|
Tafluprost
Tafluprost (trade names Taflotan by Santen Pharmaceutical, Zioptan by Merck in the US and Saflutan by Mundipharma in Australia) is a prostaglandin analogue. It is used topically (as eye drops) to control the progression of open-angle glaucoma and in the management of ocular hypertension, alone or in combination with other medication. It reduces intraocular pressure by increasing the outflow of aqueous fluid from the eyes. Adverse effects The most common side effect is conjunctival hyperemia, which occurs in 4 to 20% of patients. Less common side effects include stinging of the eyes, headache, and respiratory infections. Rare side effects are dyspnoea (breathing difficulties), worsening of asthma, and macular oedema. Interactions Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can either reduce or increase the effect of tafluprost. Timolol eye drops, a common kind of glaucoma medication, does not negatively interact with this drug. No interactions with systemic (for examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Travoprost
Travoprost, sold under the brand name Travatan among others, is a medication used to treat high pressure inside the eye including glaucoma. Specifically it is used for open angle glaucoma when other agents are not sufficient. It is used as an eye drop. Effects generally occur within two hours. Common side effects include red eyes, blurry vision, eye pain, dry eyes, and change in color of the eyes. Other significant side effects may include cataracts. Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding is generally not recommended. It is a prostaglandin analog and works by increasing the outflow of aqueous fluid from the eyes. Travoprost was approved for medical use in the United States and in the European Union in 2001. It is available as a generic medication in the United Kingdom. In 2020, it was the 304th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1million prescriptions. Medical uses Travoprost is used to treat high pressure inside the eye including glaucom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latanoprost
Latanoprost, sold under the brand name Xalatan among others, is a medication used to treat increased pressure inside the eye. This includes ocular hypertension and open angle glaucoma. It is applied as eye drops to the eyes. Onset of effects is usually within four hours, and they last for up to a day. Common side effects include blurry vision, redness of the eye, itchiness, and darkening of the iris. Latanoprost is in the prostaglandin analogue family of medications. It works by increasing the outflow of aqueous fluid from the eyes through the uveoscleral tract. Latanoprost was approved for medical use in the United States in 1996. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Latanoprost is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 77th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States with more than 9million prescriptions. It is available as a combination with netarsudil and with timolol. Medical uses Open-angle glaucoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmic Drug Administration
Ophthalmic drug administration is the administration of a drug to the eyes, most typically as an eye drop formulation. Topical formulations are used to combat a multitude of diseased states of the eye. These states may include bacterial infections, eye injury, glaucoma, and dry eye. However, there are many challenges associated with topical delivery of drugs to the cornea of the eye. Eye drop formulations Two of the largest challenges faced when using topicals to treat pathological states of the eye include patient compliance and ineffective absorbance of drugs into the cornea. In fact, researchers in this field of drug delivery agree that less than 7% of drugs delivered to the eye reach and penetrate the corneal barrier, therefore, increasing the frequency of dosing used for topicals. This is one of the fundamental problem associated with using topicals to deliver drugs to the cornea and therefore leads to the increased demand for patient compliance. Together, these two fact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prodrug
A prodrug is a medication or compound that, after intake, is metabolized (i.e., converted within the body) into a pharmacologically active drug. Instead of administering a drug directly, a corresponding prodrug can be used to improve how the drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted ( ADME). Prodrugs are often designed to improve bioavailability when a drug itself is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. A prodrug may be used to improve how selectively the drug interacts with cells or processes that are not its intended target. This reduces adverse or unintended effects of a drug, especially important in treatments like chemotherapy, which can have severe unintended and undesirable side effects. History Many herbal extracts historically used in medicine contain glycosides (sugar derivatives) of the active agent, which are hydrolyzed in the intestines to release the active and more bioavailable aglycone. For example, salicin is a β-D-glucopy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucuronidated
Glucuronidation is often involved in drug metabolism of substances such as drugs, pollutants, bilirubin, androgens, estrogens, mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, fatty acid derivatives, retinoids, and bile acids. These linkages involve glycosidic bonds. Mechanism Glucuronidation consists of transfer of the glucuronic acid component of uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid to a substrate by any of several types of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase. UDP-glucuronic acid (glucuronic acid linked via a glycosidic bond to uridine diphosphate) is an intermediate in the process and is formed in the liver. One example is the N-glucuronidation of an aromatic amine, 4-aminobiphenyl, by UGT1A4 or UGT1A9 from human, rat, or mouse liver. : The substances resulting from glucuronidation are known as glucuronides (or glucuronosides) and are typically much more water-soluble than the non-glucuronic acid-containing substances from which they were originally synthesised. The human body uses glucuronidatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
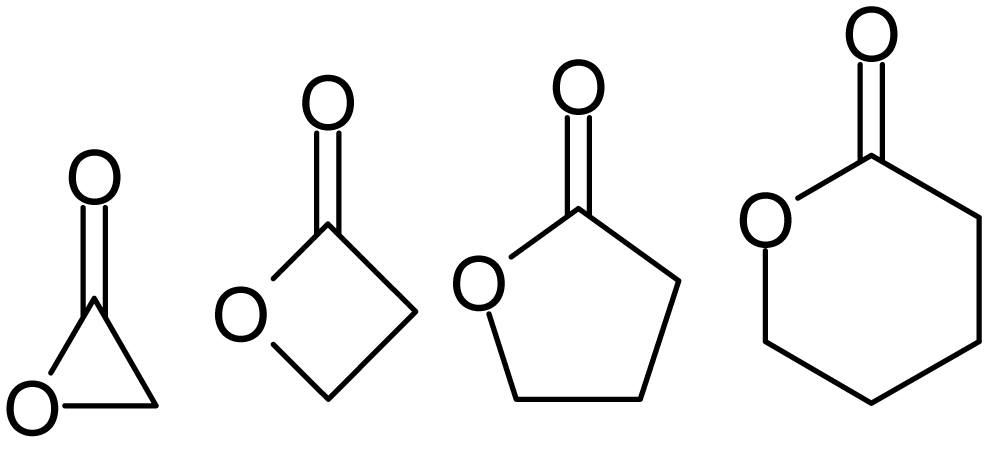
Lactone
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters, containing a 1-oxacycloalkan-2-one structure (), or analogues having unsaturation or heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring. Lactones are formed by intramolecular esterification of the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids, which takes place spontaneously when the ring that is formed is five- or six-membered. Lactones with three- or four-membered rings (α-lactones and β-lactones) are very reactive, making their isolation difficult. Special methods are normally required for the laboratory synthesis of small-ring lactones as well as those that contain rings larger than six-membered. Nomenclature Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (''aceto'' = 2 carbon atoms, ''propio'' = 3, ''butyro'' = 4, ''valero'' = 5, ''capro'' = 6, etc.), with a ''-lactone'' suffix and a Greek letter prefix that specifies the number of carbon atoms in the heterocycle — that is, the distance between the relevant -OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxylic Acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion. Examples and nomenclature Carboxylic acids are commonly identified by their trivial names. They at oftentimes have the suffix ''-ic acid''. IUPAC-recommended names also exist; in this system, carboxylic acids have an ''-oic acid'' suffix. For example, butyric acid (C3H7CO2H) is butanoic acid by IUPAC guidelines. For nomenclature of complex molecules containing a carboxylic acid, the carboxyl can be considered position one of the parent chain even if there are other substituents, such as 3-chloropropanoic acid. Alternately, it can be named as a "carboxy" or "carboxylic acid" substituent on ano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
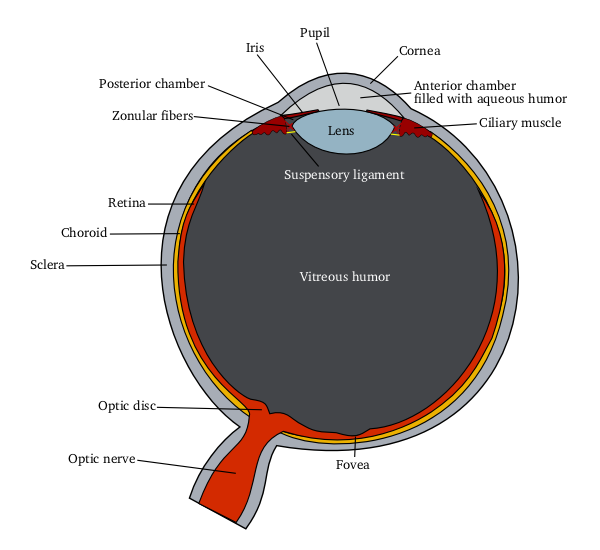
Cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical power. In humans, the refractive power of the cornea is approximately 43 dioptres. The cornea can be reshaped by surgical procedures such as LASIK. While the cornea contributes most of the eye's focusing power, its focus is fixed. Accommodation (the refocusing of light to better view near objects) is accomplished by changing the geometry of the lens. Medical terms related to the cornea often start with the prefix "'' kerat-''" from the Greek word κέρας, ''horn''. Structure The cornea has unmyelinated nerve endings sensitive to touch, temperature and chemicals; a touch of the cornea causes an involuntary reflex to close the eyelid. Because transparency is of prime importance, the healthy cornea does not have or need blood ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol; they are important in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils. Esters typically have a pleasant smell; those of low molecular weight are commonly used as fragrances and are found in essential oils and pheromones. They perform as high-grade solvents for a broad array of plastics, plasticizers, resins, and lacquers, and are one of the largest classes of synthetic lubricants on the commercial market. Polyesters are important plastics, with monomers linked by ester moieties. Phosphoesters form the backbone of DNA molecules. Nitrate esters, such as nitroglycerin, are known for their explosive properties. '' Nomenclature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipophilic
Lipophilicity (from Greek λίπος "fat" and φίλος "friendly"), refers to the ability of a chemical compound to dissolve in fats, oils, lipids, and non-polar solvents such as hexane or toluene. Such non-polar solvents are themselves lipophilic (translated as "fat-loving" or "fat-liking"), and the axiom that "like dissolves like" generally holds true. Thus lipophilic substances tend to dissolve in other lipophilic substances, but hydrophilic ("water-loving") substances tend to dissolve in water and other hydrophilic substances. Lipophilicity, hydrophobicity, and non-polarity may describe the same tendency towards participation in the London dispersion force, as the terms are often used interchangeably. However, the terms "lipophilic" and "hydrophobic" are not synonymous, as can be seen with silicones and fluorocarbons, which are hydrophobic but not lipophilic. __TOC__ Surfactants Hydrocarbon-based surfactants are compounds that are amphiphilic (or amphipathic), having ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostaglandin F Receptor
Prostaglandin F receptor (FP) is a receptor belonging to the prostaglandin (PG) group of receptors. FP binds to and mediates the biological actions of Prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α). It is encoded in humans by the ''PTGFR'' gene. Gene The ''PTGFR'' gene is located on human chromosome 1 at position p31.1 (i.e. 1p31.1), contains 7 exons, and codes for a G protein coupled receptor (GPCR) of the rhodopsin-like receptor family, Subfamily A14 (see rhodopsin-like receptors#Subfamily A14). ''PTGFR'' is expressed as two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms, FPA and FPB, which have different C-terminal lengths. MicroRNA miR-590-3p binds to the Three prime untranslated region of the FP gene to repress its translation. miR-590-3p thus appears to be a negative regulator of FP expression in various cell types. Expression In humans, FP mRNA and/or protein is highly expressed in the uterine myometrium; throughout the eye (endothelium and smooth muscle cells o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist. Etymology From the Greek αγωνιστής (agōnistēs), contestant; champion; rival < αγων (agōn), contest, combat; exertion, struggle < αγω (agō), I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive Types of agonists can be activated by either endogenous agonists (such as[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |