|
Trans-European High-speed Rail Network
The Trans-European high-speed rail network (TEN-R), together with the Trans-European conventional rail network, make up the Trans-European Rail network, which in turn is one of a number of the European Union's Trans-European transport networks (TEN-T). It was defined by the Council Directive 96/48/EC of 23 July 1996. The European Union council decision 2002/735/EC defines technical standards for interoperability of the system. Description The aim of this EU Directive is to achieve the interoperability of the European high-speed train network at the various stages of its design, construction and operation. The network is defined as a system consisting of a set of infrastructures, fixed installations, logistic equipment and rolling stock. By definition of the EC decision, a high-speed line must have one of these three infrastructure characteristics: * specially built high-speed lines equipped for speeds generally equal to or greater than 250 km/h * specially upgraded high-sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans-European Conventional Rail Network
The Trans-European conventional rail network, together with the Trans-European high-speed rail network, make up the Trans-European Rail network, which in turn is one of a number of the European Union's Trans-European transport networks (TEN-T). It was defined by the Council Directive 2001/16/EC of 19 March 2001. The aim of this EU Directive is to achieve the interoperability of the European conventional rail network at the various stages of its design, construction and operation. The network is defined as a system consisting of a set of infrastructures, fixed installations, logistic equipment and rolling stock. By definition of the EC decision, the conventional rail network may be subdivided into the following categories: * lines intended for passenger services * lines intended for mixed traffic (passengers and freight) * lines specially designed or upgraded for freight services * passenger hubs * freight hubs, including inter-modal terminals * lines connecting the components me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Brussels Hoofdstedelijk Gewest), is a region of Belgium comprising 19 municipalities, including the City of Brussels, which is the capital of Belgium. The Brussels-Capital Region is located in the central portion of the country and is a part of both the French Community of Belgium and the Flemish Community, but is separate from the Flemish Region (within which it forms an enclave) and the Walloon Region. Brussels is the most densely populated region in Belgium, and although it has the highest GDP per capita, it has the lowest available income per household. The Brussels Region covers , a relatively small area compared to the two other regions, and has a population of over 1.2 million. The five times larger metropolitan area of Brusse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans-European Combined Transport Network
The Trans-European Combined Transport network is one of a number of the Trans-European Transport Networks (TEN-T) of the European Union. According to Article 14 of the Decision No 1692/96/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 July 1996 on Community guidelines for the development of the trans-European transport network, the Trans-European Combined Transport network comprises the following: * Railways and inland waterways suitable for combined transport and shipping which, combined where appropriate with the shortest possible initial and/or terminal road haulage, permit the long-distance transport of goods * Inter-modal terminals equipped with installations permitting transhipment between railways, inland waterways, shipping routes and roads * Suitable rolling stock, on a provisional basis, where the characteristics of the infrastructure Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans-European Airport Network
The Trans-European Airport network is one of a number of the Trans-European Transport Networks (TEN-T) of the European Union. According to Article 13 of the Decision No 1692/96/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 July 1996 on Community guidelines for the development of the trans-European transport network, the Trans-European Airport network comprises airports situated within the territory of the Community which are open to commercial air traffic. Similarly to the seaports included in the Trans-European Transport network, the airports must correspond to one of the following three categories of connecting points: A. International connecting points: All airports or airport systems with a total annual traffic volume of no less than: * 5,000,000 passenger movements minus 10%, or * 100,000 commercial aircraft movements, or * 150,000 tonnes freight throughput, or * 1,000,000 extra-Community passenger movements; or * any new airport constructed to replace an existin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans-European Seaport Network
The Trans-European Seaport network is one of a number of the Trans-European Transport Networks (TEN-T) of the European Union. According to Article 12 of the Decision No 1692/96/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 July 1996 on Community guidelines for the development of the trans-European transport network, the Trans-European Seaport network should permit the development of sea transport, and should constitute shipping links for islands and the points of interconnection between sea transport and other modes of transport. They should also provide equipment and services to transport operators. Their infrastructure should provide a range of services for passenger and freight transport, including ferry services and short- and long-distance shipping services, which also includes coastal shipping, within the Community and between the latter and non-member countries. The seaports included in the Trans-European Transport network must correspond to one of the following thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motorways Of The Sea
Motorways of the Sea is a concept in the transport policy of the European Union, stressing the importance of sea transport. The main aim of these Motorways of the Sea is to improve port communications with peripheral regions of the European continent and thus strengthen the networks between the EU candidate countries and those countries already part of the European Union. History The concept came about in the White paper ''European transport policy for 2010: time to decide'' of the European Commission, which was adopted in June 2001 in Gothenburg, as an alternative to motorways on land. Routes The routes selected to be Motorways of the Sea should be able to maintain a series of quality criteria; these pertain to frequency, port to port costs, simplicity of administrative tasks. Future routes should compensate for congestion experienced, for example when crossing the Channel (as the similar road networks should do for routes crossing the Alps or the Pyrenees). One envisaged impact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans-European Inland Waterway Network
The Trans-European Inland Waterway network is one of a number of the Trans-European Transport Networks (TEN-T) of the European Union. According to Article 11 of the Decision No 1692/96/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 July 1996 on Community guidelines for the development of the Trans-European Transport Network, the Trans-European Inland waterway network is made up of rivers and canals, and the various branches and links which connect them. In particular, it should render possible the interconnection between industrial regions and major conurbations and link them to ports. The minimum technical characteristics for waterways forming part of the network should be those laid down for a class IV waterway in the classification of European Inland Waterways (CEMT), which allows the passage of a vessel or a pushed train and . Where a waterway forming part of the network is modernized or constructed, the technical specifications should correspond at least to class IV, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans-European Rail Network
The Trans-European Rail network is made up of the Trans-European high-speed rail network as well as the Trans-European conventional rail network. The rail network is one of a number of the European Union's Trans-European transport networks (TEN-T). According to Article 10 of the Decision No 1692/96/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 July 1996 on Community guidelines for the development of the trans-European transport network, the rail network should include the infrastructures and the facilities which enable rail and road and, where appropriate, maritime services and air transport services to be integrated. In this regard, particular attention should be paid to the connection of regional airports to the network. One or more of the following functions should be met by any component of the rail network: * it should play an important role in long-distance passenger traffic * it should permit interconnection with airports, where appropriate * it should permit ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans-European Transport Networks
The Trans-European Transport Network (TEN-T) is a planned network of roads, railways, airports and water infrastructure in the European Union. The TEN-T network is part of a wider system of Trans-European Networks (TENs), including a telecommunications network (eTEN) and a proposed energy network (TEN-E or Ten-Energy). The European Commission adopted the first action plans on trans-European networks in 1990.timeline of TEN-T priority axes and projects as of 2005 , p. 7, PDF document, 14 MB TEN-T envisages coordinated improvements to primary roads, railways, inland waterways, airports, seaports, inland ports and traffic management systems, providing integrated and intermodal long-distance, high-speed routes. A decision to adopt TEN-T was made by the E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
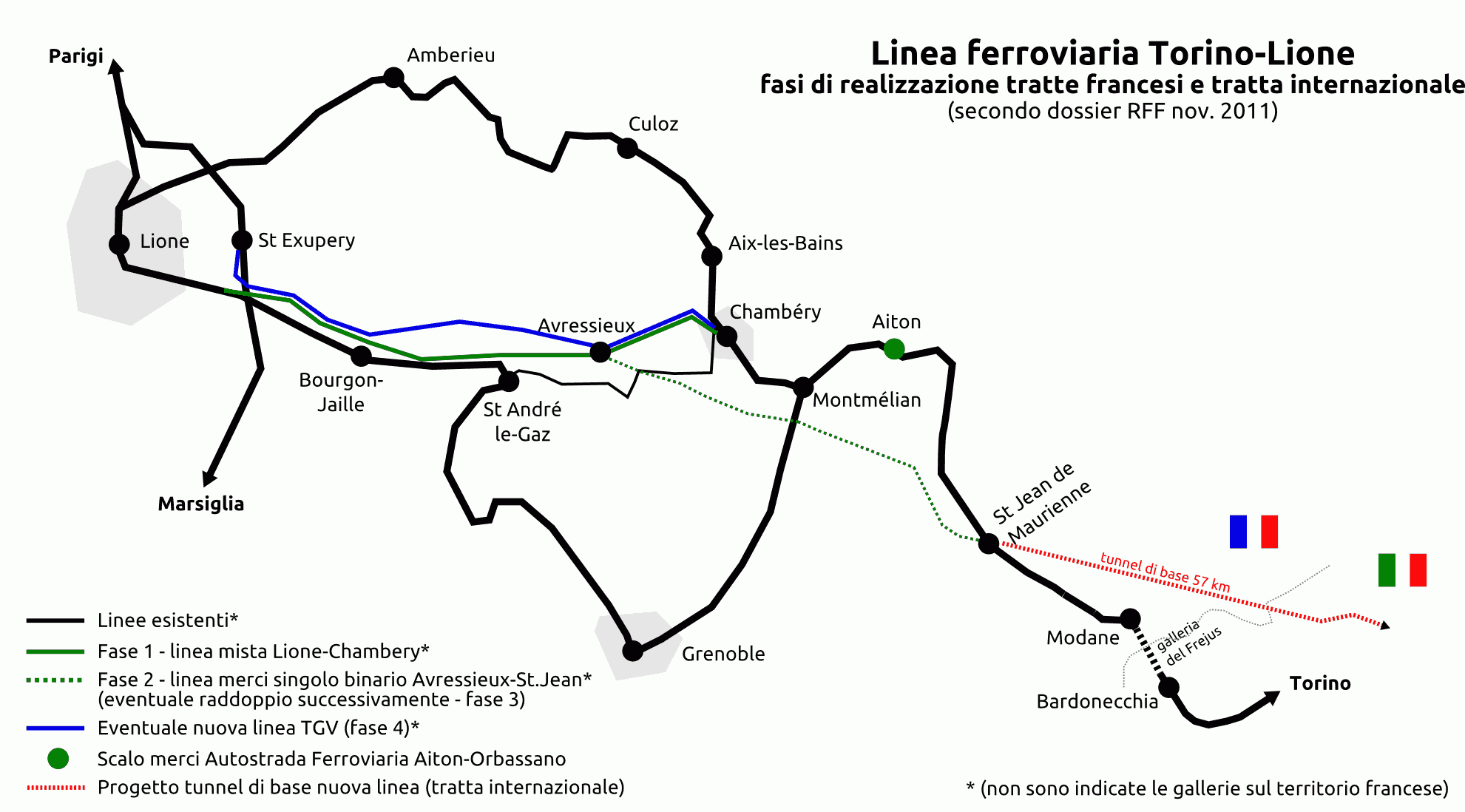
Lyon-Budapest Railway Axis
The Lyon–Budapest railway axis (officially designated as Railway axis Lyon-Trieste-Divača/Koper-Divača-Ljubljana-Budapest-Ukrainian border) is a project of the Trans-European high-speed rail network ( TEN-R), which involves the creation of a high-speed rail line between Lyon and Budapest, finally heading to the Ukrainian border. Sections Lyon-Turin The Turin–Lyon high-speed railway is a planned -long, railway line Nuova linea Torino-Lione parte comune tratta italiana - Progetto in variante - Studio d'impatto ambientale - sintesi non tecnica 9-7-2010 (document PP2 C3C TS3 0105A AP NOT) that will connect the two cities and link the Italian and French high-speed rail networks. The core of the project is a base tunnel measuring 57.5 km crossing the Alps between the Susa valley in Italy and Maurienne in France. The tunnel will be the longest rail tunnel in the world, being longer than the Gotthard Base Tunnel, which measures 57.1 km, and it represents one third ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGV Est
The Ligne à Grande Vitesse Est européenne (East European High Speed Line), typically shortened to LGV Est, is a French high-speed rail line that connects Vaires-sur-Marne (near Paris) and Vendenheim (near Strasbourg). The line halved the travel time between Paris and Strasbourg and provides fast services between Paris and the principal cities of Eastern France as well as Luxembourg, Germany and Switzerland. The LGV Est is a segment of the Main Line for Europe project to connect Paris with Budapest with high-speed rail service. The line was built in two phases. Construction on the from Vaires-sur-Marne to Baudrecourt (near Metz and Nancy) began in 2004; the first phase entered into service in June 2007. Construction on the second phase from Baudrecourt to Vendenheim began in June 2010; the second phase opened to commercial service on 3 July 2016. Opening of the second phase was delayed after a train derailed near Eckwersheim during commissioning trials, resulting in 11 de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |