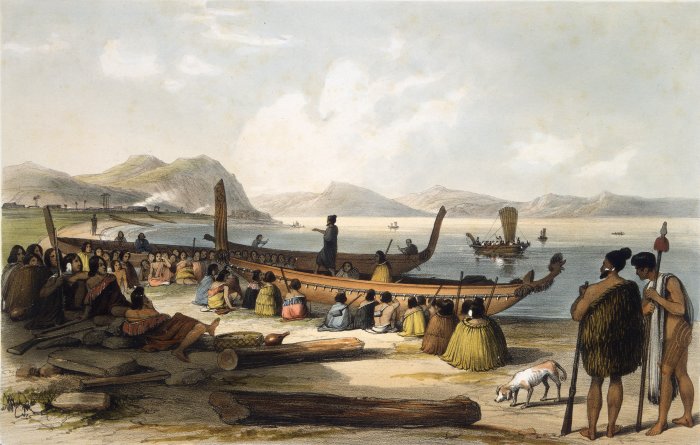|
Tūnui-ā-rangi
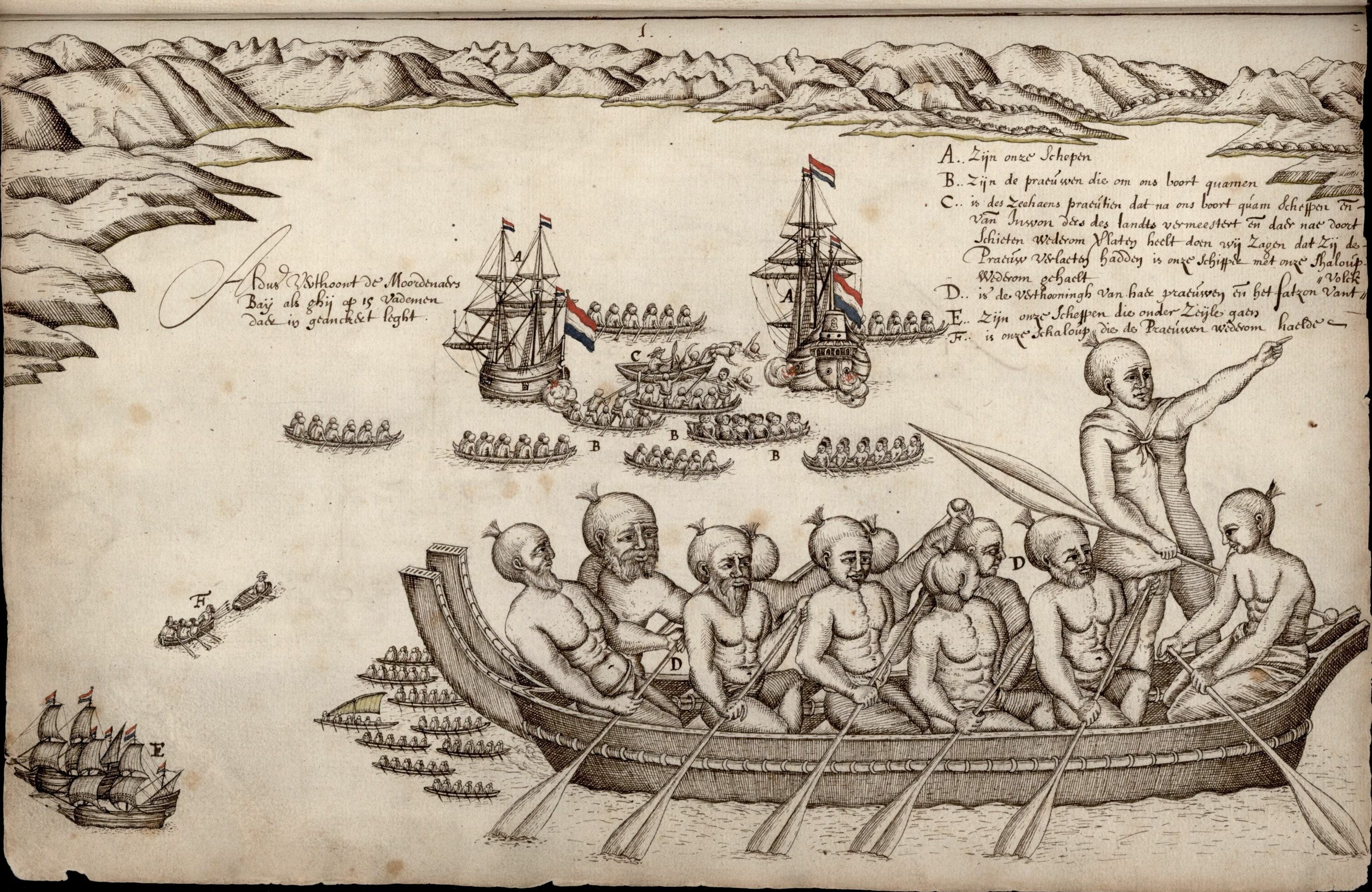
In Māori tradition, ''Tūnui-ā-rangi'' was one of the great ocean-going, voyaging canoes (or waka) that was used in the migrations that settled Aotearoa (New Zealand). The waka is linked to the Ngāi Tāhuhu iwi of the Auckland and Northland regions. The ''Tūnui-ā-rangi'' is said to have landed at Motu Kōkako (Piercy Island) in the Bay of Islands. It then traveled south to Ngunguru and Whangārei. See also *List of Māori waka This is a list of Māori people, Māori (canoes). The information in this list represents a compilation of different oral traditions from around New Zealand. These accounts give several different uses for the waka: many carried Polynesians, Poly ... References Māori waka Māori mythology {{Māori-myth-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngunguru
Ngunguru is a coastal settlement in Northland, New Zealand, north-east of Whangārei. The Ngunguru River flows between the settlement and a long low sandspit into Ngunguru Bay, which stretches southwards. North of Ngunguru are Tutukaka and Matapouri. Just off the Ngunguru coast are the Poor Knights Islands, a protected marine reserve. ''Ngunguru'' is a Māori-language word meaning "rumbling tides". History The waka Tūnui-ā-rangi, which brought Ngāi Tāhuhu to New Zealand according to traditional accounts, visited Ngunguru on its way from the Bay of Islands to Whangarei. The area was named by Puhi, captain of another waka, Mataatua. In pre-European times, there was a substantial Māori population in the area. A large battle was fought on the Ngunguru sandspit between the local Te Waiariki and Waikato tribes led by Te Wherowhero in 1832. The first chart of "Nongodo" was drawn by Captain N. C. Phillips of in 1836. James Busby, Gilbert Mair and W. J. Lewington boug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whangārei
Whangārei () is the northernmost city in New Zealand and the largest settlement of the Northland Region. It is part of the Whangarei District, created in 1989 from the former Whangarei City, Whangarei County and Hikurangi Town councils to administer both the city and its hinterland. The city population was estimated to be an increase from 47,000 in 2001. Etymology The origin of the name Whangārei is unclear, as a number of (Māori traditional stories) are associated with the harbour. One major tradition involves the sisters Reitū and Reipae of the ''Tainui (canoe), Tainui'' migratory waka, who either flew from the Waikato north on the backs of birds, or in the form of birds. Other traditions describe the meaning of Whangārei as "lying in wait to ambush", referring to warriors watching over the harbour from Castle Rock, or Whangārei meaning "to gather", referring to the harbour as a gathering place for whales or for important rangatira. History The harbour is known fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Māori Waka
This is a list of Māori people, Māori (canoes). The information in this list represents a compilation of different oral traditions from around New Zealand. These accounts give several different uses for the waka: many carried Polynesians, Polynesian migrants and explorers from Hawaiki to New Zealand; others brought supplies or made return journeys to Hawaiki; was said to be lost at sea. List of waka See also *Māori migration canoes *List of Māori iwi *Lists of marae in New Zealand References * {{DEFAULTSORT:List of Maori waka Māori waka, Māori-related lists, Waka Polynesian navigation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori Mythology
Māori mythology and Māori traditions are two major categories into which the remote oral history of New Zealand's Māori people, Māori may be divided. Māori myths concern tales of supernatural events relating to the origins of what was the observable world for the pre-European Māori, often involving gods and demigods. Māori tradition concerns more folkloric legends often involving historical or semi-historical forebears. Both categories merge in to explain the overall origin of the Māori and their connections to the world which they lived in. The Māori did not have a writing system before European contact, beginning in 1769, therefore they relied on oral retellings and recitations memorised from generation to generation. The three forms of expression prominent in Māori and Polynesian oral literature are genealogical recital, poetry, and narrative prose. Experts in these subjects were broadly known as . The rituals, beliefs, and general worldview of Māori society were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori Migration Canoes
Māori oral histories recount how their ancestors set out from their homeland in ''waka hourua'', large twin-hulled ocean-going canoes ('' waka''). Some of these traditions name a homeland called Hawaiki. Among these is the story of Kupe, who had eloped with Kūrāmarotini, the wife of Hoturapa, the owner of the great canoe '' Matahourua'', whom Kupe had murdered. To escape punishment for the murder, Kupe and Kura fled in Matahourua and discovered a land he called Aotearoa ('land of the long-white-cloud'). He explored its coast and killed the sea monster Te Wheke-a-Muturangi, finally returning to his home to spread the news of his newly discovered land. Other stories of various Māori tribes report migrations to escape famine, over-population, and warfare. These were made in legendary canoes, the best known of which are '' Aotea'', ''Te Arawa'', '' Kurahaupō'', '' Mātaatua'', '' Tainui'', '' Tākitimu'', and '' Tokomaru''. Various traditions name numerous other cano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waka (canoe)
Waka () are Māori people, Māori watercraft, usually canoes ranging in size from small, unornamented canoes (''waka tīwai'') used for fishing and river travel to large, decorated war canoes (''waka taua'') up to long. The earliest remains of a canoe in New Zealand were found near the Anaweka River, Anaweka estuary in a remote part of the Tasman District and Radiocarbon dating, radiocarbon-dated to about 1400. The canoe was constructed in New Zealand, but was a sophisticated canoe, compatible with the style of other Polynesian voyaging canoes at that time. Since the 1970s, about eight large double-hulled canoes of about 20 metres have been constructed for oceanic voyaging to other parts of the Pacific Ocean, Pacific. They are made of a blend of modern and traditional materials, incorporating features from ancient Melanesia, as well as Polynesia. Waka taua (war canoes) ''Waka taua'' (in Māori language, Māori, ''waka'' means "canoe" and ''taua'' means "army" or "war party") a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aotearoa
''Aotearoa'' () is the Māori name for New Zealand. The name was originally used by Māori in reference only to the North Island, with the whole country being referred to as ''Aotearoa me Te Waipounamu'' – where ''Te Ika-a-Māui'' means North Island, and ''Te Waipounamu'' means South Island. In the pre-European era, Māori did not have a collective name for the two islands. Several meanings for Aotearoa have been proposed; the most popular translation usually given is "land of the long white cloud", or variations thereof. This refers to the cloud formations which are believed to have helped early Polynesian navigators find the country in Māori oral tradition. Beginning in the late 20th century, ''Aotearoa'' has become widespread in the bilingual naming of national organisations and institutions. Since the 1990s, it has been customary for particular parties to sing the New Zealand national anthem, " God Defend New Zealand" (or "Aotearoa"), in both Māori and English, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auckland Region
Auckland () is one of the 16 regions of New Zealand, which takes its name from the eponymous urban areas of New Zealand, urban area. The region encompasses the Auckland, Auckland metropolitan area, smaller towns, rural areas, and the islands of the Hauraki Gulf. Containing percent of the nation's residents, it has by far the largest population and economy of any region of New Zealand, but the second-smallest land area. On 1 November 2010, the Auckland region became a unitary authority administered by the Auckland Council, replacing the previous regional council and seven local councils. In the process, an area in its southeastern corner was transferred to the neighbouring Waikato region. Since then, the Auckland Council has introduced a system of local boards to divide the region for local government. Geography On the mainland, the region extends from the mouth of the Kaipara Harbour in the north across the southern stretches of the Northland Peninsula, through the Waitā ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northland Region
Northland (), officially the Northland Region, is the northernmost of New Zealand's 16 regions of New Zealand, local government regions. New Zealanders sometimes refer to it as the Winterless North because of its mild climate all throughout the year. The major population centre is the city of Whangārei, and the largest town is Kerikeri. At the 2018 New Zealand census, Northland recorded a population growth spurt of 18.1% since the previous 2013 New Zealand census, 2013 census, placing it as the fastest growing region in New Zealand, ahead of other strong growth regions such as the Bay of Plenty Region (2nd with 15%) and Waikato (3rd with 13.5%). Geography The Northland Region occupies the northern 80% () of the Northland Peninsula, the southernmost part of which is in the Auckland region. It is bounded to the west by the Tasman Sea, and to the east by the Pacific Ocean. The land is predominantly rolling hill country. Farming and forestry occupy over half of the land and are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piercy Island (New Zealand)
Piercy Island, also known as "The Hole In The Rock" (and by its Māori-language name ), is located off the north coast of the North Island of New Zealand. It is at the very northern tip of Cape Brett in the Bay of Islands. It is Māori freehold land, which is administered by the Motu Kōkako Ahu Whenua Trust for the benefit of the descendants of the traditional owners. The island is of great cultural significance to the Ngāpuhi iwi (tribe), and was historically associated with a range of sacred customary activities. Motu Kōkako was said to be the landing place of the canoe Tūnui-a-rangi before it went to Ngunguru and Whangarei. It brings to mind the (proverb) ("the rock standing in the sea"). This refers to a person who stands against all adversity, just as a rock resists the power of the sea. It is probably the most important island in the Bay of Islands in conservation terms, being in near pristine condition, with no evidence of introduced animals. A 1987 survey of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Of Islands
The Bay of Islands is an area on the east coast of the Far North District of the North Island of New Zealand. It is one of the most popular fishing, sailing and tourist destinations in the country, and has been renowned internationally for its big-game fishing since American author Zane Grey publicised it in the 1930s. It is north-west of the city of Whangārei. Cape Reinga, at the northern tip of the country, is about by road further to the north-west. Etymology The bay is known in Māori language, Māori as Tokerau, a name given by early Māori ancestors referencing a place in the Hawaiki, Māori homeland. The wider Bay of Islands area, including the plain surrounding Waimate North, is traditionally known as Taiamai, a name shortened from the Ngāpuhi (proverb) ("the Vitex lucens, pūriri trees are laughing with joy"), a phrase used to express delight in the world, or to welcome an honoured guest. The bay's English name was given on 27 November 1769 by Captain James ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori Waka
Māori or Maori can refer to: Relating to the Māori people * Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group * Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand * Māori culture * Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the Cook Islands * Cook Islands Māori, the language of the Cook Islanders Ships * SS ''Maori'' (1893), a steamship of the Shaw Savill Line, shipwrecked 1909 * , a Royal Navy Tribal-class destroyer, sunk in 1915 * , a Royal Navy Tribal-class destroyer, launched 1936 and sunk 1942 * TEV ''Maori III'', a Union Steam Ship Company inter-island ferry, 1952–74 Sports teams * New Zealand Māori cricket team * New Zealand Māori rugby league team * New Zealand Māori rugby union team Other * ''Maori'', a 1988 novel by Alan Dean Foster * Mayotte Mayotte ( ; , ; , ; , ), officially the Department of Mayotte (), is an Overseas France, overseas Overseas departments and regions of France, department and region and single territorial collecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |