|
Tokutomi Sohō
was the pen name of a journalist and historian active from late Meiji period through mid- Shōwa period Japan. Named Tokutomi Iichirō at birth, he was the older brother of noted author, Tokutomi Roka. Biography Sohō was born in Minamata, Higo Province (now Kumamoto prefecture), into a samurai family just before the Meiji Restoration. He studied '' Eigaku'' (study of the English language as a means to acquire Western knowledge, especially after the end of Japan's period of isolation) at the ''Kumamoto Yogakko'', and later at the ''Doshisha'' (subsequently Doshisha University) in Kyoto. He left school without graduating, but later wrote of his gratitude to the school's principal, Joseph Hardy Neesima. Following a period back in Kumamoto, where he started a local newspaper, Sohō moved to Tokyo. In 1887, he established the Min'yūsha publishing company, which printed Japan's first general news magazine, the '' Kokumin no Tomo'' ("The People's Friend") from 1887 to 1898. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Template:Infobox Writer/doc
Infobox writer may be used to summarize information about a person who is a writer/author (includes screenwriters). If the writer-specific fields here are not needed, consider using the more general ; other infoboxes there can be found in :People and person infobox templates. This template may also be used as a module (or sub-template) of ; see WikiProject Infoboxes/embed for guidance on such usage. Syntax The infobox may be added by pasting the template as shown below into an article. All fields are optional. Any unused parameter names can be left blank or omitted. Parameters Please remove any parameters from an article's infobox that are unlikely to be used. All parameters are optional. Unless otherwise specified, if a parameter has multiple values, they should be comma-separated using the template: : which produces: : , language= If any of the individual values contain commas already, add to use semi-colons as separators: : which produces: : , ps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 million residents ; the city proper has a population of 13.99 million people. Located at the head of Tokyo Bay, the prefecture forms part of the Kantō region on the central coast of Honshu, Japan's largest island. Tokyo serves as Japan's economic center and is the seat of both the Japanese government and the Emperor of Japan. Originally a fishing village named Edo, the city became politically prominent in 1603, when it became the seat of the Tokugawa shogunate. By the mid-18th century, Edo was one of the most populous cities in the world with a population of over one million people. Following the Meiji Restoration of 1868, the imperial capital in Kyoto was moved to Edo, which was renamed "Tokyo" (). Tokyo was devastated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Mouthpiece
Propaganda is communication that is primarily used to Social influence, influence or persuade an audience to further an Political agenda, agenda, which may not be Objectivity (journalism), objective and may be selectively presenting facts to encourage a particular synthesis or perception, or using loaded language to produce an emotional rather than a rational response to the information that is being presented. Propaganda can be found in news and journalism, government, advertising, entertainment, education, and activism and is often associated with material which is prepared by governments as part of war efforts, political campaigns, health campaigns, revolutionaries, Corporate propaganda, big businesses, ultra-religious organizations, the Propaganda through media, media, and certain individuals such as soapboxing, soapboxers. In the 20th century, the English term ''propaganda'' was often associated with a Psychological manipulation, manipulative approach, but historically, pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katsura Tarō
