|
The Language Instinct
''The Language Instinct: How the Mind Creates Language'' is a 1994 book by Steven Pinker, written for a general audience. Pinker argues that humans are born with an innate capacity for language. He deals sympathetically with Noam Chomsky's claim that all human language shows evidence of a universal grammar, but dissents from Chomsky's skepticism that evolutionary theory can explain the human language instinct. Thesis Pinker criticizes a number of common ideas about language, for example that children must be taught to use it, that most people's grammar is poor, that the quality of language is steadily declining, that the kind of linguistic facilities that a language provides (for example, some languages have words to describe light and dark, but no words for colors) has a heavy influence on a person's possible range of thoughts (the Sapir–Whorf hypothesis), and that nonhuman animals have been taught language (see Great ape language). Pinker sees language as an ability unique to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steven Pinker
Steven Arthur Pinker (born September 18, 1954) is a Canadian-American cognitive psychologist, psycholinguist, popular science author, and public intellectual. He is an advocate of evolutionary psychology and the computational theory of mind. Pinker is the Johnstone Family Professor of Psychology at Harvard University, and his academic specializations are visual cognition and developmental linguistics. His experimental subjects include mental imagery, shape recognition, visual attention, children's language development, regular and irregular phenomena in language, the neural bases of words and grammar, as well as the psychology of cooperation and communication, including euphemism, innuendo, emotional expression, and common knowledge. He has written two technical books that proposed a general theory of language acquisition and applied it to children's learning of verbs. In particular, his work with Alan Prince published in 1989 critiqued the connectionist model of how childre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instinct
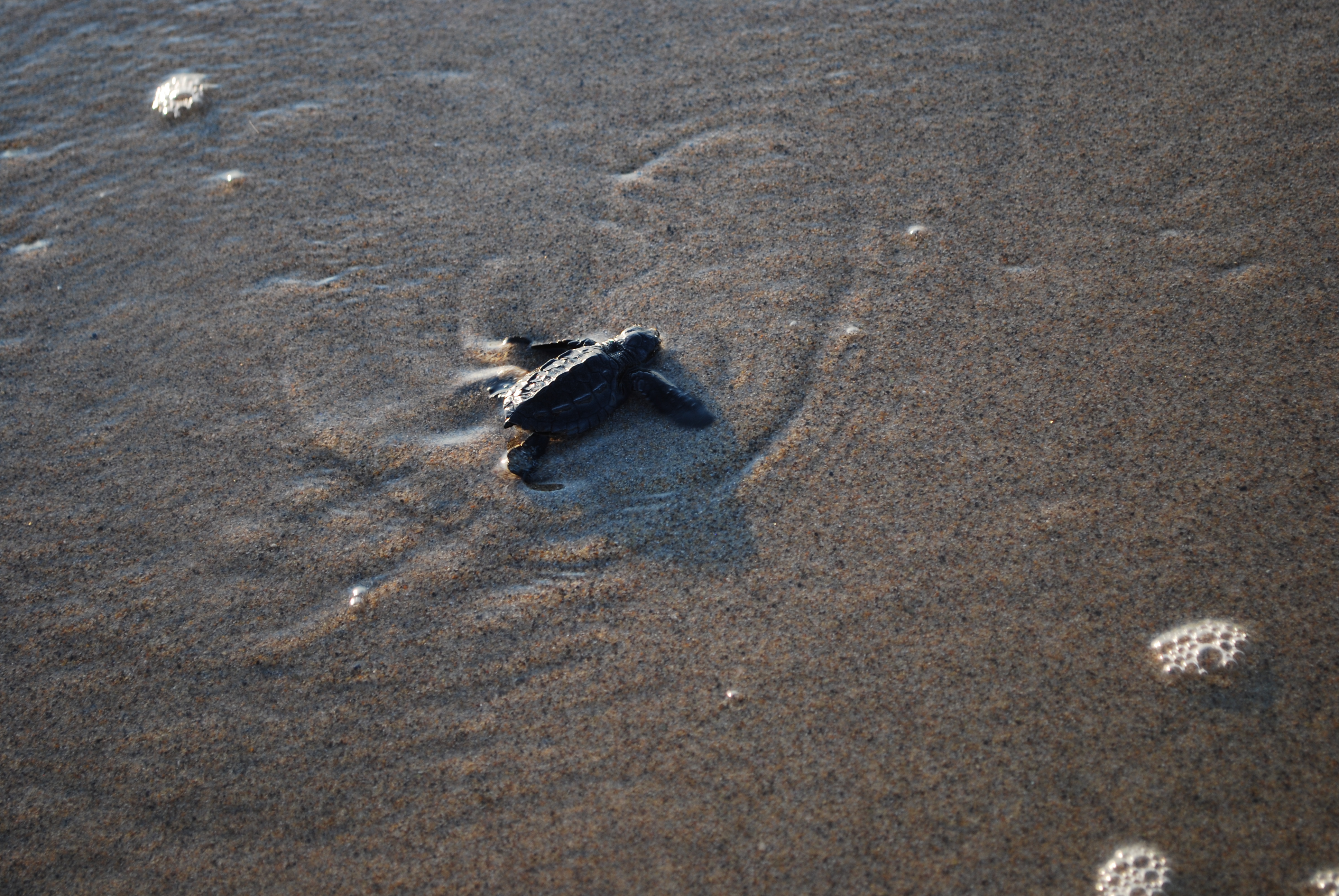
Instinct is the inherent inclination of a living organism towards a particular complex behaviour, containing both innate (inborn) and learned elements. The simplest example of an instinctive behaviour is a fixed action pattern (FAP), in which a very short to medium length sequence of actions, without variation, are carried out in response to a corresponding clearly defined stimulus. Any behaviour is instinctive if it is performed without being based upon prior experience (that is, in the absence of learning), and is therefore an expression of innate biological factors. Sea turtles, newly hatched on a beach, will instinctively move toward the ocean. A marsupial climbs into its mother's pouch upon being born. Other examples include animal fighting, animal courtship behaviour, internal escape functions, and the building of nests. Though an instinct is defined by its invariant innate characteristics, details of its performance can be changed by experience; for example, a dog can im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Principles
In philosophy and science, a first principle is a basic proposition or assumption that cannot be deduced from any other proposition or assumption. First principles in philosophy are from First Cause attitudes and taught by Aristotelians, and nuanced versions of first principles are referred to as postulates by Kantians. In mathematics, first principles are referred to as axioms or postulates. In physics and other sciences, theoretical work is said to be from first principles, or ''ab initio'', if it starts directly at the level of established science and does not make assumptions such as empirical model and parameter fitting. "First principles thinking" consists of deriving things to their fundamental proven axioms in the given arena, before reasoning up by asking which ones are relevant to the question at hand, then cross referencing conclusions based on chosen axioms and making sure conclusions do not violate any fundamental laws. Physicists include counterintuitive concepts wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critical Period
In developmental psychology and developmental biology, a critical period is a maturational stage in the lifespan of an organism during which the nervous system is especially sensitive to certain environmental stimuli. If, for some reason, the organism does not receive the appropriate stimulus during this "critical period" to learn a given skill or trait, it may be difficult, ultimately less successful, or even impossible, to develop certain associated functions later in life. Functions that are indispensable to an organism's survival, such as vision, are particularly likely to develop during critical periods. "Critical period" also relates to the ability to acquire one's first language. Researchers found that people who passed the "critical period" would not acquire their first language fluently. Some researchers differentiate between 'strong critical periods' and 'weak critical periods' (a.k.a. 'sensitive' periods) — defining 'weak critical periods' / 'sensitive periods' as mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptive Aphasia
Wernicke's aphasia, also known as receptive aphasia, sensory aphasia or posterior aphasia, is a type of aphasia in which individuals have difficulty understanding written and spoken language. Patients with Wernicke's aphasia demonstrate fluent speech, which is characterized by typical speech rate, intact syntactic abilities and effortless speech output. Writing often reflects speech in that it tends to lack content or meaning. In most cases, motor deficits (i.e. hemiparesis) do not occur in individuals with Wernicke's aphasia. Therefore, they may produce a large amount of speech without much meaning. Individuals with Wernicke's aphasia are typically unaware of their errors in speech and do not realize their speech may lack meaning. They typically remain unaware of even their most profound language deficits. Like many acquired language disorders, Wernicke's aphasia can be experienced in many different ways and to many different degrees. Patients diagnosed with Wernicke's aphas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expressive Aphasia
Expressive aphasia, also known as Broca's aphasia, is a type of aphasia characterized by partial loss of the ability to produce language ( spoken, manual, or written), although comprehension generally remains intact. A person with expressive aphasia will exhibit effortful speech. Speech generally includes important content words but leaves out function words that have more grammatical significance than physical meaning, such as prepositions and articles. This is known as "telegraphic speech". The person's intended message may still be understood, but their sentence will not be grammatically correct. In very severe forms of expressive aphasia, a person may only speak using single word utterances.ASHA.orgAppendix: Common Classifications of Aphasia. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.asha.org/Practice-Portal/Clinical-Topics/Aphasia/Common-Classifications-of-Aphasia/ Typically, comprehension is mildly to moderately impaired in expressive aphasia due to difficulty understanding complex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Style Guide
A style guide or manual of style is a set of standards for the writing, formatting, and design of documents. It is often called a style sheet, although that term also has multiple other meanings. The standards can be applied either for general use, or be required usage for an individual publication, a particular organization, or a specific field. A style guide establishes standard style requirements to improve communication by ensuring consistency both within a document, and across multiple documents. Because practices vary, a style guide may set out standards to be used in areas such as punctuation, capitalization, citing sources, formatting of numbers and dates, table appearance and other areas. The style guide may require certain best practices in writing style, usage, language composition, visual composition, orthography, and typography. For academic and technical documents, a guide may also enforce the best practice in ethics (such as authorship, research et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the most widely spoken language in the United States and in most circumstances is the de facto common language used in government, education and commerce. Since the 20th century, American English has become the most influential form of English worldwide. American English varieties include many patterns of pronunciation, vocabulary, grammar and particularly spelling that are unified nationwide but distinct from other English dialects around the world. Any American or Canadian accent perceived as lacking noticeably local, ethnic or cultural markers is popularly called "General" or "Standard" American, a fairly uniform accent continuum native to certain regions of the U.S. and associated nationally with broadcast mass media and highly educated speech. However, historical and present linguistic evidence does not sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sign Language
Sign languages (also known as signed languages) are languages that use the visual-manual modality to convey meaning, instead of spoken words. Sign languages are expressed through manual articulation in combination with non-manual markers. Sign languages are full-fledged natural languages with their own grammar and lexicon. Sign languages are not universal and are usually not mutually intelligible, although there are also similarities among different sign languages. Linguists consider both spoken and signed communication to be types of natural language, meaning that both emerged through an abstract, protracted aging process and evolved over time without meticulous planning. Sign language should not be confused with body language, a type of nonverbal communication. Wherever communities of deaf people exist, sign languages have developed as useful means of communication and form the core of local Deaf cultures. Although signing is used primarily by the deaf and hard of hearing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pidgin
A pidgin , or pidgin language, is a grammatically simplified means of communication that develops between two or more groups of people that do not have a language in common: typically, its vocabulary and grammar are limited and often drawn from several languages. It is most commonly employed in situations such as trade, or where both groups speak languages different from the language of the country in which they reside (but where there is no common language between the groups). Linguists do not typically consider pidgins as full or complete languages. Fundamentally, a pidgin is a simplified means of linguistic communication, as it is constructed impromptu, or by convention, between individuals or groups of people. A pidgin is not the native language of any speech community, but is instead learned as a second language. A pidgin may be built from words, sounds, or body language from a multitude of languages as well as onomatopoeia. As the lexicon of any pidgin will be limited to co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creole Language
A creole language, or simply creole, is a stable natural language that develops from the simplifying and mixing of different languages into a new one within a fairly brief period of time: often, a pidgin evolved into a full-fledged language. While the concept is similar to that of a mixed or hybrid language, creoles are often characterized by a tendency to systematize their inherited grammar (e.g., by eliminating irregularities or regularizing the conjugation of otherwise irregular verbs). Like any language, creoles are characterized by a consistent system of grammar, possess large stable vocabularies, and are acquired by children as their native language. These three features distinguish a creole language from a pidgin. Creolistics, or creology, is the study of creole languages and, as such, is a subfield of linguistics. Someone who engages in this study is called a creolist. The precise number of creole languages is not known, particularly as many are poorly attested or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derek Bickerton
Derek Bickerton (March 25, 1926 – March 5, 2018) was an English-born linguist and professor at the University of Hawaii in Manoa. Based on his work in creole languages in Guyana and Hawaii, he has proposed that the features of creole languages provide powerful insights into the development of language both by individuals and as a feature of the human species. He is the originator and main proponent of the language bioprogram hypothesis according to which the similarity of creoles is due to their being formed from a prior pidgin by children who all share a universal human innate grammar capacity. Bickerton also wrote several novels. His novels have been featured in the works of the Sun Ra Revival Post Krautrock Archestra, through spoken word and musical themes. Background Bickerton was born in Cheshire in 1926. A graduate of the University of Cambridge, England in 1949, Derek Bickerton entered academic life in the 1960s, first as a lecturer in English Literature at the Unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)