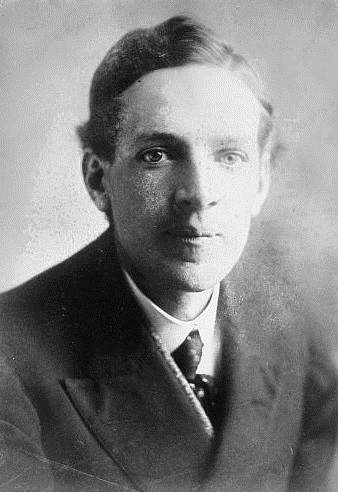|
The Sackbut
''The Sackbut'' was a British music journal published from 1920 to 1934 by the Curwen Press. It published general articles on mainly contemporary, both British and foreign, music as well as reports on performances and records. It was founded by the composer critics Cecil Gray and Philip Heseltine (aka Peter Warlock). The singer and composer Ursula Greville was an editor from July 1921 to 1934. The journal's editions ran from May 1920 (Vol. 1, no. 1) to February 1934 (Vol. 14, no. 7) and was published roughly speaking as a monthly, with exceptions in the first two years and last few years. Noted contributors included Harry Farjeon, William G. Whittaker, Aylmer Maude, Rutland Boughton, Upton Sinclair and Owen Rutter Edward Owen Rutter (7 November 1889 – 2 August 1944) was an English historian, novelist and travel writer. After serving with the North Borneo Civil Service from 1910 to 1915, Rutter returned to Britain during the First World War and was commis ....ProQuest - Pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curwen Press
The Curwen Press was founded by the Reverend John Curwen in 1863 to publish sheet music for the "tonic sol-fa" system. The Press was based in Plaistow, Newham, east London, England, where Curwen was a pastor from 1844. The Curwen Press is best known for its work in the period 1919-1939. The Press's output included books, advertising posters and published ephemera which typically used three interrelated elements: typography, decoration, and publicity which together give the Press a unique and memorable style. The work of the Press provides important evidence that the fine printing of the interwar years was not confined to private presses. The Curwen Press, under the management of Harold Curwen, John's grandson, was at the vanguard of the design revolution that saw expression in British printing in the early 20th century. An underlying ethos of the Curwen Press was that its craftsmanship could and should take both craftsman and consumer on an emotional and aesthetic voyage. Haro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cecil Gray (composer)
Cecil William Turpie Gray (19 May 1895 – 9 September 1951) was a Scottish music critic, author and composer. Biography Born in Edinburgh, he took an arts degree at the University of Edinburgh and studied composition privately with the Anglo-Canadian composer Healey Willan. From there he developed his career as editor, music critic, and author. Gray first met Philip Heseltine (another writer/critic who also composed music under the name Peter Warlock) at the Cafe Royal in the spring of 1916 and they were soon sharing a studio – 2 Anhalt Studios, close to Battersea Park. This led to Gray's first musical venture, the co-sponsoring with Heseltine in 1917 of a concert of works by the then completely unknown composer Bernard van Dieren. Three years later Gray co-founded the early music periodical ''The Sackbut'', also with Heseltine. Gray subsequently worked as music critic for publications including ''The Daily Telegraph'', ''The Manchester Guardian'', and ''The Morning Post'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Warlock
Philip Arnold Heseltine (30 October 189417 December 1930), known by the pseudonym Peter Warlock, was a British composer and music critic. The Warlock name, which reflects Heseltine's interest in occult practices, was used for all his published musical works. He is best known as a composer of songs and other vocal music; he also achieved notoriety in his lifetime through his unconventional and often scandalous lifestyle. As a schoolboy at Eton College, Heseltine met the British composer Frederick Delius, with whom he formed a close friendship. After a failed student career in Oxford and London, Heseltine turned to musical journalism, while developing interests in folk-song and Elizabethan music. His first serious compositions date from around 1915. Following a period of inactivity, a positive and lasting influence on his work arose from his meeting in 1916 with the Dutch composer Bernard van Dieren; he also gained creative impetus from a year spent in Ireland, studying Celtic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ursula Greville
Ursula Greville (1894 – 1991) was a British soprano and folksong singer, songwriter, writer and editor of '' The Sackbut'' (a critical music magazine). She has been credited as the first woman recording engineer. Career Singer Greville was first taught by her mother, who studied with Marchesi. She studied with Field Hyde in London and went to Milan to study with Alfredo Morelli in the early 1920s. She studied diction with Plunkett Greene. Her first recital in London was in 1920. She performed in England, Germany, Austria, and Spain. She did multiple tours in the US. Greville performed a recital at the Town Hall in New York on 16 and 24 October 1926. Sackbut magazine Greville became editor of '' The Sackbut'' in July 1921 and she remained editor until 1934. She was in a relationship with John Kenneth Curwen, the publisher of the magazine, and had no prior experience so the decision was seen as controversial. She also composed some songs which were published through her husba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry Farjeon
Harry Farjeon (6 May 1878 – 29 December 1948) was a British composer and an influential teacher of harmony and composition at the Royal Academy of Music for more than 45 years. Early life and studies Harry Farjeon was born in Hohokus Township, New Jersey, United States, the eldest son of author Benjamin Farjeon, who was from the East End of London, and Margaret, the daughter of American actor Joseph Jefferson. His parents returned to Britain when he was a baby, and he lived in Hampstead in London for the rest of his life. His younger sister, Eleanor Farjeon (b. 1881), with whom he shared a rich imaginary life, wrote children's books and poetry, including the hymn, ''Morning Has Broken''. His younger brothers were J. Jefferson Farjeon (b. 1883), novelist, and Herbert Farjeon (b. 1887), writer of theatrical revues. Harry studied music privately with Landon Ronald and John Storer, then in 1895 he entered the Royal Academy of Music in London, where he studied composition with Bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William G
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the given name ''Wilhelm'' (cf. Proto-Germanic ᚹᛁᛚᛃᚨᚺᛖᛚᛗᚨᛉ, ''*Wiljahelmaz'' > German '' Wilhelm'' and Old Norse ᚢᛁᛚᛋᛅᚼᛅᛚᛘᛅᛋ, ''Vilhjálmr''). By regular sound changes, the native, inherited English form of the name shoul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aylmer Maude
Aylmer Maude (28 March 1858 – 25 August 1938) and Louise Maude (1855–1939) were English translators of Leo Tolstoy's works, and Aylmer Maude also wrote his friend Tolstoy's biography, ''The Life of Tolstoy''. After living many years in Russia the Maudes spent the rest of their life in England translating Tolstoy's writing and promoting public interest in his work. Aylmer Maude was also involved in a number of early 20th century progressive and idealistic causes. Family & Russia Aylmer Maude was born in Ipswich, the son of a Church of England clergyman, Reverend F.H. Maude, and his wife Lucy, who came from a Quaker background. The family lived near the newly built Holy Trinity Church where Rev. Maude's preaching helped draw a large congregation. A few of the vicar's earlier sermons were published with stirring titles like ''Nineveh: A Warning to England!'', but later he moved from Evangelical Anglicanism towards the Anglo-Catholic Church Union. After boarding at Christ's Hos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutland Boughton
Rutland Boughton (23 January 187825 January 1960) was an English composer who became well known in the early 20th century as a composer of opera and choral music. He was also an influential communist activist within the Communist Party of Great Britain (CPGB). His oeuvre includes three symphonies, several concertos, part-songs, songs, chamber music and opera (which he called "music drama" after Wagner). His best known work was the opera ''The Immortal Hour''. His ''Bethlehem'' (1915), based on the Coventry Nativity Play and notable for its choral arrangements of traditional Christmas carols, also became very popular with choral societies worldwide. Among his many works, the prolific Boughton composed a complete series of five operas of Arthurian mythos, written over a period of thirty-five years: ''The Birth of Arthur'' (1909), ''The Round Table'' (1915–16), ''The Lily Maid'' (1933–34), ''Galahad'' (1943–44) and ''Avalon'' (1944–45). Other operas by Boughton include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upton Sinclair
Upton Beall Sinclair Jr. (September 20, 1878 – November 25, 1968) was an American writer, muckraker, political activist and the 1934 Democratic Party nominee for governor of California who wrote nearly 100 books and other works in several genres. Sinclair's work was well known and popular in the first half of the 20th century, and he won the Pulitzer Prize for Fiction in 1943. In 1906, Sinclair acquired particular fame for his classic muck-raking novel, '' The Jungle'', which exposed labor and sanitary conditions in the U.S. meatpacking industry, causing a public uproar that contributed in part to the passage a few months later of the 1906 Pure Food and Drug Act and the Meat Inspection Act. In 1919, he published '' The Brass Check'', a muck-raking exposé of American journalism that publicized the issue of yellow journalism and the limitations of the "free press" in the United States. Four years after publication of ''The Brass Check'', the first code of ethics fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Owen Rutter
Edward Owen Rutter (7 November 1889 – 2 August 1944) was an English historian, novelist and travel writer. After serving with the North Borneo Civil Service from 1910 to 1915, Rutter returned to Britain during the First World War and was commissioned in June 1915. Rutter served with the 7th Battalion of the Wiltshire Regiment in France and on the Salonika front. He edited the ''Balkan News'' which included, under the pseudonym "Klip-Klip", his parody of Henry Wadsworth Longfellow's ''The Song of Hiawatha'' in serial form. Entitled ''Song of Tiadatha'' it has been described as "one of the masterpieces of Great War verse". Later published as a book, ''Tiadatha'' ("Tired Arthur") was the story of a naive, privileged young man who matures through his war experiences, particularly on the Macedonian front fighting against the Bulgarians, and including the Great Thessaloniki Fire of 1917. This volume was followed by ''Travels of Tiadatha'' (1922). Accompanied by his wife, who also took ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defunct Magazines Published In The United Kingdom
{{Disambiguation ...
Defunct (no longer in use or active) may refer to: * ''Defunct'' (video game), 2014 * Zombie process or defunct process, in Unix-like operating systems See also * * :Former entities * End-of-life product * Obsolescence Obsolescence is the state of being which occurs when an object, service, or practice is no longer maintained or required even though it may still be in good working order. It usually happens when something that is more efficient or less risky r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Magazines Published In The United Kingdom
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspect of all human societies, a cultural universal. While scholars agree that music is defined by a few specific elements, there is no consensus on their precise definitions. The creation of music is commonly divided into musical composition, musical improvisation, and musical performance, though the topic itself extends into academic disciplines, criticism, philosophy, and psychology. Music may be performed or improvised using a vast range of instruments, including the human voice. In some musical contexts, a performance or composition may be to some extent improvised. For instance, in Hindustani classical music, the performer plays spontaneously while following a partially defined structure and using characteristic motifs. In modal jazz t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

.jpg)