|
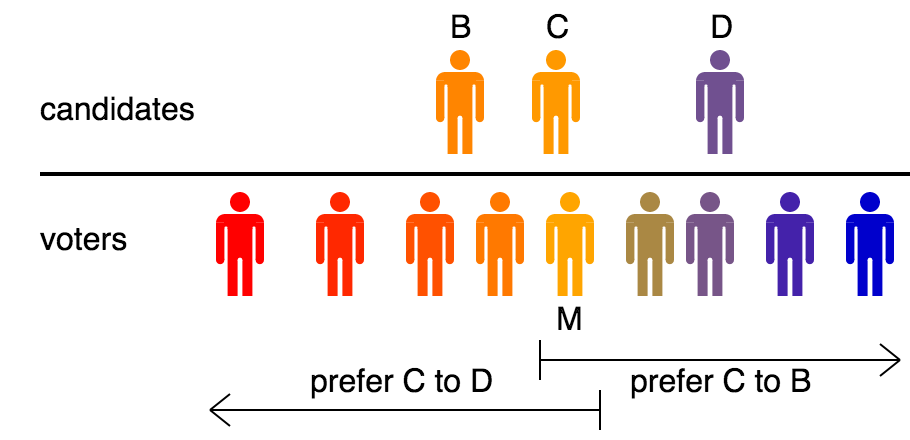
Median Voter Theorem
The median voter theorem is a proposition relating to ranked preference voting put forward by Duncan Black in 1948.Duncan Black, "On the Rationale of Group Decision-making" (1948). It states that if voters and policies are distributed along a one-dimensional spectrum, with voters ranking alternatives in order of proximity, then any voting method which satisfies the Condorcet criterion will elect the candidate closest to the median voter. In particular, a majority vote between two options will do so. The theorem is associated with public choice economics and statistical political science. Partha Dasgupta and Eric Maskin have argued that it provides a powerful justification for voting methods based on the Condorcet criterion. Plott's majority rule equilibrium theorem extends this to two dimensions. A loosely related assertion had been made earlier (in 1929) by Harold Hotelling. It is not a true theorem and is more properly known as the median voter theory or median voter model. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranked Voting
The term ranked voting (also known as preferential voting or ranked choice voting) refers to any voting system in which voters rank their candidates (or options) in a sequence of first or second (or third, etc.) on their respective ballots. Ranked voting systems differ on the basis of how the ballots are marked, how the preferences are tabulated and counted, how many seats are filled, and whether voters are allowed to rank candidates equally. An electoral system that uses ranked voting uses one of the many available counting methods to select the winning candidate or candidates. There is also variation among ranked voting electoral systems in that in some ranked voting systems, officials require voters to rank a set number of candidates, sometimes all of them; in others, citizens may rank as many candidates as they see fit. Election of single members using ranked votes is often instant-runoff voting. Election of multiple members using ranked votes is usually single transfera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
An Economic Theory Of Democracy
''An Economic Theory of Democracy'' is a treatise of economics written by Anthony Downs, published in 1957. The book set forth a model with precise conditions under which economic theory could be applied to non-market political decision-making. It also suggested areas of empirical research that could be tested to confirm the validity of his conclusions in the model. Much of this offshoot research eventually became integrated into public choice theory. Downs' theory abstains from making normative statements about public policy choices and instead focuses on what is rational, given the relevant incentives, for government to do. Contents In chapter eight of the book Downs explains how the concept of ideology is central to his theory. Depending on the ideological distribution of voters in a given political community, electoral outcomes can be stable and peaceful or wildly varied and even result in violent revolution. The likely number of political parties can also be identif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranked Voting
The term ranked voting (also known as preferential voting or ranked choice voting) refers to any voting system in which voters rank their candidates (or options) in a sequence of first or second (or third, etc.) on their respective ballots. Ranked voting systems differ on the basis of how the ballots are marked, how the preferences are tabulated and counted, how many seats are filled, and whether voters are allowed to rank candidates equally. An electoral system that uses ranked voting uses one of the many available counting methods to select the winning candidate or candidates. There is also variation among ranked voting electoral systems in that in some ranked voting systems, officials require voters to rank a set number of candidates, sometimes all of them; in others, citizens may rank as many candidates as they see fit. Election of single members using ranked votes is often instant-runoff voting. Election of multiple members using ranked votes is usually single transfera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median Mechanism
A median mechanism is a voting rule that allows people to decide on a value in a one-dimensional domain. Each person votes by writing down his/her ideal value, and the rule selects a single value which is (in the basic mechanism) the '' median'' of all votes. The median mechanism can be used, for example, to decide on the size of the country's budget: each person says what the ideal budget size should be, and the chosen size is the median of the declared values. Another possible application is deciding how long the annual school vacation should be: each person says the ideal length in days, and the median is selected. A third example is: deciding what temperature the air-conditioner in an office should be set to. A fourth example is a facility location problem in one dimension. An important feature of the median mechanism is that it is ''truthful'': if the utility of each voter is higher whenever the chosen value is closer to his ideal value, then an optimal strategy for each vote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrow's Impossibility Theorem
Arrow's impossibility theorem, the general possibility theorem or Arrow's paradox is an impossibility theorem in social choice theory that states that when voters have three or more distinct alternatives (options), no ranked voting electoral system can convert the ranked preferences of individuals into a community-wide (complete and transitive) ranking while also meeting the specified set of criteria: ''unrestricted domain'', ''non-dictatorship'', ''Pareto efficiency'', and ''independence of irrelevant alternatives''. The theorem is often cited in discussions of voting theory as it is further interpreted by the Gibbard–Satterthwaite theorem. The theorem is named after economist and Nobel laureate Kenneth Arrow, who demonstrated the theorem in his doctoral thesis and popularized it in his 1951 book ''Social Choice and Individual Values''. The original paper was titled "A Difficulty in the Concept of Social Welfare". In short, the theorem states that no rank-order electoral syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Share
Market share is the percentage of the total revenue or sales in a market that a company's business makes up. For example, if there are 50,000 units sold per year in a given industry, a company whose sales were 5,000 of those units would have a 10percent share in that market. "Marketers need to be able to translate and incorporate sales targets into market share because this will demonstrate whether forecasts are to be attained by growing with the market or by capturing share from competitors. The latter will almost always be more difficult to achieve. Market share is closely monitored for signs of change in the competitive landscape, and it frequently drives strategic or tactical action."Farris, Paul W.; Neil T. Bendle; Phillip E. Pfeifer; David J. Reibstein (2010). ''Marketing Metrics: The Definitive Guide to Measuring Marketing Performance.'' Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Pearson Education, Inc. . The Marketing Accountability Standards Board (MASB) endorses the definitions, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hotelling's Law
Hotelling's law is an observation in economics that in many markets it is rational for producers to make their products as similar as possible. This is also referred to as the principle of minimum differentiation as well as Hotelling's linear city model. The observation was made by Harold Hotelling (1895–1973) in the article "Stability in Competition" in ''Economic Journal'' in 1929. The opposing phenomenon is product differentiation, which is usually considered to be a business advantage if executed properly. Example Suppose there are two competing shops located along the length of a street running north and south, with customers spread equally along the street. Both shop owners want their shops to be where they will get most market share of customers. If both shops sell the same range of goods at the same prices then the locations of the shops are themselves the 'products'. Each customer will always choose the nearer shop as it is disadvantageous to travel to the fart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median Plott
In statistics and probability theory, the median is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a data sample, a population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as "the middle" value. The basic feature of the median in describing data compared to the mean (often simply described as the "average") is that it is not skewed by a small proportion of extremely large or small values, and therefore provides a better representation of a "typical" value. Median income, for example, may be a better way to suggest what a "typical" income is, because income distribution can be very skewed. The median is of central importance in robust statistics, as it is the most resistant statistic, having a breakdown point of 50%: so long as no more than half the data are contaminated, the median is not an arbitrarily large or small result. Finite data set of numbers The median of a finite list of numbers is the "middle" number, when those numbers are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparison Of Electoral Systems
