|
Tan Lun
Tan Lun (, courtesy name Zili 子理, 以詔; Art name Erhua 二華, (1519 –1577) was an eminent Han Chinese official, military general, of the Jiajing Emperor of mid-Ming Dynasty in China. Tan Lun raised and organized Qi Jiguang and several other generals to fight effectively against the Jiajing wokou pirates and along with other prominent figures restored the stability of the Ming Dynasty. He was known for his strategic perception, administrative skill, and for consolidating military strength during the middle Ming Dynasty. He was also known for his ruthlessness in the execution of his policies. Tan also exemplified loyalty in an era of chaos. He died in 1577, where he was bestowed the posthumous honour of Grand Guardian of the Heir Apparent (). Popular culture The 1975 King Hu film '' The Valiant Ones'' features Tan Lun. References *''History of Ming The ''History of Ming'' or the ''Ming History'' (''Míng Shǐ'') is one of the official Chinese historical works kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yihuang County
Yihuang County () is a county of Jiangxi province, People's Republic of China. It is under the jurisdiction of the prefecture-level city A prefecture-level city () or prefectural city is an administrative division of the People's Republic of China (PRC), ranking below a province and above a county in China's administrative structure. During the Republican era, many of China ... of Fuzhou. Administrative divisions In the present, Yihuang County has 7 towns and 5 townships. ;7 towns ;5 townships Demographics The population of the district was in 1999. National Population Statistics Materials by County and City - 1999 Period, ''in'China County & City Population 1999, Harvard China Historical GIS/ref> Climate Notes and references External links *Government site- County-level divisions of Jiangxi Fuzhou, Jiangxi {{Jiangxi-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ray Huang
Ray Huang (; 25 June 19188 January 2000) was a Chinese-American historian and philosopher who was an officer in the National Revolutionary Army and fought in the Burma Campaign. In 1964, Huang earned a Ph.D. in history from the University of Michigan. He worked with Joseph Needham and was a contributor to Needham's ''Science and Civilisation in China''. Huang taught history at universities in the US and the UK, and he is best known in his later years for the idea of macro-history. Early life Ray Huang was born in Ningxiang, Hunan Province, in 1918. He was the oldest of three children. His father, Huang Zhenbai (), was an early member of the revolutionary group Tongmenghui but became less active in the group over the years. Ray Huang grew up in Hunan and went on to study electrical engineering at Nankai University, Tianjin, in 1936. At the outbreak of the Second Sino-Japanese War in 1938, he returned to Changsha and wrote for the ''Anti-Japanese War Report'' (). Soon after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Fuzhou, Jiangxi
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ming Dynasty Generals
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han people, the majority ethnic group in China. Although the primary capital of Beijing fell in 1644 to a rebellion led by Li Zicheng (who established the short-lived Shun dynasty), numerous rump regimes ruled by remnants of the Ming imperial family—collectively called the Southern Ming—survived until 1662. The Ming dynasty's founder, the Hongwu Emperor (r. 1368–1398), attempted to create a society of self-sufficient rural communities ordered in a rigid, immobile system that would guarantee and support a permanent class of soldiers for his dynasty: the empire's standing army exceeded one million troops and the navy's dockyards in Nanjing were the largest in the world. He also took great care breaking the power of the court eunuchs and unr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1577 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 1577 ( MDLXXVII) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events January–June * January 9 – The second Union of Brussels is formed, first without the Protestant counties of Holland and Zeeland (which is accepted by King Philip II of Spain), later with the Protestants, which means open rebellion of the whole of the Netherlands. * March 17 – The Cathay Company is formed, to send Martin Frobisher back to the New World for more gold. * May 28 – The ''Bergen Book'', better known as the ''Solid Declaration'' of the Formula of Concord, one of the Lutheran confessional writings, is published. The earlier version, known as the ''Torgau Book'' (1576), had been condensed into an ''Epitome''; both documents are part of the 1580 ''Book of Concord''. July–December * July 9 – Ludvig Munk is appointed Governor-General of Norway. * September 17 – The Treaty of Bergerac is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1519 Births
__NOTOC__ Year 1519 ( MDXIX) was a common year starting on Saturday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar, the 1519th year of the Common Era (CE) and ''Anno Domini'' (AD) designations, the 519th year of the 2nd millennium, the 19th year of the 16th century, and the 10th and last year of the 1510s decade. Events January–June * January 1 – Ulrich Zwingli preaches for the first time, as people's priest of the Great Minister in Zürich. * March 4 – Hernán Cortés and his conquistadores land in Mexico. * April 21 (Maundy Thursday) – Hernán Cortés reaches San Juan de Ulúa; next day (Good Friday) he sets foot on the beach of modern-day Veracruz. * May 2 – 67-year-old Leonardo da Vinci dies. * June 28 – Charles I of Spain becomes Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor (rules until 1556). July–December * July 4 – Martin Luther joins the debate regarding papal authority, against Johann Eck at Leipzig. * J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minister Of War
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in some the minister is only in charge of general budget matters and procurement of equipment; while in others the minister is also an integral part of the operational military chain of command. A defence minister could be titled Minister for Defense, ''Minister of National Defense'', Secretary of Defense, ''Secretary of State for Defence'', Minister of War or some similar variation. Lists * List of current defence ministers See also * Chief of Defence * Commander-in-chief * Ministry of defence * War cabinet References {{Types of government minister Defence Defense or defence may refer to: Tactical, martial, and political acts or groups * Defense (military), forces primarily intended for warfare * Civil defense, the organizing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
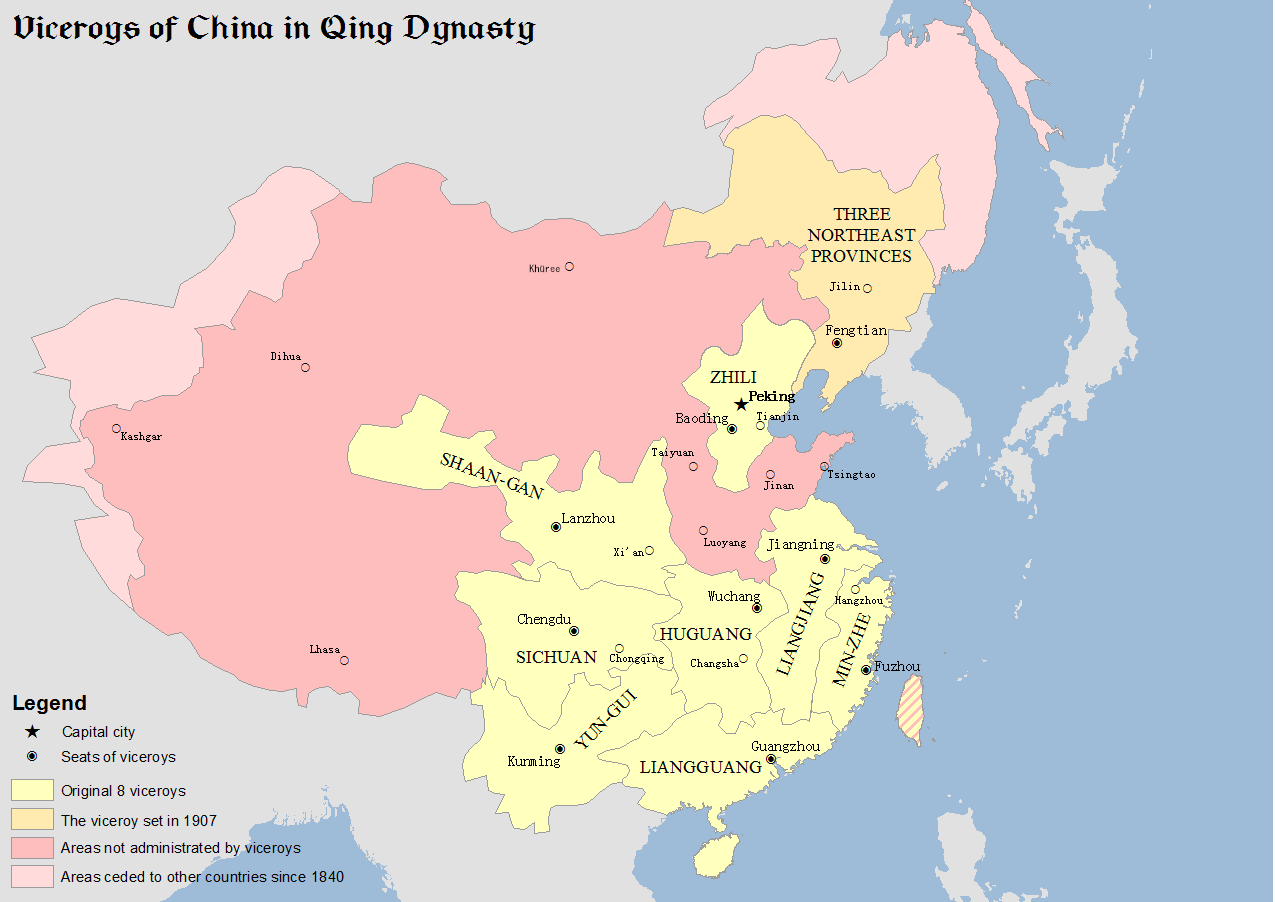
Zongdu
Zongdu (Tsung-tu; ; Manchu: ''Uheri kadalara amban''), usually translated as Viceroy, Head of State or Governor-General, governed one territory or more provinces of China during the Ming and Qing dynasties. One of the most important was the Viceroy of Zhili (Chihli), since it encompassed the imperial capital. Yuan Shikai, later President of Republican China, held this office. Ming dynasty Zhu Yuanzhang, the founding emperor of the Ming dynasty (1368 A.D. to 1644 A.D.), continued the provincial system of the Yuan dynasty but separated Xingsheng into 13 Cheng Xuan Bu Zheng Shi Si, aimed to spread the central government policies. However, later the Ming government found out they needed a coordinator to deal with the conflict between several provinces or suppress rebellion. The viceroy system began in 1441, the 6th year of Zhengtong period, when the minister of war was assigned to cope with the rebellion in Yunnan. From the late 15th century, the Ming central vicer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viceroy Of Liangguang
The Viceroy of Liangguang or Viceroy of the Two Guangs, was one of eight regional Viceroys during the Ming and Qing dynasties. The two ''Guang'' referred to Guangdong and Guangxi provinces. The areas under the Viceroy's jurisdiction included present-day Guangdong and Guangxi provinces, as well as Hainan Province. Name Its full name in Chinese is Governor-General, Commander and Quartermaster, Supervisor of Waterways, and Inspector-General of the Two Expanses and Surrounding Areas. History Ming dynasty The office of the Viceroy of Liangguang originated in 1452 during the Ming dynasty. The Jingtai Emperor accepted Yu Qian's proposal to create the office and appointed Wang Ao (王翱) as the first viceroy. In 1465, the Chenghua Emperor appointed Han Yong (韓雍) as Left Censor-in-Chief and Viceroy of Liangguang. The office was formalised in 1469, with the administrative headquarters fixed in Wuzhou, Guangxi. In 1536, during the reign of the Jiajing Emperor, the viceroy Qia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its capital is Fuzhou, while its largest city by population is Quanzhou, both located near the coast of the Taiwan Strait in the east of the province. While its population is predominantly of Chinese ethnicity, it is one of the most culturally and linguistically diverse provinces in China. The dialects of the language group Min Chinese were most commonly spoken within the province, including the Fuzhou dialect of northeastern Fujian and various Hokkien dialects of southeastern Fujian. Hakka Chinese is also spoken, by the Hakka people in Fujian. Min dialects, Hakka and Mandarin Chinese are mutually unintelligible. Due to emigration, a sizable amount of the ethnic Chinese populations of Taiwan, Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia, and the Philippin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Coordinator
A ''xunfu'' was an important imperial Chinese provincial office under both the Ming (14th–17th centuries) and Qing (17th–20th centuries) dynasties. However, the purview of the office under the two dynasties differed markedly. Under the Ming dynasty, the post originated around 1430 as a kind of inspector-general and ad hoc provincial-level administrator; such a ''xunfu'' is usually translated as a . However, since the mid-17th century, ''xunfu'' became the title of a regular provincial governor overseeing civil administration in the Qing dynasty. Under both dynasties, the ''xunfu'' was subordinate in military affairs to the multi-provincial '' zongdu'' ( 總督), usually translated as "supreme commander" under the Ming and "governor-general" or "viceroy" under the Qing. Ming grand coordinator The "grand coordinator" of the Ming dynasty (1368–1644) was one of several institutional innovations promoted by the Xuande Emperor (r. 1425–1435). Following precedents set by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Ming Dynasty In Decline
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with pronouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of pronoun ''thee'') when followed by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_1938.jpg)






.png)