|
Tin(II) Ethylhexanoate
Tin(II) 2-ethylhexanoate or tin(II) octoate or stannous octoate (Sn(Oct)2) is a compound of tin. Produced by the reaction of tin(II) oxide and 2-ethylhexanoic acid, it is a clear colorless liquid at room temperature, though often appears yellow due to impurities, likely resulting from oxidation of Sn(II) to Sn(IV). It is sometimes used as a catalyst for ring-opening polymerization In polymer chemistry, ring-opening polymerization (ROP) is a form of chain-growth polymerization, in which the terminus of a polymer chain attacks cyclic monomers to form a longer polymer (see figure). The reactive center can be radical, anion ..., such as for the production of polylactic acid.{{cite journal , doi = 10.1002/(SICI)1099-0518(19971130)35:163.0.CO;2-G , title = More about the polymerization of lactides in the presence of stannous octoate , year = 1997 , last1 = Schwach , first1 = G. , last2 = Coudane , first2 = J. , last3 = Engel , first3 = R. , last4 = Vert , first4 = M. , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tin(II) Oxide
Tin(II) oxide (stannous oxide) is a compound with the formula SnO. It is composed of tin and oxygen where tin has the oxidation state of +2. There are two forms, a stable blue-black form and a metastable red form. Preparation and reactions Blue-black SnO can be produced by heating the tin(II) oxide hydrate, SnO·xH2O (x<1) precipitated when a tin(II) salt is reacted with an alkali hydroxide such as NaOH.Egon Wiberg, Arnold Frederick Holleman (2001) ''Inorganic Chemistry'', Elsevier Metastable, red SnO can be prepared by gentle heating of the precipitate produced by the action of aqueous ammonia on a tin(II) salt. SnO may be prepared as a pure substance in the laboratory, by controlled heating of tin(II) oxalate (stannous oxalate) in the absence of air or under a CO2 atmosphere. This method is also applied to the production of ferrous oxide and manganous oxide. :SnC2O4� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-ethylhexanoic Acid
2-Ethylhexanoic acid is the organic compound with the formula CH3(CH2)3CH(C2H5)CO2H. It is a carboxylic acid that is widely used to prepare lipophilic metal derivatives that are soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. 2-Ethylhexanoic acid is a colorless viscous oil. It is supplied as a racemic mixture. Production 2-Ethylhexanoic acid is produced industrially from propylene, which is hydroformylated to give butyraldehyde. Aldol condensation of the aldehyde gives 2-ethylhexenal, which is hydrogenated to 2-ethylhexanal. Oxidation of this aldehyde gives the carboxylic acid. Metal ethylhexanoates 2-Ethylhexanoic acid forms compounds with metal cations that have stoichiometry as metal acetates. These ethylhexanoate complexes are used in organic and industrial chemical synthesis. They function as catalysts in polymerizations as well as for oxidation reactions as "oil drying agents." They are highly soluble in nonpolar solvents. These metal complexes are often described as sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usually gaseous or liquid) as the reactant, or heterogeneous, whose components are not in the same phase. Enzymes and other biocatalysts are often considered as a third category. Catalysis is ubiquitous in chemical industry of all kinds. Estimates are that 90% of all commercially produced chemical products involve catalysts at some s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
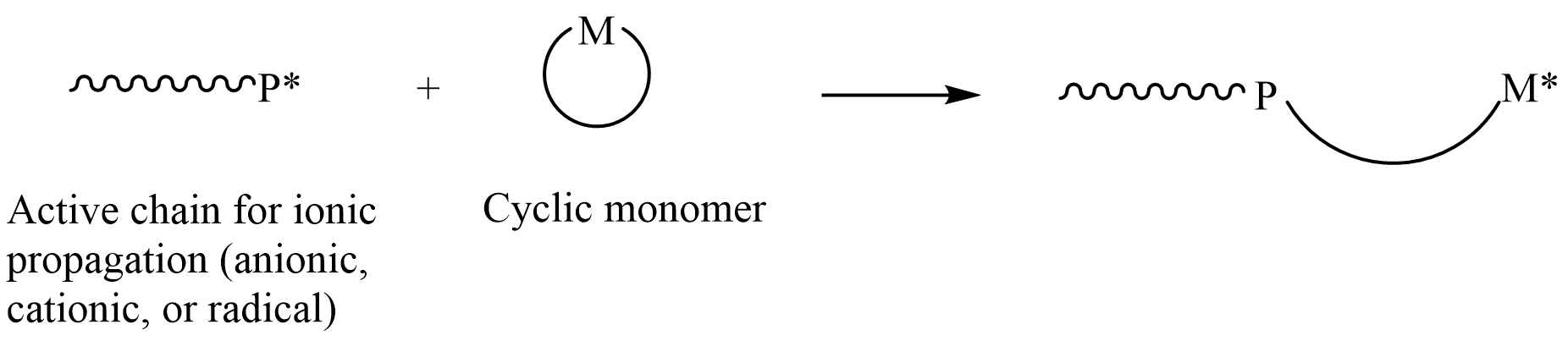
Ring-opening Polymerization
In polymer chemistry, ring-opening polymerization (ROP) is a form of chain-growth polymerization, in which the terminus of a polymer chain attacks cyclic monomers to form a longer polymer (see figure). The reactive center can be radical, anionic or cationic. Some cyclic monomers such as norbornene or cyclooctadiene can be polymerized to high molecular weight polymers by using metal catalysts. ROP is a versatile method for the synthesis of biopolymers. Ring-opening of cyclic monomers is often driven by the relief of bond-angle strain. Thus, as is the case for other types of polymerization, the enthalpy change in ring-opening is negative. Monomers Cyclic monomers that are amenable to ROP include epoxides, cyclic trisiloxanes, some lactones, lactides, cyclic carbonates, and amino acid N-carboxyanhydrides. Many strained cycloalkenes, e.g norbornene, are suitable monomers via ring-opening metathesis polymerization. History Ring-opening polymerization has been used since the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polylactic Acid
Polylactic acid, also known as poly(lactic acid) or polylactide (PLA), is a thermoplastic polyester with backbone formula or , formally obtained by condensation of lactic acid with loss of water (hence its name). It can also be prepared by ring-opening polymerization of lactide , the cyclic dimer of the basic repeating unit. PLA has become a popular material due to it being economically produced from renewable resources. In 2021, PLA had the highest consumption volume of any bioplastic of the world, although it is still not a commodity polymer. Its widespread application has been hindered by numerous physical and processing shortcomings. PLA is the most widely used plastic filament material in 3D printing. Its low melting point, high strength, low thermal expansion, good layer adhesion, and high heat resistance when annealed make it an ideal material for this purpose. Without annealing, however, PLA has the lowest heat resistance of the common 3D printing plastics. Althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tin(II) Compounds
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal. Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, the so-called "tin cry" can be heard as a result of twinning in tin crystals; this trait is shared by indium, cadmium, zinc, and mercury in the solid state. Pure tin after solidifying presents a mirror-like appearance similar to most metals. In most tin alloys (such as pewter) the metal solidifies with a dull gray color. Tin is a post-transition metal in group 14 of the periodic table of elements. It is obtained chiefly from the mineral cassiterite, which contains stannic oxide, . Tin shows a chemical similarity to both of its neighbors in group 14, germanium and lead, and has two main oxidation states, +2 and the slightly more stable +4. Tin is the 49th most abundant element on Earth and has, with 10 stable isotopes, the larges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2.jpg)