Electoral systems are the rules for conducting elections, a main component of which is the algorithm for determining the winner (or several winners) from the ballots cast. This article discusses methods and results of comparing different electoral systems, both those which elect a unique candidate in a 'single-winner' election and those which elect a group of representatives in a multiwinner election. There are 4 main types of reasoning which have been used to try to determine the best voting method: # Argument by example # Adherence to logical criteria # Results of simulated elections # Results of real elections Expert opinions on single-winner voting methods In 2010, a panel of 22 experts on voting procedures were asked: "What is the best voting rule for your town to use to elect the mayor?". One member abstained. Approval voting was used to decide between 18 single-winner voting methods. The ranking (with number ''N'' of approvers from a maximum of 21) of the various syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median
In statistics and probability theory, the median is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a data sample, a population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as "the middle" value. The basic feature of the median in describing data compared to the mean (often simply described as the "average") is that it is not skewed by a small proportion of extremely large or small values, and therefore provides a better representation of a "typical" value. Median income, for example, may be a better way to suggest what a "typical" income is, because income distribution can be very skewed. The median is of central importance in robust statistics, as it is the most resistant statistic, having a breakdown point of 50%: so long as no more than half the data are contaminated, the median is not an arbitrarily large or small result. Finite data set of numbers The median of a finite list of numbers is the "middle" number, when those numbers are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
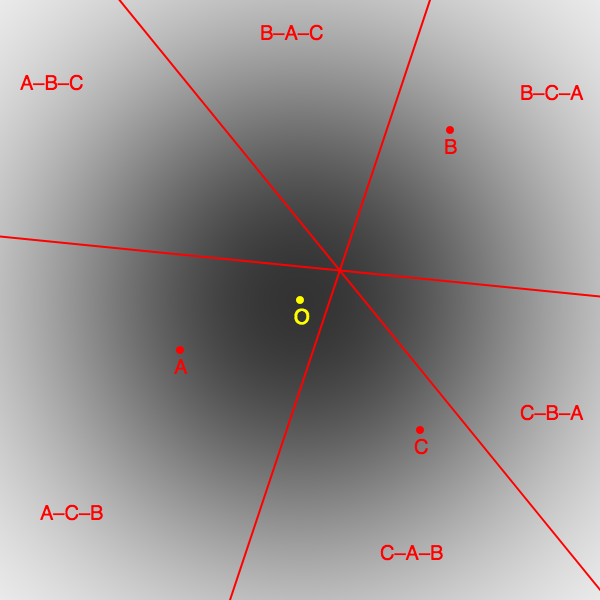
McKelvey–Schofield Chaos Theorem
The McKelvey–Schofield chaos theorem is a result in social choice theory. It states that if preferences are defined over a multidimensional policy space, then majority rule is in general unstable: there is no Condorcet winner. Furthermore, any point in the space can be reached from any other point by a sequence of majority votes. The theorem can be thought of as showing that Arrow's impossibility theorem holds when preferences are restricted to be concave in \mathbb^. The median voter theorem shows that when preferences are restricted to be single-peaked on the real line, Arrow's theorem does not hold, and the median voter's ideal point is a Condorcet winner. The chaos theorem shows that this good news does not continue in multiple dimensions. Richard McKelvey initially proved the theorem for Euclidean preferences. Norman Schofield extended the theorem to the more general class of concave preferences. The figure shows an example. There are three voters in the electorate, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voting Paradox Example
Voting is a method by which a group, such as a meeting or an electorate, can engage for the purpose of making a collective decision or expressing an opinion usually following discussions, debates or election campaigns. Democracies elect holders of high office by voting. Residents of a jurisdiction represented by an elected official are called "constituents," and the constituents who choose to cast a ballot for their chosen candidate are called "voters." There are different systems for collecting votes, but while many of the systems used in decision-making can also be used as electoral systems, any which cater for proportional representation can only be used in elections. In smaller organizations, voting can occur in many different ways. Formally via ballot to elect others for example within a workplace, to elect members of political associations or to choose roles for others. Informally voting could occur as a spoken agreement or as a verbal gesture like a raised hand or ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |