|
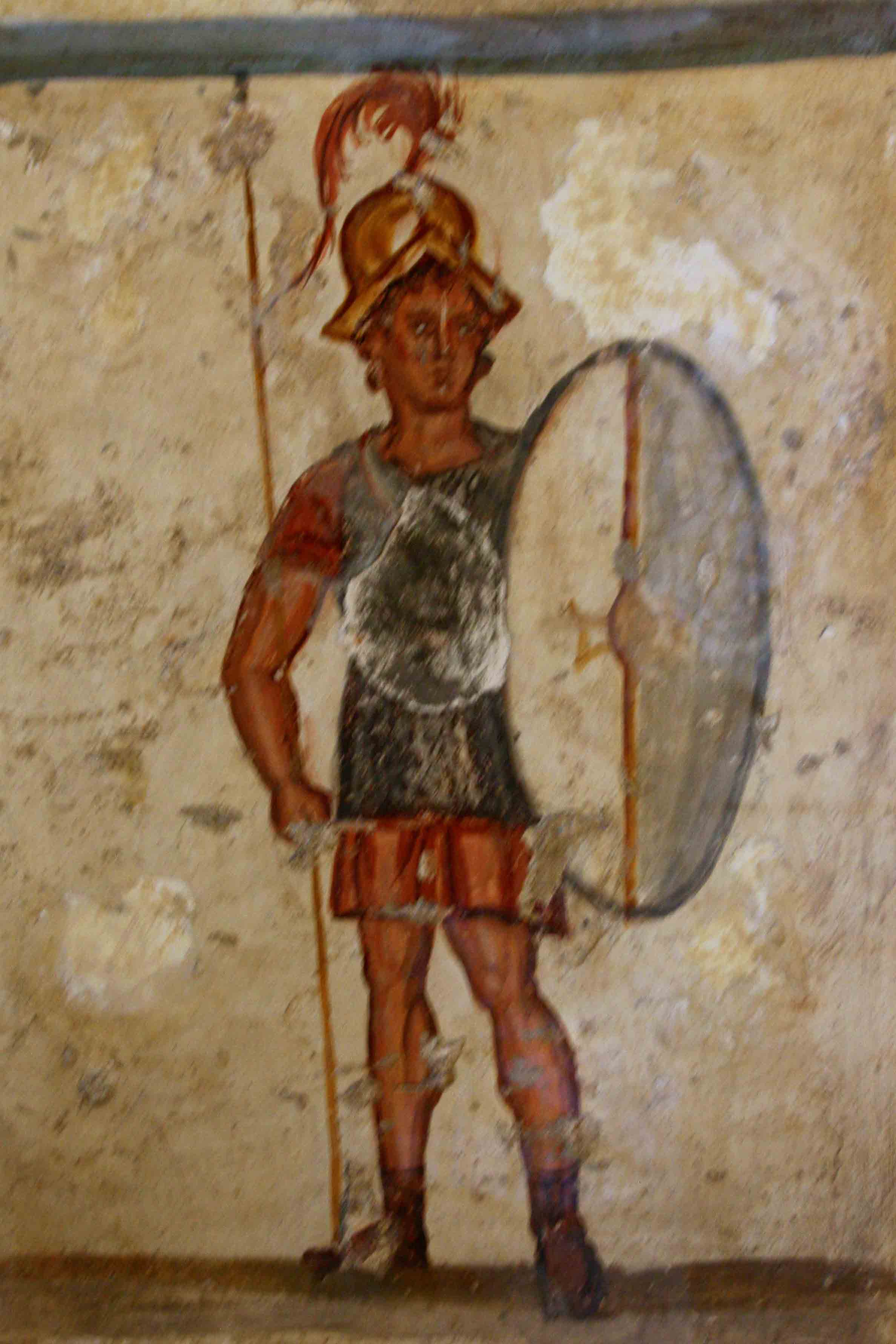
Thorakitai
The ''thorakitai'' ( el, θωρακίται, singular: θωρακίτης, ''thorakites'') were a type of soldier in Hellenistic armies similar to the ''thureophoroi''. The literal translation of the term is "cuirassiers", which suggests that they may have worn a short Celtic mail shirt or possibly a ''linothorax''. Role ''Thorakitai'' were used in armies of the Hellenistic period in a variety of tactical situations. They were a type of armoured but mobile infantry who did not require a rigid formation to be effective in combat. From their name we can deduce that most wore armor and helmet. They bore a ''thureos'', an oval shield, and were armed with sword, javelins and spear, which were used according to their tactical use. It seems that the ''thorakitai'' were heavily armored ''thureophoroi'', able to bear spears and do battle in a phalanx as well as engage in irregular warfare in situations when such an action was required for tactical reasons, like to exploit or challenge rough ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thureophoroi
The ''thyreophoroi'' or ''thureophoroi'' ( el, θυρεοφόροι; singular: ''thureophoros''/''thyreophoros'', θυρεοφόρος) were a type of infantry soldier, common in the 3rd to 1st centuries BC, who carried a large oval shield called a ''thyreos'' which had a type of metal strip boss and a central spine. They were armed with a long thrusting spear, javelins and a sword. They also usually wore an iron or bronze Macedonian helmet. The ''thureos'' was probably originally an adapted form of a Celtic shield. Thracian and Illyrian infantry probably adopted the shield before the Greeks. However, it has been suggested that the ''thureos'' was brought to Greece after Pyrrhus of Epirus' campaigns in Italy, as his Oscan allies and Roman enemies used the '' scutum''. Role ''Thyreophoroi'' are usually distinguished from both skirmishers and the phalanx and seem to have operated in a role intermediate between the two types. They often supported light troops and seemed to be capabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mail (armour)
Chain mail (properly called mail or maille but usually called chain mail or chainmail) is a type of armour consisting of small metal rings linked together in a pattern to form a mesh. It was in common military use between the 3rd century BC and the 16th century AD in Europe, and longer in Asia and North Africa. A coat of this armour is often called a hauberk, and sometimes a byrnie. History The earliest examples of surviving mail were found in the Carpathian Basin at a burial in Horný Jatov, Slovakia dated at 3rd century BC, and in a chieftain's burial located in Ciumești, Romania. Its invention is commonly credited to the Celts, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legionaries
