|
Thiosulfuric Acid
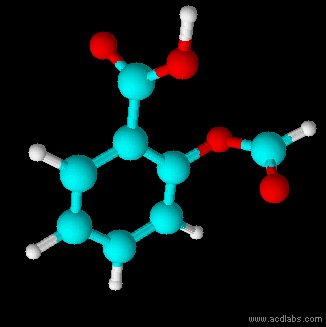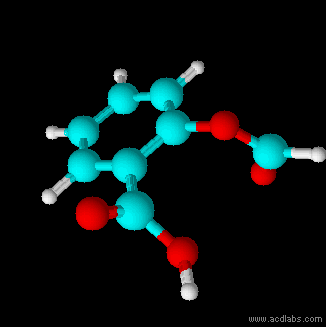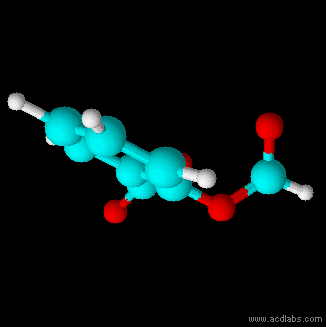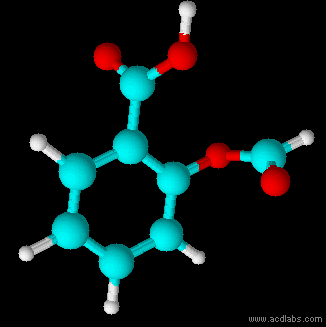
Thiosulfuric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It has attracted academic interest as a simple, easily accessed compound that is labile. It has few practical uses. Preparation and degradation The acid cannot be made by acidifying aqueous thiosulfate salt solutions as the acid readily decomposes in water. The decomposition products can include sulfur, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, polysulfanes, sulfuric acid and polythionates, depending on the reaction conditions.. Anhydrous methods of producing the acid were developed by Max Schmidt: : : : The anhydrous acid also decomposes above −5 °C: : Structure The isomer is more stable than the isomer as established by Hartree–Fock/ ab initio calculations with a 6-311 G** basis set and MP2 to MP4 refinements. The theoretically predicted structure conforms with the double bond rule. An isomer of thiosulfuric acid is the adduct An adduct (from the Latin ''adductus'', "drawn toward" alternative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemsketch
ACD/ChemSketch is a molecular modeling program used to create and modify images of chemical structures. Also, there is a software that allows molecules and molecular models displayed in two and three dimensions, to understand the structure of chemical bonds and the nature of the functional groups. Features The program offers some advanced features that allows the molecules rotate and apply color to improve visualization. It has several templates with ions and functional groups with the possibility to add text and use other tools to optimize productions created by the software. Applications Using ACD/ChemSketch is primarily for educational use. With this program it is possible to write and perform chemical equations, diagrams laboratories and chemical structures of various entity. See also * ChemDraw * Software design * 3D graphics software * Molecule editor A molecule editor is a computer program for creating and modifying representations of chemical structures. Molecu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfuric Acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formula . It is a colorless, odorless and viscous liquid that is miscible with water. Pure sulfuric acid does not exist naturally on Earth due to its strong affinity to water vapor; it is hygroscopic and readily absorbs water vapor from the air. Concentrated sulfuric acid is highly corrosive towards other materials, from rocks to metals, since it is an oxidant with powerful dehydrating properties. Phosphorus pentoxide is a notable exception in that it is not dehydrated by sulfuric acid, but to the contrary dehydrates sulfuric acid to sulfur trioxide. Upon addition of sulfuric acid to water, a considerable amount of heat is released; thus the reverse procedure of adding water to the acid should not be performed since the heat released may boi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Compounds
Hydrogen compounds are compounds containg the element hydrogen. In these compounds, hydrogen can form in the +1 and -1 oxidation states. Hydrogen can form compounds both ionically and in covalent substances. It is a part of many organic compounds such as hydrocarbons as well as water and other organic substances. The ion is often called a proton because it has one proton and no electrons, although the proton does not move freely. Brønsted–Lowry acids are capable of donating ions to bases. Covalent and organic compounds While is not very reactive under standard conditions, it does form compounds with most elements. Hydrogen can form compounds with elements that are more electronegative, such as halogens (F, Cl, Br, I), or oxygen; in these compounds hydrogen takes on a partial positive charge. When bonded to a more electronegative element, particularly fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen, hydrogen can participate in a form of medium-strength noncovalent bonding with another elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Trioxide
Sulfur trioxide (alternative spelling sulphur trioxide, also known as ''nisso sulfan'') is the chemical compound with the formula SO3. It has been described as "unquestionably the most important economically" sulfur oxide. It is prepared on an industrial scale as a precursor to sulfuric acid. Sulfur trioxide exists in several forms - gaseous monomer, crystalline trimer, and solid polymer. Sulfur trioxide is a solid at just below room temperature with a relatively narrow liquid range. Gaseous SO3 is the primary precursor to acid rain. Molecular structure and bonding Monomer The molecule SO3 is trigonal planar. As predicted by VSEPR theory, its structure belongs to the D3h point group. The sulfur atom has an oxidation state of +6 and may be assigned a formal charge value as low as 0 (if all three sulfur-oxygen bonds are assumed to be double bonds) or as high as +2 (if the Octet Rule is assumed). When the formal charge is non-zero, the S-O bonding is assumed to be delocalized. In a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adduct
An adduct (from the Latin ''adductus'', "drawn toward" alternatively, a contraction of "addition product") is a product of a direct addition of two or more distinct molecules, resulting in a single reaction product containing all atoms of all components. The resultant is considered a distinct molecular species. Examples include the addition of sodium bisulfite to an aldehyde to give a sulfonate. It can just be considered as a single product resulting from the direct combination of different molecules which comprises all the reactant molecules' atoms. Adducts often form between Lewis acids and Lewis bases. A good example is the formation of adducts between the Lewis acid borane and the oxygen atom in the Lewis bases, tetrahydrofuran (THF): BH3·O(CH2)4 or diethyl ether: BH3·O(CH3CH2)2. Many Lewis acids and Lewis bases reacting in the gas phase or in non-aqueous solvents to form adducts have been examined in the ECW model. Trimethylboron, trimethyltin chloride and bis(hexaflu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Bond Rule
In chemistry, the double bond rule states that elements with a principal quantum number greater than 2 for their valence electrons (period 3 elements and higher) tend not to form multiple bonds (e.g. double bonds and triple bonds). The double bonds, when they exist, are often weak due to poor orbital overlap. Although such compounds are not intrinsically unstable, they instead tend to polymerize. An example is the rapid polymerization that occurs upon condensation of disulfur, the heavy analogue of . Numerous violations to the rule exist. Other meanings Another unrelated double bond rule exists that relates to the enhanced reactivity of sigma bonds attached to an atom adjacent to a double bond. In bromoalkenes, the C–Br bond is very stable, but in an allyl bromide, this bond is very reactive. Likewise, bromobenzenes are generally inert, whereas benzylic bromides are reactive. The first to observe the phenomenon was Conrad Laar Conrad Peter Laar (22 March 1853 – 11 Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basis Set (chemistry)
In theoretical and computational chemistry, a basis set is a set of functions (called basis functions) that is used to represent the electronic wave function in the Hartree–Fock method or density-functional theory in order to turn the partial differential equations of the model into algebraic equations suitable for efficient implementation on a computer. The use of basis sets is equivalent to the use of an approximate resolution of the identity: the orbitals , \psi_i\rangle are expanded within the basis set as a linear combination of the basis functions , \psi_i\rangle \approx \sum_\mu c_ , \mu\rangle, where the expansion coefficients c_ are given by c_ = \sum_\nu \langle \mu, \nu \rangle^ \langle \nu , \psi_i \rangle. The basis set can either be composed of atomic orbitals (yielding the linear combination of atomic orbitals approach), which is the usual choice within the quantum chemistry community; plane waves which are typically used within the solid state community, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ab Initio Calculation
''Ab initio'' quantum chemistry methods are computational chemistry methods based on quantum chemistry. The term was first used in quantum chemistry by Robert Parr and coworkers, including David Craig in a semiempirical study on the excited states of benzene. The background is described by Parr. ''Ab initio'' means "from first principles" or "from the beginning", implying that the only inputs into an ''ab initio'' calculation are physical constants. ''Ab initio'' quantum chemistry methods attempt to solve the electronic Schrödinger equation given the positions of the nuclei and the number of electrons in order to yield useful information such as electron densities, energies and other properties of the system. The ability to run these calculations has enabled theoretical chemists to solve a range of problems and their importance is highlighted by the awarding of the Nobel prize to John Pople and Walter Kohn. Accuracy and scaling ''Ab initio'' electronic structure method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HS2O3anion
HS or Hs can stand for: Businesses and brands * HS Produkt, a Croatian firearms manufacturer * ''Helsingin Sanomat'', a newspaper in Finland * Hawker Siddeley, aircraft manufacturing group * Henschel & Son, in aircraft prefixes; e.g., Hs 117 * Head & Shoulders or H&S, a shampoo brand * Harris Scarfe and HS Home, a chain of Australian department stores Science and technology Chemistry * Hassium, symbol Hs, a chemical element * Bisulfide, HS−, a chemical compound derived from H2S * Mercapto radical, •, a radical molecule * Hun stuff (a World War I name for mustard gas) Medicine * hs, medical abbreviation for "hours of sleep" * '' h.s.'', medical abbreviation for the Latin phrase ''hora somni'' ("at bedtime") * Hereditary spherocytosis, a genetic disorder marked by hemolytic anemia * Hidradenitis suppurativa, a skin condition affecting apocrine sweat glands and hair follicles Other uses in science and technology * '.hs', the Haskell programming language's typical filename ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polythionates
Polythionates are oxoanions with the formula (''n'' ≥ 0). They occur naturally and are the products of redox reactions of thiosulfate. Polythionates are readily isolable, unlike the parent polythionic acids. Preparation Many members of the polythionates have been characterized: dithionate, trithionate, tetrathionate, pentathionate, etc. These salts are often generated by oxidation of thiosulfate. For example, tetrathionate is obtained by oxidation of thiosulfate ion with iodine (reaction is used in iodometry): : More specialized routes involve reactions of sulfur chlorides with bisulfite salts: : : : Potassium pentathionate ion has been obtained from , sodium thiosulfate, and potassium acetate. Initially prismatic crystals of potassium tetrathionate appear, then lamellar crystals of potassium pentathionate, from which the influence of tartaric acid makes an aqueous solution of pentathionic acid. Potassium hexathionate has been synthesized by combining and in concentrated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysulfane
A polysulfane is a chemical compound of formula , where ''n'' > 1 (although disulfane () is sometimes excluded). Polysulfanes consist of unbranched chains of sulfur atoms terminated with hydrogen atoms. Compounds containing 2 – 8 concatenated sulfur atoms have been isolated, longer chain compounds have been detected, but only in solution. is colourless, higher members are yellow with the colour increasing with the sulfur content. Even a trace of alkali will cause chemical decomposition, and containers need to be treated with acid to remove any traces of alkali. In the chemical literature the term polysulfanes is sometimes used for compounds containing , e.g. organic polysulfanes . Since sulfur is a chalcogen, polysulfanes can be classed as hydrogen chalcogenides. Chemistry and properties Polysulfanes are thermodynamically unstable with respect to decomposition (disproportionation) to and sulfur: : where is ''cyclo''-octasulfur or cyclooctasulfane, one of the allotropes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |