|
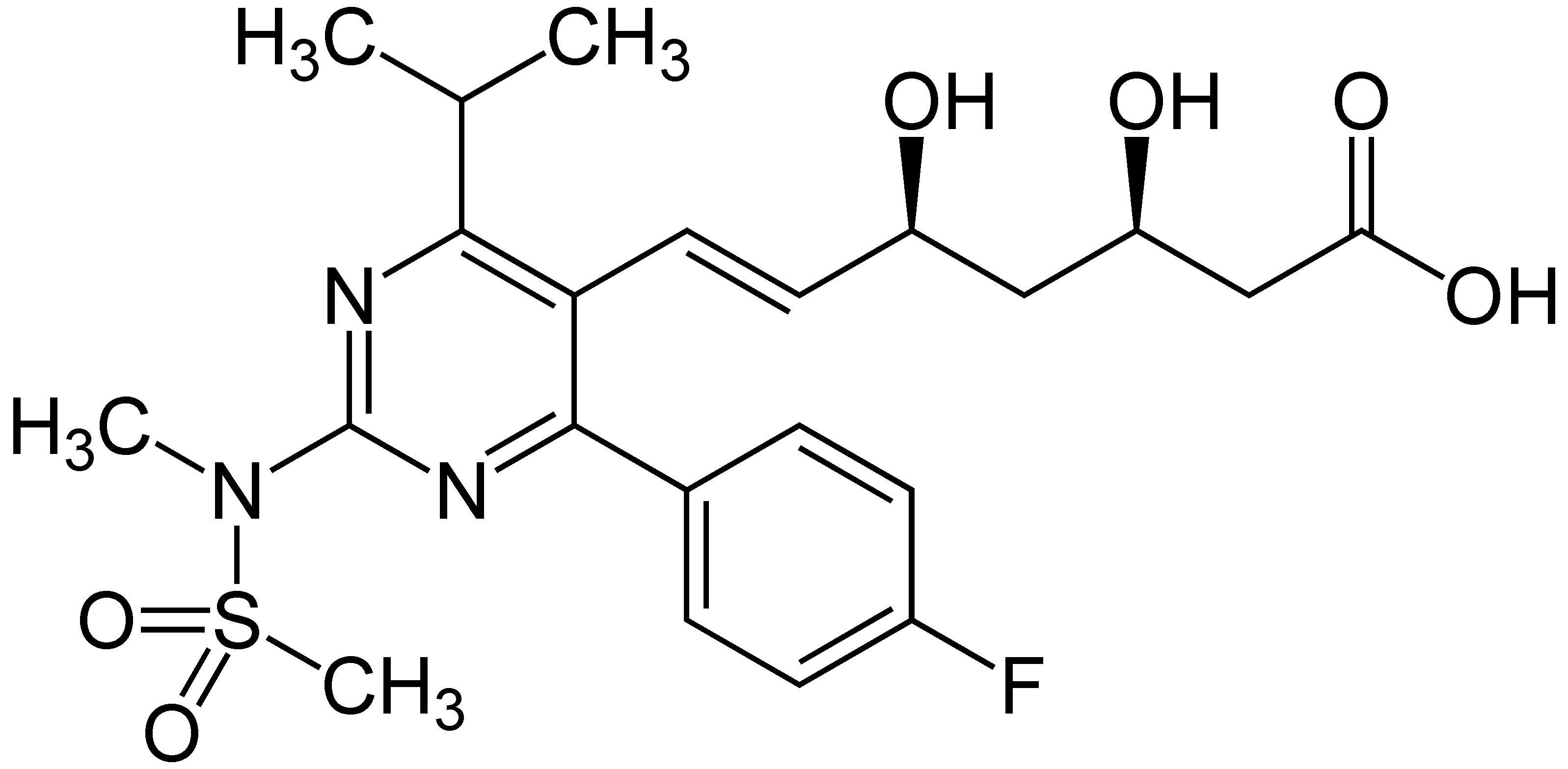
Tafamidis
Tafamidis, sold under the brand names Vyndaqel and Vyndamax, is a medication used to delay disease progression in adults with certain forms of transthyretin amyloidosis. It can be used to treat both hereditary forms, familial amyloid cardiomyopathy and familial amyloid polyneuropathy, as well as wild-type transthyretin amyloidosis, which formerly was called senile systemic amyloidosis. It works by stabilizing the quaternary structure of the protein transthyretin. In people with transthyretin amyloidosis, transthyretin falls apart and forms clumps called (amyloid) that harm tissues including nerves and the heart. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration considers tafamidis to be a first-in-class medication. Medical use Tafamidis is used to delay nerve damage in adults who have transthyretin amyloidosis with polyneuropathy, or heart disease in adults who have transthyretin amyloidosis with cardiomyopathy. It is taken by mouth. Women should not get pregnant while taking it and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amyloidosis
Amyloidosis is a group of diseases in which abnormal proteins, known as amyloid fibrils, build up in tissue. There are several non-specific and vague signs and symptoms associated with amyloidosis. These include fatigue, peripheral edema, weight loss, shortness of breath, palpitations, and feeling faint with standing. In AL amyloidosis, specific indicators can include enlargement of the tongue and periorbital purpura. In wild-type ATTR amyloidosis, non-cardiac symptoms include: bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome, lumbar spinal stenosis, biceps tendon rupture, small fiber neuropathy, and autonomic dysfunction. There are about 36 different types of amyloidosis, each due to a specific protein misfolding. Within these 36 proteins, 19 are grouped into localized forms, 14 are grouped as systemic forms, and 3 proteins can identify as either. These proteins can become irregular due to genetic effects, as well as through acquired environmental factors. The four most common types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy
Familial amyloid polyneuropathy, also called transthyretin-related hereditary amyloidosis, transthyretin amyloidosis abbreviated also as ATTR (hereditary form), or Corino de Andrade's disease, is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disease. It is a form of amyloidosis, and was first identified and described by Portuguese neurologist Mário Corino da Costa Andrade, in 1952. FAP is distinct from senile systemic amyloidosis (SSA), which is not inherited, and which was determined to be the primary cause of death for 70% of supercentenarians who have been autopsied. FAP can be ameliorated by liver transplantation. Presentation Usually manifesting itself between 20 and 40 years of age, it is characterized by pain, paresthesia, muscular weakness and autonomic dysfunction. In its terminal state, the kidneys and the heart are affected. FAP is characterized by the systemic deposition of amyloidogenic variants of the transthyretin protein, especially in the peripheral nervous syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wild-type Transthyretin Amyloid
Wild-type transthyretin amyloid (WTTA), also known as senile systemic amyloidosis (SSA), is a disease that typically affects the heart and tendons of elderly people. It is caused by accumulation of a wild-type (that is to say a normal) protein called transthyretin. This is in contrast to a related condition called transthyretin-related hereditary amyloidosis where a genetically mutated transthyretin protein tends to deposit at a much earlier age than in WTTA, due to abnormal conformation and bioprocessing. It belongs to a group of diseases called amyloidosis, chronic progressive conditions linked to abnormal deposition of normal or abnormal proteins, because these proteins are misshapen and cannot be properly degraded and eliminated by the cell metabolism. Signs and symptoms Wild-type transthyretin amyloid accumulates mainly in the heart, where it causes stiffness and often thickening of its walls, leading consequently to shortness of breath and intolerance to exercise, called dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meglumine
Meglumine is a sugar alcohol derived from glucose that contains an amino group modification. It is often used as an excipient in pharmaceuticals and in conjunction with iodinated compounds in contrast media such as diatrizoate meglumine, iothalamate meglumine and iodipamide meglumine. chemicalland21.com See also * Flunixin meglumine *Meglumine antimoniate
Meglumine antimoniate is a medicine used to treat leishmaniasis. This includes visceral, mucocutaneous, and cutaneous leishmaniasis. It is given by injection into a muscle or into t ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drugs Acting On The Nervous System
A drug is any chemical substance that causes a change in an organism's physiology or psychology when consumed. Drugs are typically distinguished from food and substances that provide nutritional support. Consumption of drugs can be via inhalation, injection, smoking, ingestion, absorption via a patch on the skin, suppository, or dissolution under the tongue. In pharmacology, a drug is a chemical substance, typically of known structure, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. A pharmaceutical drug, also called a medication or medicine, is a chemical substance used to treat, cure, prevent, or diagnose a disease or to promote well-being. Traditionally drugs were obtained through extraction from medicinal plants, but more recently also by organic synthesis. Pharmaceutical drugs may be used for a limited duration, or on a regular basis for chronic disorders. Pharmaceutical drugs are often classified into drug classes—groups of related drugs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therapeutic Goods Administration
The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) is the medicine and therapeutic regulatory agency of the Australian Government. As part of the Department of Health and Aged Care, the TGA regulates the quality, supply and advertising of medicines, pathology devices, medical devices, blood products and most other therapeutics. Any items that claim to have a therapeutic effect, are involved in the administration of medication, or are otherwise covered by the ''Therapeutic Goods Act 1989'', the ''Therapeutic Goods Regulations 1990'', or a ministerial order, must be approved by the TGA and registered in the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods. Structure of the TGA and medical regulation in Australia In Australia, medical products are regulated by the TGA and, for controlled drugs such as cannabis, the Office of Drug Control (ODC). Together, the TGA and ODC form the Health Products Regulation Group within the Department of Health and Aged Care. The Health Products Regulation Group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orphan Drug
An orphan drug is a pharmaceutical agent developed to treat medical conditions which, because they are so rare, would not be profitable to produce without government assistance. The conditions are referred to as orphan diseases. The assignment of orphan status to a disease and to drugs developed to treat it is a matter of public policy in many countries and has yielded medical breakthroughs that might not otherwise have been achieved, due to the economics of drug research and development. In the U.S. and the EU, it is easier to gain marketing approval for an orphan drug. There may be other financial incentives, such as an extended period of exclusivity, during which the producer has sole rights to market the drug. All are intended to encourage development of drugs which would otherwise lack sufficient profit motive to attract corporate research budgets and personnel. Definition According to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an orphan drug is defined as one "intended for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Medicines Agency
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) in charge of the evaluation and supervision of medicinal products. Prior to 2004, it was known as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products or European Medicines Evaluation Agency (EMEA).Set up by EC Regulation No. 2309/93 as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, and renamed by EC Regulation No. 726/2004 to the European Medicines Agency, it had the acronym EMEA until December 2009. The European Medicines Agency does not call itself EMA either – it has no official acronym but may reconsider if EMA becomes commonly accepted (secommunication on new visual identity an). The EMA was set up in 1995, with funding from the European Union and the pharmaceutical industry, as well as indirect subsidy from member states, its stated intention to harmonise (but not replace) the work of existing national medicine regulatory bodies. The hope was that this plan would not o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pfizer
Pfizer Inc. ( ) is an American multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered on 42nd Street in Manhattan, New York City. The company was established in 1849 in New York by two German entrepreneurs, Charles Pfizer (1824–1906) and his cousin Charles F. Erhart (1821–1891). Pfizer develops and produces medicines and vaccines for immunology, oncology, cardiology, endocrinology, and neurology. The company has several blockbuster drugs or products that each generate more than billion in annual revenues. In 2020, 52% of the company's revenues came from the United States, 6% came from each of China and Japan, and 36% came from other countries. Pfizer was a component of the Dow Jones Industrial Average stock market index from 2004 to August 2020. The company ranks 64th on the Fortune 500 and 49th on the Forbes Global 2000. History 1849–1950: Early history Pfizer was founded in 1849 by Charles Pfizer and Charles F. Erhart, two cousins who ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Development
Drug development is the process of bringing a new pharmaceutical drug to the market once a lead compound has been identified through the process of drug discovery. It includes preclinical research on microorganisms and animals, filing for regulatory status, such as via the United States Food and Drug Administration for an investigational new drug to initiate clinical trials on humans, and may include the step of obtaining regulatory approval with a new drug application to market the drug. The entire process – from concept through preclinical testing in the laboratory to clinical trial development, including Phase I–III trials – to approved vaccine or drug typically takes more than a decade. New chemical entity development Broadly, the process of drug development can be divided into preclinical and clinical work. Pre-clinical New chemical entities (NCEs, also known as new molecular entities or NMEs) are compounds that emerge from the process of drug discovery. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_I_(cropped).jpg)