The Roman legionary (in Latin ''legionarius'', plural ''legionarii'') was a professional heavy infantryman of the Roman army after the Marian reforms. These soldiers would conquer and defend the territories of ancient Rome during the late Republic and Principate eras, alongside auxiliary and cavalry detachments. At its height, Roman legionaries were viewed as the foremost fighting force in the Roman world, with commentators such as Vegetius praising their fighting effectiveness centuries after the classical Roman legionary disappeared. Roman legionaries were recruited from Roman citizens under age 45. They were first predominantly made up of recruits from Roman Italy, but more were recruited from the provinces as time went on. As legionaries moved into newly conquered provinces, they helped Romanize the native population and helped integrate the disparate regions of the Roman Empire into one polity. They enlisted in a legion for 25 years of service, a change from the early practic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The region is bounded by the Turkish Straits to the northwest, the Black Sea to the north, the Armenian Highlands to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. The Sea of Marmara forms a connection between the Black and Aegean seas through the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits and separates Anatolia from Thrace on the Balkan peninsula of Southeast Europe. The eastern border of Anatolia has been held to be a line between the Gulf of Alexandretta and the Black Sea, bounded by the Armenian Highlands to the east and Mesopotamia to the southeast. By this definition Anatolia comprises approximately the western two-thirds of the Asian part of Turkey. Today, Anatolia is sometimes considered to be synonymous w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidon
Sidon ( ; he, צִידוֹן, ''Ṣīḏōn'') known locally as Sayda or Saida ( ar, صيدا ''Ṣaydā''), is the third-largest city in Lebanon. It is located in the South Governorate, of which it is the capital, on the Mediterranean coast. Tyre to the south and Lebanese capital Beirut to the north are both about away. Sidon has a population of about 80,000 within city limits, while its metropolitan area has more than a quarter-million inhabitants. Name The Phoenician name ''Ṣīdūn'' (, ) probably meant "fishery" or "fishing town". It is mentioned in Papyrus Anastasi I as Djedouna. It appears in Biblical Hebrew as ''Ṣīḏōn'' ( he, צִידוֹן) and in Syriac as ''Ṣidon'' (). This was Hellenised as ''Sidṓn'' ( grc-gre, Σιδών), which was Latinised as '. The name appears in Classical Arabic as ''Ṣaydūn'' () and in Modern Arabic as ''Ṣaydā'' (). As a Roman colony, it was notionally refounded and given the formal name ' to honour its imper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
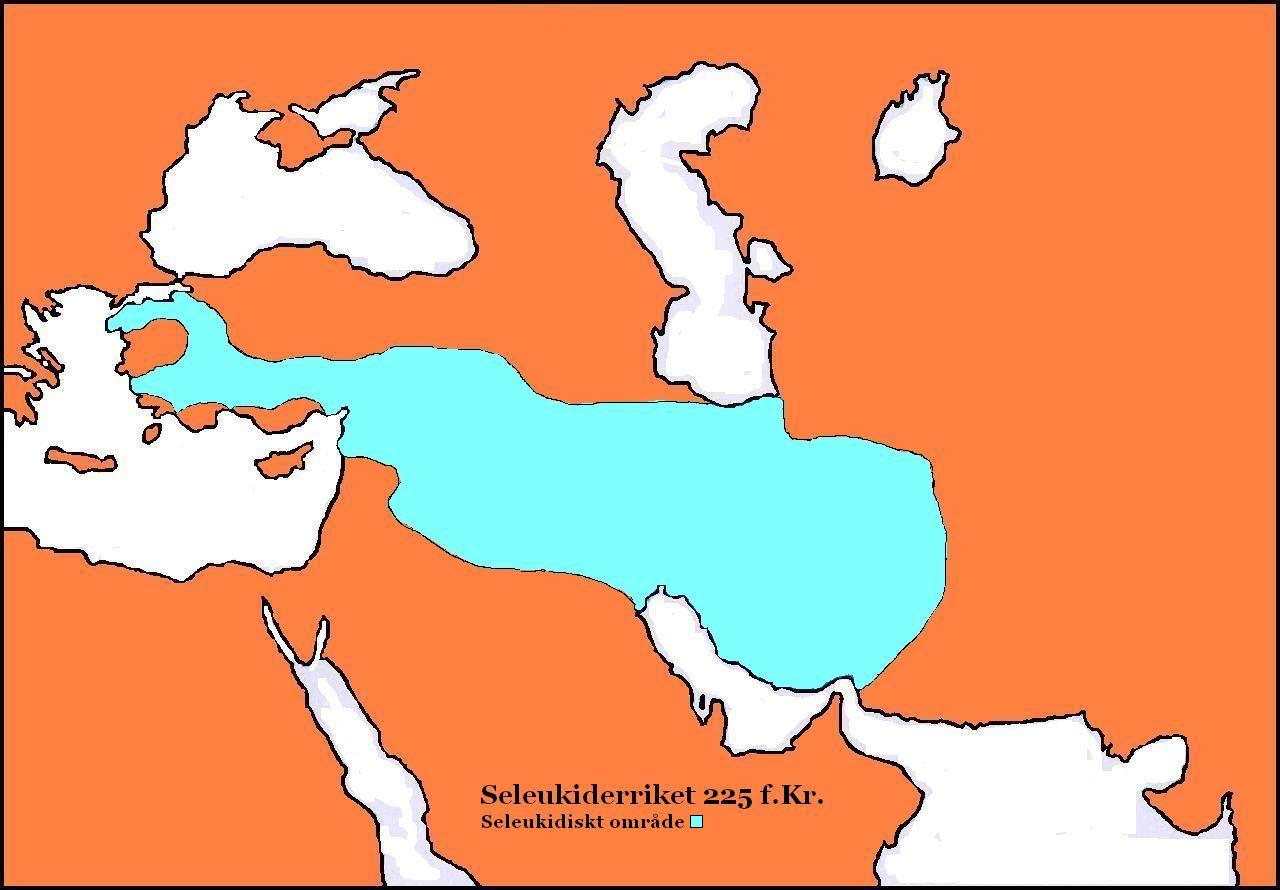
Antiochus III
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the rest of western Asia towards the end of the 3rd century BC. Rising to the throne at the age of eighteen in 222 BC, his early campaigns against the Ptolemaic Kingdom were unsuccessful, but in the following years Antiochus gained several military victories and substantially expanded the empire's territory. His traditional designation, ''the Great'', reflects an epithet he assumed. He also assumed the title ''Basileus Megas'' (Greek for "Great King"), the traditional title of the Persian kings. A militarily active ruler, Antiochus restored much of the territory of the Seleucid Empire, before suffering a serious setback, towards the end of his reign, in his war against Rome. Declaring himself the "champion of Greek freedom against Roman domin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucid Army
The Seleucid army was the army of the Seleucid Empire, one of the numerous Hellenistic states that emerged after the death of Alexander the Great. As with the other major Hellenistic armies, the Seleucid army fought primarily in the Greco-Macedonian style, with its main body being the phalanx. The phalanx was a large, dense formation of men armed with small shields and a long pike called the '' sarissa''. This form of fighting had been developed by the Macedonian army in the reign of Philip II of Macedon and his son Alexander the Great. Alongside the phalanx, the Seleucid armies used a great deal of native and mercenary troops to supplement their Greek forces, which were limited due to the distance from the Seleucid rulers' Macedonian homeland. Manpower The distance from Greece put a strain on the Seleucid military system, as it was primarily based around the recruitment of Greeks as the key segment of the army. In order to increase the population of Greeks in their kingdom, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaean League
The Achaean League ( Greek: , ''Koinon ton Akhaion'' "League of Achaeans") was a Hellenistic-era confederation of Greek city states on the northern and central Peloponnese. The league was named after the region of Achaea in the northwestern Peloponnese, which formed its original core. The first league was formed in the fifth century BC. The second Achaean League was established in 280 BC. As a rival of Antigonid Macedon and an ally of Rome, the league played a major role in the expansion of the Roman Republic into Greece. This process eventually led to the League's conquest and dissolution by the Romans in 146 BC. The League represents the most successful attempt by the Greek city states to develop a form of federalism, which balanced the need for collective action with the desire for local autonomy. Through the writings of the Achaean statesman Polybius, this structure has had an influence on the constitution of the United States and other modern federal states. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peltast
A ''peltast'' ( grc-gre, πελταστής ) was a type of light infantryman, originating in Thrace and Paeonia, and named after the kind of shield he carried. Thucydides mentions the Thracian peltasts, while Xenophon in the Anabasis distinguishes the Thracian and Greek peltast troops. The peltast often served as a skirmisher in Hellenic and Hellenistic armies. In the Medieval period, the same term was used for a type of Byzantine infantryman. Description ''Pelte'' shield ''Peltasts'' carried a crescent-shaped wicker shield called a "''pelte''" (Ancient Greek grc, πέλτη, peltē, label=none; Latin: ) as their main protection, hence their name. According to Aristotle, the ''pelte'' was rimless and covered in goat- or sheepskin. Some literary sources imply that the shield could be round, but in art it is usually shown as crescent-shaped. It also appears in Scythian art and may have been a common type in Central Europe. The shield could be carried with a central strap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoplite
Hoplites ( ) ( grc, ὁπλίτης : hoplítēs) were citizen-soldiers of Ancient Greek city-states who were primarily armed with spears and shields. Hoplite soldiers used the phalanx formation to be effective in war with fewer soldiers. The formation discouraged the soldiers from acting alone, for this would compromise the formation and minimize its strengths. The hoplites were primarily represented by free citizens – propertied farmers and artisans – who were able to afford a linen armour or a bronze armour suit and weapons (estimated at a third to a half of its able-bodied adult male population). Most hoplites were not professional soldiers and often lacked sufficient military training. Some states maintained a small elite professional unit, known as the '' epilektoi'' ("chosen") since they were picked from the regular citizen infantry. These existed at times in Athens, Argos, Thebes, and Syracuse, among other places. Hoplite soldiers made up the bulk of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt the following year. The Ancient Greek word ''Hellas'' (, ''Hellás'') was gradually recognized as the name for Greece, from which the word ''Hellenistic'' was derived. "Hellenistic" is distinguished from "Hellenic" in that the latter refers to Greece itself, while the former encompasses all ancient territories under Greek influence, in particular the East after the conquests of Alexander the Great. After the Macedonian invasion of the Achaemenid Empire in 330 BC and its disintegration shortly after, the Hellenistic kingdoms were established throughout south-west Asia ( Seleucid Empire, Kingdom of Pergamon), north-east Africa ( Ptolemaic Kingdom) and South Asia ( Greco-Bactrian Kingdom, Indo-Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |