|
Tiebout Model
The Tiebout model, also known as Tiebout sorting, Tiebout migration, or Tiebout hypothesis, is a positive political theory model first described by economist Charles Tiebout in his article "A Pure Theory of Local Expenditures" (1956). The essence of the model is that there is in fact a non-political solution to the free rider problem in local governance. Specifically, competition across local jurisdictions places competitive pressures on the provision of local public goods such that these local governments are able to provide the optimal level of public goods. Overview Tiebout first proposed the model informally as a graduate student in a seminar with Richard Musgrave, who argued that the free rider problem necessarily required a political solution. Later, after obtaining his PhD, Tiebout fully described his hypothesis in a seminal article published in 1956 by the '' Journal of Political Economy''. Tiebout believes that the ideas of shopping and competition could be brought int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Political Theory
Positive political theory (PPT) or explanatory political theory is the study of politics using formal methods such as social choice theory, game theory, and statistical analysis. In particular, social choice theoretic methods are often used to describe and (axiomatically) analyze the performance of rules or institutions. The outcomes of the rules or institutions described are then analyzed by game theory, where the individuals/parties/nations involved in a given interaction are modeled as ''rational'' agents playing a game, guided by self-interest. Based on this assumption, the outcome of the interactions can be predicted as an equilibrium of the game. The founder of the field was William H. Riker. In his book '' The Theory of Political Coalitions'' (1962), he applied the principles of game theory to the study of politics. The original creation of PPT was developed while Riker was the leader of Rochester School of Political Science, generating the Rochester School movement. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exit-Voice-Loyalty-Neglect Model
The Exit, Voice, Loyalty (EVL) model or Exit, Voice, Loyalty, Neglect (EVLN) is used in the fields of comparative politics and organizational behavior. It is an extensive form game used to model interactions typically involving negative changes to one player's environment by another player. These concepts first appeared in Albert Hirschman's more broadly focused 1970 book, '' Exit, Voice, and Loyalty: Responses to Decline in Firms, Organizations, and States.'' A common use in political science is between citizens and their government. Usually in this use the Citizen player is any group within a society ranging from a single individual to the citizenry as a whole. Model The EVL Model involves two agents and their responses to a change initiated before the game began. The first agent is commonly referred to as the Citizen and the second is commonly referred to as the Government. EVL assumes that the change implemented before the game began was performed by the Government and nega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foot Voting
Foot voting is expressing one's preferences through one's actions, by voluntarily participating in or withdrawing from an activity, group, or process; especially, physical migration to leave a situation one does not like, or to move to a situation one regards as more beneficial. People who engage in foot voting are said to "vote with their feet". Legal scholar Ilya Somin has described foot voting as "a tool for enhancing political freedom: the ability of the people to choose the political regime under which they wish to live". Communist leader Vladimir Lenin commented, "They voted with their feet," regarding Russian soldiers deserting the army of the Tsar. The concept has also been associated with Charles Tiebout, who pioneered the concept (although he did not use the ''term'' "foot voting") in a 1956 paper, and with Ronald Reagan, who advocated migration between states of the United States as a solution to unsatisfactory local conditions. Law and politics Legal scholar Ilya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exit, Voice, And Loyalty
''Exit, Voice, and Loyalty'' (1970) is a treatise written by Albert O. Hirschman. The work hinges on a conceptual ultimatum that confronts consumers in the face of deteriorating quality of goods: either '' exit'' or ''voice''. The book has been described as influential. The framework presented in the book has been applied to topics such as protest movements, migration, political parties, and interest groups, as well as to personal relationships. Summary The Exit, Voice and Loyalty model states that members of an organization, whether a business, a nation or any other form of human grouping, have essentially two possible responses when they perceive that the organization is demonstrating a decrease in quality or benefit to the member: they can ''exit'' (withdraw from the relationship); or, they can ''voice'' (attempt to repair or improve the relationship through communication of the complaint, grievance or proposal for change). For example, the citizens of a country may respond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bill Bishop (author)
Bill Bishop is an American author, journalist and social commentator. He co-wrote a book with retired college professor Robert Cushing entitled ''The Big Sort: Why the Clustering of Like-Minded America is Tearing Us Apart''. His ideas have influenced the speeches of former U.S. President Bill Clinton. He is the co-founder and contributing editor of the ''Daily Yonder'', a blog about rural issues in the United States. Bishop has worked for several newspapers: the '' Austin American-Statesman'', '' Lexington Herald-Leader'', and ''The Mountain Eagle''. He has a degree from Duke University. His wife, Julie Ardery, is also a co-founder and contributing editor of the ''Daily Yonder''. The couple previously owned a newspaper: the ''Bastrop County Times''. They currently live in La Grange, Texas La Grange ( ) is a city in Fayette County, Texas, United States, near the Colorado River. La Grange is in the center of the Texas-German belt. The population was 4,391 at the 2020 census, and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economies Of Scale
In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, and are typically measured by the amount of output produced per unit of time. A decrease in cost per unit of output enables an increase in scale. At the basis of economies of scale, there may be technical, statistical, organizational or related factors to the degree of market control. This is just a partial description of the concept. Economies of scale apply to a variety of the organizational and business situations and at various levels, such as a production, plant or an entire enterprise. When average costs start falling as output increases, then economies of scale occur. Some economies of scale, such as capital cost of manufacturing facilities and friction loss of transportation and industrial equipment, have a physical or engineering basis. The economic concept dates back to Adam Smith and the idea of obtaining larger production returns through the use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
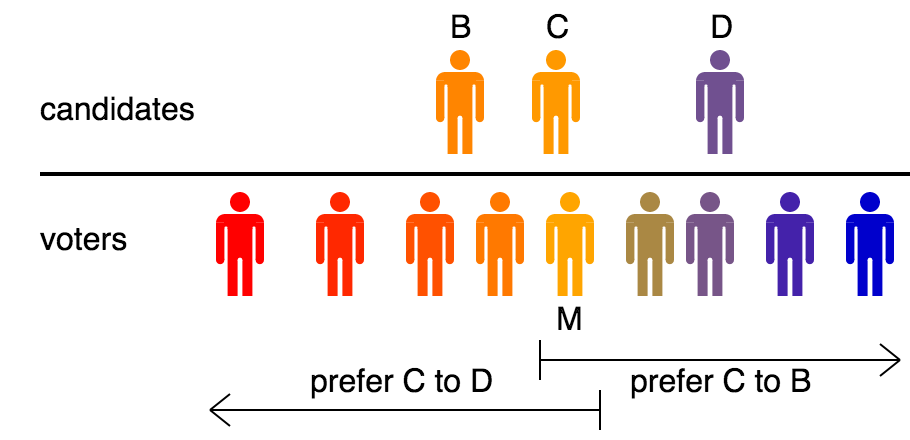
Median Voter Theorem
The median voter theorem is a proposition relating to ranked preference voting put forward by Duncan Black in 1948.Duncan Black, "On the Rationale of Group Decision-making" (1948). It states that if voters and policies are distributed along a one-dimensional spectrum, with voters ranking alternatives in order of proximity, then any voting method which satisfies the Condorcet criterion will elect the candidate closest to the median voter. In particular, a majority vote between two options will do so. The theorem is associated with public choice economics and statistical political science. Partha Dasgupta and Eric Maskin have argued that it provides a powerful justification for voting methods based on the Condorcet criterion. Plott's majority rule equilibrium theorem extends this to two dimensions. A loosely related assertion had been made earlier (in 1929) by Harold Hotelling. It is not a true theorem and is more properly known as the median voter theory or median voter model. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Competition
Tax competition, a form of regulatory competition, exists when governments use reductions in fiscal burdens to encourage the inflow of productive resources or to discourage the exodus of those resources. Often, this means a governmental strategy of attracting foreign direct investment, foreign indirect investment (financial investment), and high value human resources by minimizing the overall taxation level and/or special tax preferences, creating a comparative advantage. Scholars generally consider economic development incentives to be inefficient, economically costly, and distortionary. History From the mid 1900s governments had more freedom in setting their taxes, as the barriers to free movement of capital and people were high. The gradual process of globalization is lowering these barriers and results in rising capital flows and greater manpower mobility. Impact According to a 2020 study, tax competition "primarily reduces taxes for mobile firms and is unlikely to substanti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aggregation Problem
An ''aggregate'' in economics is a summary measure. It replaces a vector that is composed of many real numbers by a single real number, or a scalar. Consequently there occur various problems that are inherent in the formulations that use aggregated variables.Franklin M. Fisher (1987). "aggregation problem," '' The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics'', v. 1, pp.53-55 The aggregation problem is the difficult problem of finding a valid way to treat an empirical or theoretical aggregate as if it reacted like a less-aggregated measure, say, about behavior of an individual agent as described in general microeconomic theory. The second meaning of "aggregation problem" is the theoretical difficulty in using and treating laws and theorems that include aggregate variables. A typical example is the aggregate production function. Another famous problem is Sonnenschein-Mantel-Debreu theorem. Most of macroeconomic statements comprise this problem. Examples of aggregates in micro- and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Tiebout
Charles Mills Tiebout ( "TEE-bow") (1924–1968) was an American economist and geographer most known for his development of the Tiebout model, which suggested that there were actually non-political solutions to the free rider problem in local governance. He earned recognition in the area of local government and fiscal federalism with his widely cited 1956 paper "A Pure Theory of Local Expenditures". Tiebout graduated from Wesleyan University in 1950, and received a PhD in economics in University of Michigan in 1957. From 1954 to 1958, Tiebout served as a lecturer and assistant professor of economics at Northwestern University. From 1958 to 1962 was an assistant then associate professor of economics at UCLA. He was Professor of Economics and Geography and was co-director for the Center for Urban and Regional Studies at the University of Washington. He died suddenly on January 16, 1968, at age 43. Tiebout is frequently associated with the concept of foot voting Foot voting is expr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preference Revelation
In public choice theory, preference revelation (also preference revelation problem) is an area of study concerned with ascertaining the public's demand for public goods. According to some economists, if government planners do not have "full knowledge of individual preference functions", then it is likely that public goods will be under- or over-supplied. When there is no market to induce people to reveal their subjective valuations, economists say that there is a “problem of preference revelation.” When perfect compensation is possible in principle, it may be impossible in fact because of the problem of preference revelation Overview Unlike private goods, public goods are non-excludable and non-rivalrous. This means that it is possible for people to benefit from a public good without having to help contribute to its production. Given that information about marginal benefits is available only from the individuals themselves, people have an incentive to under report their v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Good (economics)
In economics, a public good (also referred to as a social good or collective good)Oakland, W. H. (1987). Theory of public goods. In Handbook of public economics (Vol. 2, pp. 485-535). Elsevier. is a good that is both non-excludable and non-rivalrous. For such goods, users cannot be barred from accessing or using them for failing to pay for them. Also, use by one person neither prevents access of other people nor does it reduce availability to others. Therefore, the good can be used simultaneously by more than one person. This is in contrast to a common good, such as wild fish stocks in the ocean, which is non-excludable but rivalrous to a certain degree. If too many fish were harvested, the stocks would deplete, limiting the access of fish for others. A public good must be valuable to more than one user, otherwise, the fact that it can be used simultaneously by more than one person would be economically irrelevant. Capital goods may be used to produce public goods or services t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)