|
Thirty-Eighth Army (Japan)
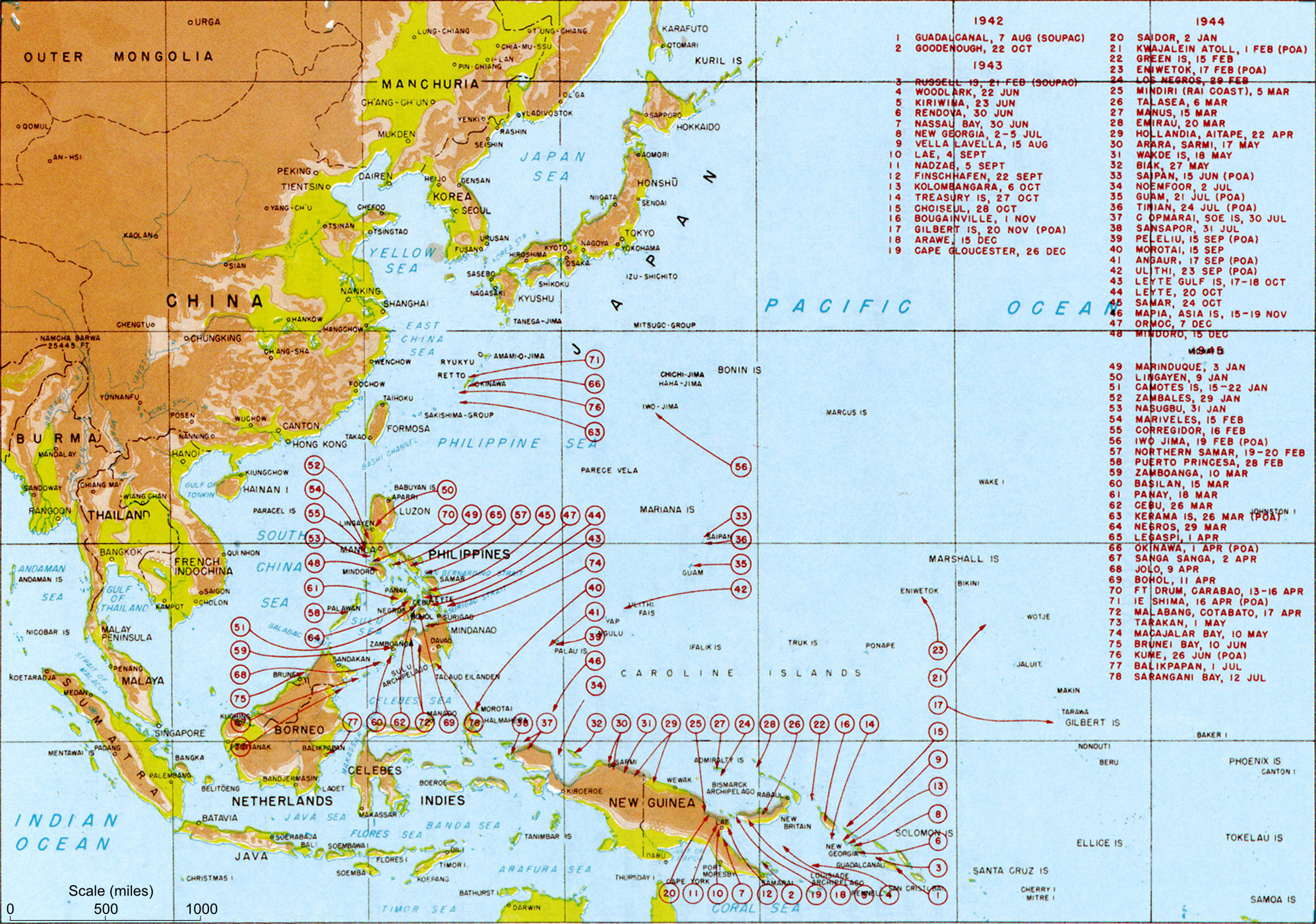
The was an army of the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II. History The was formed on September 9, 1942 under the Southern Expeditionary Army Group following the Japanese invasion and occupation of French Indochina. On November 12, 1944, with the threat of possible landings of Allied forces to retake French Indochina increasing, the organizational structure of the Southern Expeditionary Army changed, and the Indochina Garrison Army was re-designated the Japanese Thirty-Eighth Army. It remained stationed in French Indochina as a garrison force as before. The Japanese 38th Army was involved in the Meigo Sakusen (Operation ''Bright Moon'') of March 1945, which resulted in the proclamation of the Empire of Vietnam independent from French rule. The Japanese 38th Army was demobilized at the surrender of Japan on August 15, 1945 at Hanoi Hanoi or Ha Noi ( or ; vi, Hà Nội ) is the capital and second-largest city of Vietnam. It covers an area of . It consists of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire Of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent formation of modern Japan. It encompassed the Japanese archipelago and several colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories. Under the slogans of and following the Boshin War and restoration of power to the Emperor from the Shogun, Japan underwent a period of industrialization and militarization, the Meiji Restoration, which is often regarded as the fastest modernisation of any country to date. All of these aspects contributed to Japan's emergence as a great power and the establishment of a colonial empire following the First Sino-Japanese War, the Boxer Rebellion, the Russo-Japanese War, and World War I. Economic and political turmoil in the 1920s, including the Great Depression, led to the rise of militarism, nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Expeditionary Army
The was a general army of the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II. It was responsible for all military operations in South East Asian and South West Pacific campaigns of World War II. Its military symbol was NA. The Southern Expeditionary Army Group was formed on November 6, 1941, under the command of '' Gensui'' Count Terauchi Hisaichi, with orders to attack and occupy Allied territories and colonies in South East Asia and the South Pacific. Operational history The Philippines Plans for an invasion of the Philippines were finalized on November 13–15, by Lt General Masaharu Homma, Lt General Hideyoshi Obata, Vice Admiral Ibō Takahashi and Vice Admiral Nishizo Tsukahara. These plans called for air attacks against the Philippines, beginning on '' X-Day'', by the 5th Army Air Force Division and the 11th Naval Air Fleet. At this time, Imperial Japanese Army and Imperial Japanese Navy units were to land on Batan Island, Luzon (at Aparri, Cagayan, Vigan, and Legazp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Units And Formations Established In 1942
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Armies
Japanese may refer to: * Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia * Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan * Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture ** Japanese diaspora, Japanese emigrants and their descendants around the world * Japanese citizens, nationals of Japan under Japanese nationality law ** Foreign-born Japanese, naturalized citizens of Japan * Japanese writing system, consisting of kanji and kana * Japanese cuisine, the food and food culture of Japan See also * List of Japanese people * * Japonica (other) * Japonicum * Japonicus * Japanese studies Japanese studies (Japanese: ) or Japan studies (sometimes Japanology in Europe), is a sub-field of area studies or East Asian studies involved in social sciences and humanities research on Japan. It incorporates fields such as the study of Japanese ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Units And Formations Disestablished In 1945
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teiji Koudo
Teiji (written: 貞治, 貞司, 貞二, 悌二 or 悌次) is a masculine Japanese given name. Notable people with the name include: *, Japanese ice hockey player *, Japanese composer *, Japanese voice actor and actor *, Japanese mathematician *, Japanese actor {{given name Japanese masculine given names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuitsu Tsuchihashi
was a lieutenant general in the Imperial Japanese Army in World War II. Biography Early career Tsuchihashi was born in Saga prefecture and graduated from the 24th class of Imperial Japanese Army Academy in 1912 and the 32nd class of the Army War College (Japan), Army Staff College in 1920. In 1921 he was assigned to the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office, and from 1923 to 1924 was assigned to learn French language, French at the Tokyo Foreign Language School in Kanda, Tokyo. He was stationed in Europe between 1924 and 1927 as a military attache to France and the League of Nations. After his return to Tokyo, he served as a battalion commander in the 1st Infantry Regiment, and in various administrative posts within the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff. In August 1935, on his promotion to colonel, he was given command of the IJA 20th Infantry Regiment. In August 1937, he was assigned as a military liaison to France. World War II After his promotion to major general in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazumoto Machijiri
Viscount was a lieutenant general in the Imperial Japanese Army during World War II. Biography Machijiri was the fourth son of the ''kuge'' Mibu Motonaka (1835–1906) from an ancient court nobility family of Kyoto. He was adopted into the ''kazoku'' peerage by Viscount Machijiri Kazuhiro and inherited the title of ''shishaku''. His wife was the elder daughter of Prince Kaya Kuninori, Yukiko. Machijiri graduated from the 21st class of the Imperial Japanese Army Academy in 1909, where his classmates included Kanji Ishiwara, Jo Iimura and Harukichi Hyakutake. He later graduated from the 29th class of the Army Staff College in 1917. He was a military attaché to France from 1919–1921, participated for three months in the Versailles Peace Treaty Negotiations, and remained as a resident officer in Paris from 1921–1923, and again from 1925–1926. Machijiri was Aide-de-camp to the Emperor of Japan from 1930–1935. From 1935–1936, he commanded the Artillery Regiment of the Imperi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surrender Of Japan
The surrender of the Empire of Japan in World War II was announced by Emperor Hirohito on 15 August and formally signed on 2 September 1945, bringing the war's hostilities to a close. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) had become incapable of conducting major operations and an Allied invasion of Japan was imminent. Together with the United Kingdom and China, the United States called for the unconditional surrender of the Japanese armed forces in the Potsdam Declaration on 26 July 1945—the alternative being "prompt and utter destruction". While publicly stating their intent to fight on to the bitter end, Japan's leaders (the Supreme Council for the Direction of the War, also known as the "Big Six") were privately making entreaties to the publicly neutral Soviet Union to mediate peace on terms more favorable to the Japanese. While maintaining a sufficient level of diplomatic engagement with the Japanese to give them the impression they might be wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demobilization
Demobilization or demobilisation (see spelling differences) is the process of standing down a nation's armed forces from combat-ready status. This may be as a result of victory in war, or because a crisis has been peacefully resolved and military force will not be necessary. The opposite of demobilization is mobilization. Forceful demobilization of a defeated enemy is called demilitarization. The United Nations defined demobilization as "a multifaceted process that officially certifies an individual's change of status from being a member of a military grouping of some kind to being a civilian". Persons undergoing demobilization are removed from the command and control of their armed force and group and the transformation from a military mindset to that of a civilian begins. Although combatants become civilians when they acquire their official discharge documents the mental connection and formal ties to their military command structure still exist. To prevent soldiers from rejoini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire Of Vietnam
The Empire of Vietnam (; Literary Chinese and Contemporary Japanese: ; Modern Japanese: ja, ベトナム帝国, Betonamu Teikoku, label=none) was a short-lived puppet state of Imperial Japan governing the former French protectorates of Annam and Tonkin between March 11 and August 25, 1945. At the end of its rule, the empire also successfully reclaimed Cochinchina as part of Vietnam. History During World War II, after the fall of France and establishment of Vichy France, the French had lost practical control in French Indochina to the Japanese, but Japan stayed in the background while giving the Vichy French administrators nominal control. This changed on 9 March 1945 when Japan officially took over. To gain the support of the Vietnamese people, Imperial Japan declared that it would return sovereignty to Vietnam. On 11 March 1945, Bảo Đại was permitted to announce the Vietnamese "independence", this declaration had been prepared by Yokoyama Seiko, Minister for Economi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |