|
TDRSS
The U.S. Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System (TDRSS) is a network of American communications satellites (each called a tracking and data relay satellite, TDRS) and ground stations used by NASA for space communications. The system was designed to replace an existing network of ground stations that had supported all of NASA's crewed flight missions. The prime design goal was to increase the time spacecraft were in communication with the ground and improve the amount of data that could be transferred. Many Tracking and Data Relay Satellites were launched in the 1980s and 1990s with the Space Shuttle and made use of the Inertial Upper Stage, a two-stage solid rocket booster developed for the shuttle. Other TDRS were launched by Atlas IIa and Atlas V rockets. The most recent generation of satellites provides ground reception rates of 6 Mbit/s in the S-band and 800 Mbit/s in the Ku- and Ka-bands. This is mainly used by the United States military. Origins To satisfy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TDRS Program Logo
A tracking and data relay satellite (TDRS) is a type of communications satellite that forms part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System (TDRSS) used by NASA and other United States government agencies for communications to and from independent "User Platforms" such as satellites, balloons, aircraft, the International Space Station, and remote bases like the Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station. This system was designed to replace an existing worldwide network of ground stations that had supported all of NASA's crewed flight missions and uncrewed satellites in low-Earth orbits. The primary system design goal was to increase the amount of time that these spacecraft were in communication with the ground and improve the amount of data that could be transferred. These TDRSS satellites are all designed and built to be launched to and function in geosynchronous orbit, above the surface of the Earth. The first seven TDRSS satellites were built by the TRW corporation. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracking And Data Relay Satellite
A tracking and data relay satellite (TDRS) is a type of communications satellite that forms part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System (TDRSS) used by NASA and other United States government agencies for communications to and from independent "User Platforms" such as satellites, balloons, aircraft, the International Space Station, and remote bases like the Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station. This system was designed to replace an existing worldwide network of ground stations that had supported all of NASA's crewed flight missions and uncrewed satellites in low-Earth orbits. The primary system design goal was to increase the amount of time that these spacecraft were in communication with the ground and improve the amount of data that could be transferred. These TDRSS satellites are all designed and built to be launched to and function in geosynchronous orbit, above the surface of the Earth. The first seven TDRSS satellites were built by the TRW corporation. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TDRS Satellite
A tracking and data relay satellite (TDRS) is a type of communications satellite that forms part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System (TDRSS) used by NASA and other United States government agencies for communications to and from independent "User Platforms" such as satellites, balloons, aircraft, the International Space Station, and remote bases like the Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station. This system was designed to replace an existing worldwide network of ground stations that had supported all of NASA's crewed flight missions and uncrewed satellites in low-Earth orbits. The primary system design goal was to increase the amount of time that these spacecraft were in communication with the ground and improve the amount of data that could be transferred. These TDRSS satellites are all designed and built to be launched to and function in geosynchronous orbit, above the surface of the Earth. The first seven TDRSS satellites were built by the TRW corporation. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracking And Data Relay Satellite
A tracking and data relay satellite (TDRS) is a type of communications satellite that forms part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System (TDRSS) used by NASA and other United States government agencies for communications to and from independent "User Platforms" such as satellites, balloons, aircraft, the International Space Station, and remote bases like the Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station. This system was designed to replace an existing worldwide network of ground stations that had supported all of NASA's crewed flight missions and uncrewed satellites in low-Earth orbits. The primary system design goal was to increase the amount of time that these spacecraft were in communication with the ground and improve the amount of data that could be transferred. These TDRSS satellites are all designed and built to be launched to and function in geosynchronous orbit, above the surface of the Earth. The first seven TDRSS satellites were built by the TRW corporation. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manned Space Flight Network
The Manned Space Flight Network (abbreviated MSFN, pronounced "''misfin''") was a set of tracking stations built to support the American Mercury, Gemini, Apollo, and Skylab space programs. There were two other NASA space communication networks at the time, the Spacecraft Tracking and Data Acquisition Network (STADAN) for tracking satellites in low Earth orbit, and the Deep Space Network (DSN) for tracking more distant uncrewed missions. After the end of Skylab, the MSFN and STADAN were merged to form the Spaceflight Tracking and Data Network (STDN). STDN was in turn replaced by the satellite-based Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System (TDRSS) during the Space Shuttle program, being used . Orbital versus deep space tracking Tracking vehicles in low Earth orbits (LEO) is quite different from tracking deep space missions. Deep space missions are visible for long periods of time from a large portion of the Earth's surface, and so require few stations (the DSN uses only three, ). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inertial Upper Stage
The Inertial Upper Stage (IUS), originally designated the Interim Upper Stage, was a two-stage, solid-fueled space launch system developed by Boeing for the United States Air Force beginning in 1976 for raising payloads from low Earth orbit to higher orbits or interplanetary trajectories following launch aboard a Titan 34D or Titan IV rocket as its upper stage, or from the payload bay of the Space Shuttle as a space tug. Development During the development of the Space Shuttle, NASA, with support from the Air Force, wanted an upper stage that could be used on the Shuttle to deliver payloads from low earth orbit to higher energy orbits such as GTO or GEO or to escape velocity for planetary probes. The candidates were the Centaur, propelled by liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen, the Transtage, propelled by hypergolic storable propellants Aerozine-50 and , and the Interim Upper Stage, using solid propellant. The DOD reported that Transtage could support all defense needs, but could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
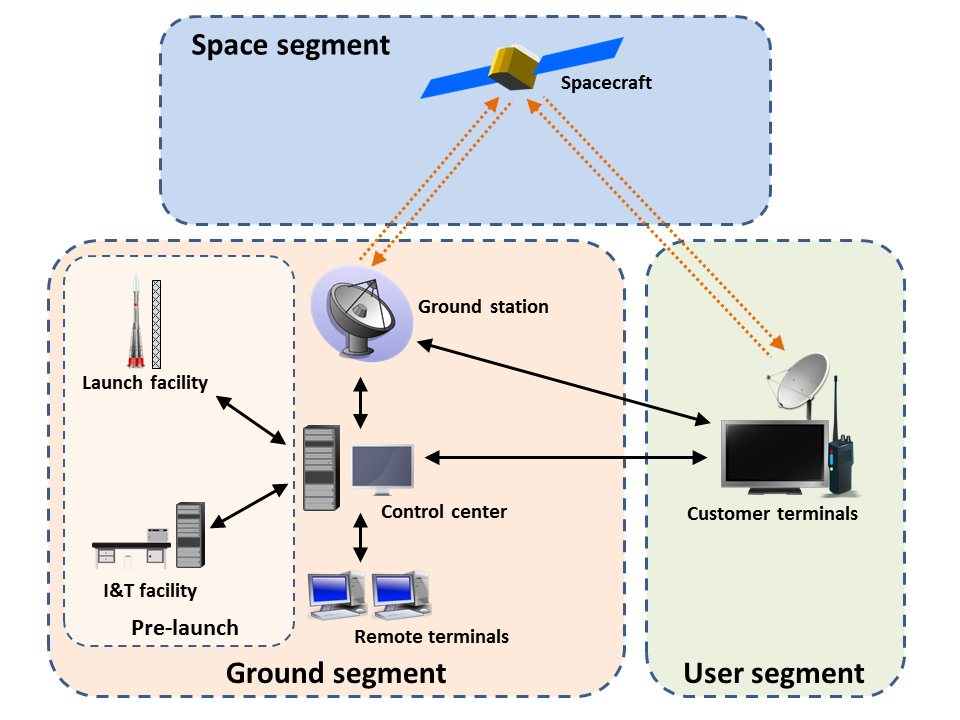
Ground Segment
A ground segment consists of all the ground-based elements of a space system used by operators and support personnel, as opposed to the space segment and user segment. The ground segment enables management of a spacecraft, and distribution of payload data and telemetry among interested parties on the ground. The primary elements of a ground segment are: * Ground (or Earth) stations, which provide radio interfaces with spacecraft * Mission control (or operations) centers, from which spacecraft are managed * Remote terminals, used by support personnel * Spacecraft integration and test facilities * Launch facilities * Ground networks, which allow for communication between the other ground elements These elements are present in nearly all space missions, whether commercial, military, or scientific. They may be located together or separated geographically, and they may be operated by different parties. Some elements may support multiple spacecraft simultaneously. Elements Groun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Application Technology Satellite
The Applications Technology Satellites (ATS) were a series of experimental satellites launched by NASA, under the supervision of, among others, Wernher von Braun. The program was launched in 1966 to test the feasibility of placing a satellite into geosynchronous orbit. The satellites were primarily designed to act as communication satellites, but also carried equipment related to meteorology and navigation. ATS-6 was the world's first educational satellite as well as world's first experimental Direct Broadcast Satellite (DBS) as part of the Satellite Instructional Television Experiment (SITE) between NASA and ISRO. Summary of Missions See also * Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite * Synchronous Meteorological Satellite The Synchronous Meteorological Satellite (SMS) program, was a program where NASA developed two weather satellites; which were placed into geosynchronous orbit. History SMS-1 was launched May 17, 1974 and SMS-2 was launched February 6, 197 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenbelt, Maryland
Greenbelt is a city in Prince George's County, Maryland, United States, and a suburb of Washington, D.C. At the 2020 census, the population was 24,921. Greenbelt is the first and the largest of the three experimental and controversial New Deal Greenbelt Towns, the others being Greenhills, Ohio, and Greendale, Wisconsin. Greenbelt was planned and built by the Federal government. The cooperative community was conceived in 1935 by Undersecretary of Agriculture Rexford Guy Tugwell, whose perceived collectivist ideology attracted opposition to the Greenbelt Towns project throughout its short duration. The project came into legal existence on April 8, 1935, when Congress passed the Emergency Relief Appropriation Act of 1935. Under the authority granted to him by this legislation, President Franklin D. Roosevelt issued an executive order, on May 1, 1935, establishing the United States Resettlement Administration (RA/RRA). First called ''Maryland Special Project No. 1'', the project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goddard Space Flight Center
The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately northeast of Washington, D.C. in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959 as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC employs approximately 10,000 civil servants and contractors. It is one of ten major NASA field centers, named in recognition of American rocket propulsion pioneer Robert H. Goddard. GSFC is partially within the former Goddard census-designated place; it has a Greenbelt mailing address.CENSUS 2000 BLOCK MAP: GODDARD CDP " . Retrieved on September 1, 2018. 1990 Census map of Prince ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Control Center Data System
The Network Control Center Data System (NCCDS) is an element of NASA's Space Network (SN) ground segment. Collocated with the White Sands Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System The U.S. Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System (TDRSS) is a network of American communications satellites (each called a tracking and data relay satellite, TDRS) and ground stations used by NASA for space communications. The system was desig ..., the NCCDS is the operations control facility for the network. It schedules most Space Network elements and supporting elements and provides interfaces for planning, acquisition, control, and status of the Space Network. The NCCDS is the point-of-contact between customers (who have satellites in orbit) and the Space Network for most scheduling and real-time performance. A customer may obtain Space Network support by submitting specific schedule requests to or establishing generic requirements with the NCCDS. The NCCDS translates customers’ requirements into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)