Prince was a Japanese politician and general of the Imperial Japanese Army who served as the Prime Minister of Japan from 1901 to 1906, from 1908 to 1911, and from 1912 to 1913. Katsura was a distinguished general of the First Sino-Japanese War and a '' genrō'' of the Meiji government who served as Governor-General of Taiwan and Minister of War. Katsura was appointed Prime Minister in 1901 as a military candidate and positioned himself as a conservative outside party politics. Katsura's first and second premierships oversaw several major events in modern Japanese history, including the Russo-Japanese War and the annexation of Korea. Katsura's third premiership triggered the Taisho Political Crisis, and he resigned three months later after a vote of no confidence. Katsura is the second-longest serving Prime Minister of Japan, after Shinzō Abe, and served for 2883 days over his three terms from 1901 to 1913. Early life Katsura was born on 4 January 1848 in Hagi, Nag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamagata Aritomo
'' Gensui'' Prince , also known as Prince Yamagata Kyōsuke, was a senior-ranking Japanese military commander, twice-elected Prime Minister of Japan, and a leading member of the ''genrō'', an élite group of senior statesmen who dominated Japan after the Meiji Restoration. As the Imperial Japanese Army's inaugural Chief of Staff, he was the chief architect of the Empire of Japan's military and its reactionary ideology. For this reason, some historians consider Yamagata to be the “father” of Japanese militarism. During the latter part of the Meiji Era, Yamagata vied against Marquess Itō Hirobumi for control over the nation's policies. After Itō was assassinated in 1909, he became the most powerful figure in Japan save for the Emperor himself. Henceforth, Prince Yamagata oversaw all policymaking within the empire until a falling-out with the Imperial family resulted in him losing power shortly before his death in February 1922. Early career Yamagata Tatsunosuke was bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Minister Of Japan
The prime minister of Japan ( Japanese: 内閣総理大臣, Hepburn: ''Naikaku Sōri-Daijin'') is the head of government of Japan. The prime minister chairs the Cabinet of Japan and has the ability to select and dismiss its Ministers of State. The prime minister also serves as the civilian commander-in-chief of the Japan Self Defence Forces and as a sitting member of the House of Representatives. The individual is appointed by the emperor of Japan after being nominated by the National Diet The is the national legislature of Japan. It is composed of a lower house, called the House of Representatives (, ''Shūgiin''), and an upper house, the House of Councillors (, '' Sangiin''). Both houses are directly elected under a parall ... and must retain the nomination of the lower house and answer to parliament to remain in office. The position and nature of this title allow the holder to reside in and work at the Prime Minister's Official Residence in Nagatacho, Chiyod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiji Oligarchy
The Meiji oligarchy was the new ruling class of Meiji period Japan. In Japanese, the Meiji oligarchy is called the . The members of this class were adherents of ''kokugaku'' and believed they were the creators of a new order as grand as that established by Japan's original founders. Two of the major figures of this group were Ōkubo Toshimichi (1832–78), son of a Satsuma retainer, and Satsuma ''samurai'' Saigō Takamori (1827–77), who had joined forces with Chōshū, Tosa, and Hizen to overthrow the Tokugawa shogunate. Okubo became minister of finance and Saigō a field marshal; both were imperial councillors. Kido Koin (1833–77), a native of Chōshū, student of Yoshida Shōin, and conspirator with Ōkubo and Saigō, became minister of education and chairman of the Governors' Conference and pushed for constitutional government. Also prominent were Iwakura Tomomi (1825–83), a Kyoto native who had opposed the Tokugawa and was to become the first ambassador to the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
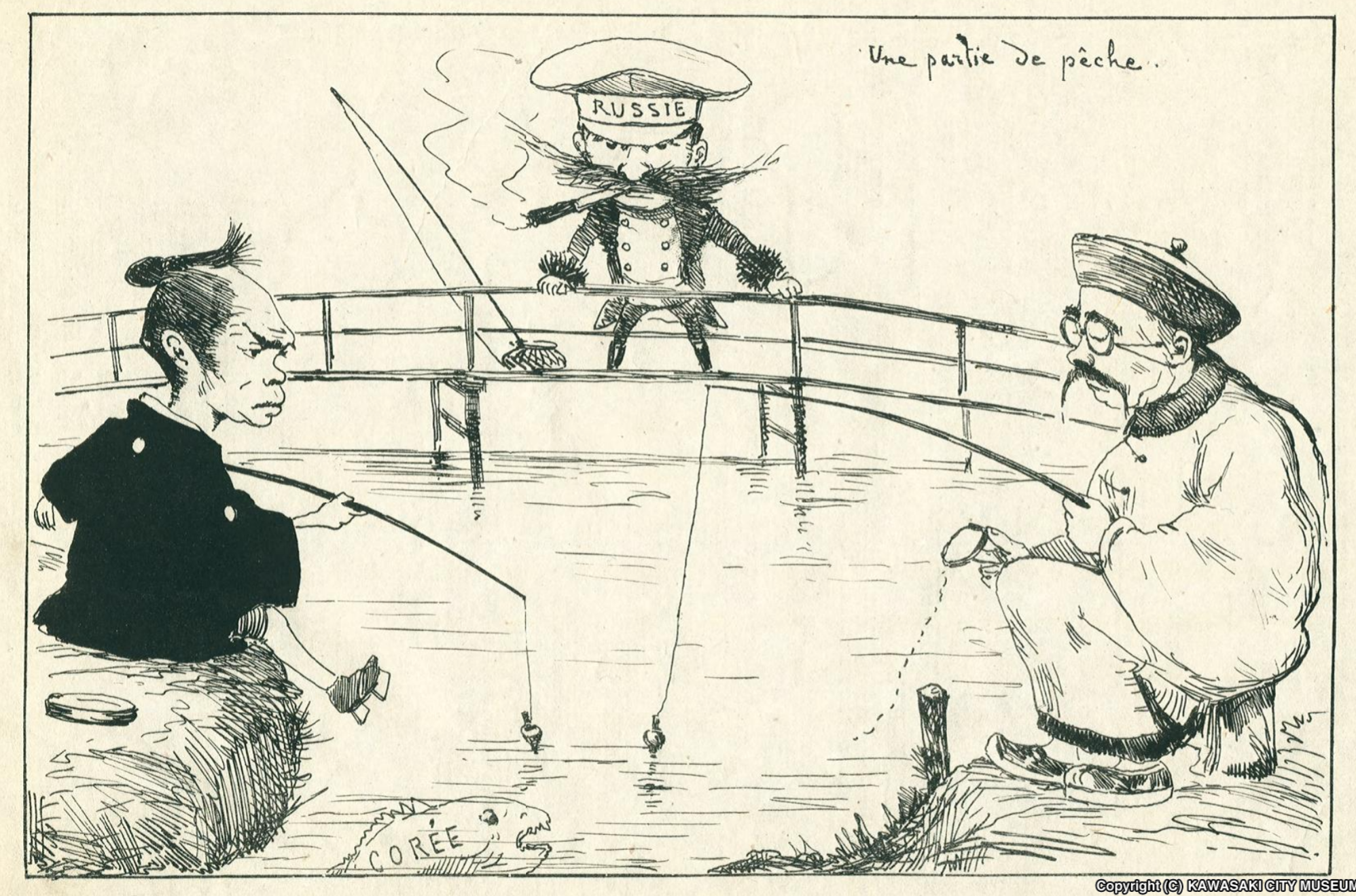
Triple Intervention
The Tripartite Intervention or was a diplomatic intervention by Russia, Germany, and France on 23 April 1895 over the harsh terms of the Treaty of Shimonoseki imposed by Japan on the Qing dynasty of China that ended the First Sino-Japanese War. The goal was to stop Japanese expansion in China. The Japanese reaction against the Triple Intervention was one of the causes of the subsequent Russo-Japanese War.Kowner, '' Historical Dictionary of the Russo-Japanese War'', p. 375. Treaty of Shimonoseki Per the terms of the Treaty of Shimonoseki, Japan was awarded the Liaodong Peninsula including the harbor city of Port Arthur, which it had conquered from China. Immediately after the terms of the treaty became public, Russia—with its own designs and sphere of influence in China—expressed concern about Japanese acquisition of the Liaodong Peninsula and the possible impact of the terms of the treaty on the stability of China. Russia persuaded France and Germany to apply diplomatic pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War (25 July 1894 – 17 April 1895) was a conflict between China and Japan primarily over influence in Korea. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the port of Weihaiwei, the Qing government sued for peace in February 1895. The war demonstrated the failure of the Qing dynasty's attempts to modernize its military and fend off threats to its sovereignty, especially when compared with Japan's successful Meiji Restoration. For the first time, regional dominance in East Asia shifted from China to Japan; the prestige of the Qing dynasty, along with the classical tradition in China, suffered a major blow. The humiliating loss of Korea as a tributary state sparked an unprecedented public outcry. Within China, the defeat was a catalyst for a series of political upheavals led by Sun Yat-sen and Kang Youwei, culminating in the 1911 Xinhai Revolution. The war is commonly known in China as the War o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matsukata Masayoshi
Prince was a Japanese politician who was Prime Minister of Japan from 1891 to 1892 and 1896 to 1898. Early life Matsukata Masayoshi was born on 25 February 1835, in Arata, Kagoshima, Satsuma Province (present-day Shimoarata, Kagoshima, Kagoshima Prefecture), the fourth son of Matsukata Masayasu and his wife Kesaku. His family was of the ''samurai'' warrior nobility class. Both his parents died when he was 13 years old. At the age of 13, he entered the ''Zoshikan'', the Satsuma domain's Confucian academy, where he studied the teachings of Wang Yangming, which stressed loyalty to the Emperor. He started his career as a bureaucrat of the Satsuma Domain. In 1866, he was sent to Nagasaki to study western science, mathematics and surveying. Matsukata was highly regarded by Ōkubo Toshimichi and Saigō Takamori, who used him as their liaison between Kyoto and the domain government in Kagoshima. Knowing that war was coming between Satsuma and the Tokugawa, Matsukata purchased a shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Pale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populism
Populism refers to a range of political stances that emphasize the idea of "the people" and often juxtapose this group against " the elite". It is frequently associated with anti-establishment and anti-political sentiment. The term developed in the late 19th century and has been applied to various politicians, parties and movements since that time, often as a pejorative. Within political science and other social sciences, several different definitions of populism have been employed, with some scholars proposing that the term be rejected altogether. A common framework for interpreting populism is known as the ideational approach: this defines ''populism'' as an ideology which presents "the people" as a morally good force and contrasts them against "the elite", who are portrayed as corrupt and self-serving. Populists differ in how "the people" are defined, but it can be based along class, ethnic, or national lines. Populists typically present "the elite" as comprising the po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |