichloroacetic acid (TCA; TCAA; also known as trichloroethanoic acid) is an analogue of acetic acid in which the three hydrogen atoms of the methyl group have all been replaced by chlorine atoms. Salts and esters of trichloroacetic acid are called trichloroacetates. Synthesis It is prepared by the reaction of chlorine with acetic acid in the presence of a suitable catalyst such as red phosphorus. This reaction is Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky halogenation. : + 3 → + 3 Another route to trichloroacetic acid is the oxidation of trichloroacetaldehyde. Use It is widely used in biochemistry for the precipitation of macromolecules, such as proteins, DNA, and RNA. TCA and DCA are both used in cosmetic treatments (such as chemical peels and tattoo removal) and as topical medication for chemoablation of warts, including genital warts. It can kill normal cells as well. It is considered safe for use for this purpose during pregnancy. The sodium salt (sodium trichloroacetate) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acidity Constant
In chemistry, an acid dissociation constant (also known as acidity constant, or acid-ionization constant; denoted ) is a quantitative measure of the strength of an acid in solution. It is the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction :HA A^- + H^+ known as dissociation in the context of acid–base reactions. The chemical species HA is an acid that dissociates into , the conjugate base of the acid and a hydrogen ion, . The system is said to be in equilibrium when the concentrations of its components will not change over time, because both forward and backward reactions are occurring at the same rate. The dissociation constant is defined by :K_\text = \mathrm, or :\mathrmK_\ce = - \log_ K_\text = \log_\frac where quantities in square brackets represent the concentrations of the species at equilibrium. Theoretical background The acid dissociation constant for an acid is a direct consequence of the underlying thermodynamics of the dissociation reaction; the p''K''a va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronegativity
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. The higher the associated electronegativity, the more an atom or a substituent group attracts electrons. Electronegativity serves as a simple way to quantitatively estimate the bond energy, and the sign and magnitude of a bond's chemical polarity, which characterizes a bond along the continuous scale from covalent to ionic bonding. The loosely defined term electropositivity is the opposite of electronegativity: it characterizes an element's tendency to donate valence electrons. On the most basic level, electronegativity is determined by factors like the nuclear charge (the more protons an atom has, the more "pull" it will have on electrons) and the number and locat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest of the molecule's composition. This enables systematic prediction of chemical reactions and behavior of chemical compounds and the design of chemical synthesis. The reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis. A functional group is a group of atoms in a molecule with distinctive chemical properties, regardless of the other atoms in the molecule. The atoms in a functional group are linked to each other and to the rest of the molecule by covalent bonds. For repeating units of polymers, functional groups attach to their nonpolar core of carbon atoms and thus add chemical character to carbon chai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloral
Chloral, also known as trichloroacetaldehyde or trichloroethanal, is the organic compound with the formula Cl3CCHO. This aldehyde is a colourless oily liquid that is soluble in a wide range of solvents. It reacts with water to form chloral hydrate, a once widely used sedative and hypnotic substance. Production Chloral was first prepared, and named, by the German chemist Justus von Liebig in 1832. Liebig treated anhydrous ethanol with dry chlorine gas. Chloral is produced commercially by the chlorination of acetaldehyde in the presence of hydrochloric acid, producing chloral hydrate. Ethanol can also be used as a feedstock. This reaction is catalyzed by antimony trichloride: :H3CCHO + 3 Cl2 + H2O → Cl3CCH(OH)2 + 3 HCl The chloral hydrate is distilled from the reaction mixture. The distillate is then dehydrated with concentrated sulfuric acid, after which the heavier acid layer (containing the water) is drawn off: :Cl3CCH(OH)2 → Cl3CCHO + H2O The resulting product ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |