|
Túath
''Túath'' (plural ''túatha'') is the Old Irish term for the basic political and jurisdictional unit of Gaelic Ireland. ''Túath'' can refer to both a geographical territory as well the people who lived in that territory. The smallest ''túath'' controlled by a king was about the size of a later Irish barony (about 177sq miles) and kings with greater power would have two or more ''túatha'' under their control, according to ''A Smaller Social History of Ancient Ireland.'' '' Social structure In ancient Irish terms, a household was reckoned at about 30 people per dwelling. A ''trícha cét'' ("thirty hundreds"), was an area comprising 100 dwellings or, roughly, 3,000 people. A ''túath'' consisted of a number of allied ''trícha céta'', and therefore referred to no fewer than 6,000 people. Probably a more accurate number for a ''túath'' would be no fewer than 9,000 people. Each ''túath'' was a self-contained unit, with its own executive, assembly, courts system and defence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaelic Ireland
Gaelic Ireland () was the Gaelic political and social order, and associated culture, that existed in Ireland from the late Prehistory of Ireland, prehistoric era until the 17th century. It comprised the whole island before Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland, Anglo-Normans conquered parts of Ireland in the 1170s. Thereafter, it comprised that part of the country not under foreign dominion at a given time (i.e. the part beyond The Pale). For most of its history, Gaelic Ireland was a "patchwork" hierarchy of territories ruled by a hierarchy of kings or chiefs, who were chosen or elected through tanistry. Gaelic warfare, Warfare between List of Irish kingdoms, these territories was common. Traditionally, a powerful ruler was acknowledged as High King of Ireland. Society was made up of Irish clans, clans and, like the rest of History of Europe, Europe, was structured hierarchically according to Social class, class. Throughout this period, the economy was mainly Pastoralism, pastoral a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brehon Law
Early Irish law, also called Brehon law (from the old Irish word breithim meaning judge), comprised the statutes which governed everyday life in Early Medieval Ireland. They were partially eclipsed by the Norman invasion of 1169, but underwent a resurgence from the 13th until the 17th century, over the majority of the island, and survived into Early Modern Ireland in parallel with English law. Early Irish law was often mixed with Christian influence and juristic innovation. These secular laws existed in parallel, and occasionally in conflict, with canon law throughout the early Christian period. The laws were a civil rather than a criminal code, concerned with the payment of compensation for harm done and the regulation of property, inheritance and contracts; the concept of state-administered punishment for crime was foreign to Ireland's early jurists. They show Ireland in the early medieval period to have been a hierarchical society, taking great care to define social sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cairbre Drom Cliabh
Cairbre Drom Cliabh (meaning "Ui Cairbre, the descendants of Cairbre of Drumcliff) was an Irish ''túath'' in the ancient confederation of Íochtar Connacht (Lower Connacht), now County Sligo in the west of Ireland. It is now represented by the barony of Carbury. Also known as ''Cairbre na Catha'' (Carbury of the Battles). It existed from at least the 6th century to the 16th century AD. As a frontier territory of Connacht it was a saor-túath (territory exempt from tribute) under several Irish dynasties over time, but mostly under a branch of the O'Connor dynasty called the Clann Aindrias or O'Connor Sligo The O Conor Sligo ( Ó Conchobhair Sligigh) were a branch of the Ó Conchobhair royal family who were Kings of Connacht. They were descended from Brian Luighnech Ua Conchobhair (k.1181) and were Lords of Sligo into the middle of the 17th century. For a list of chiefs of Cairbre Drom Cliabh see O'Conchobar Sligigh. Location and extent This territory is between the coast a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dartraighe
Dartraighe (older spelling: Dartraige), anglicised as ''Dartree'', ''Dartry'' or '' Dartrey'', was an Irish territory or tuath in medieval Ireland which stretched north to Clones and south to the Dromore River. It was later incorporated into County Monaghan as the barony of Dartree. History The Dartraighe were an Irish túath, also known as ''n-Dartraighi'' or ''Dairtre'' who gave their name to a territory in the western portion of what is now known as County Monaghan. The name means "calf-people". Various anglicized forms of the name were used through the years. A segment of its southern region became the Dartrey Estate, owned by Richard Dawson in the 17th century, and known as Dawson's Grove, which is now Dartrey Forest. It includes Inner Lough with its small island - probably an old crannog, which may explain the name ''Dartraige Coinn innsi'' (Dartry of the Island Chief), which occurs in the annals, perhaps to distinguish this Dartraige from another centered in Kingdom of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corann
Corann was an ancient Irish túath in northwest Connacht represented now by the present barony of Corran in County Sligo. The name is derived in legend from Corann, the harper of Dian Cecht of the Tuatha Dé Danann. Organisation Ballymote became the centre of the túath after construction of Ballymote Castle in the 13th century. History The well of Corann that alternated between sweet water and salt in time with the ebb and flow of the tide. It was first shired as part of the new County Sligo by the English Lord Deputy Sir Henry Sidney in 1564. References Medieval history of Ireland Historic Gaelic territories {{Sligo-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Celtic
Proto-Celtic, or Common Celtic, is the hypothetical ancestral proto-language of all known Celtic languages, and a descendant of Proto-Indo-European. It is not attested in writing but has been partly Linguistic reconstruction, reconstructed through the comparative method. Proto-Celtic is generally thought to have been spoken between 1300 and 800 BC, after which it began to split into different languages. Proto-Celtic is often associated with the Urnfield culture and particularly with the Hallstatt culture. Celtic languages share common features with Italic languages that are not found in other branches of Indo-European, suggesting the possibility of an earlier Italo-Celtic linguistic unity. Proto-Celtic is currently being reconstructed through the comparative method by relying on later Celtic languages. Though Continental Celtic presents much substantiation for Proto-Celtic phonology, and some for its morphology (linguistics), morphology, recorded material is too scanty to allow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
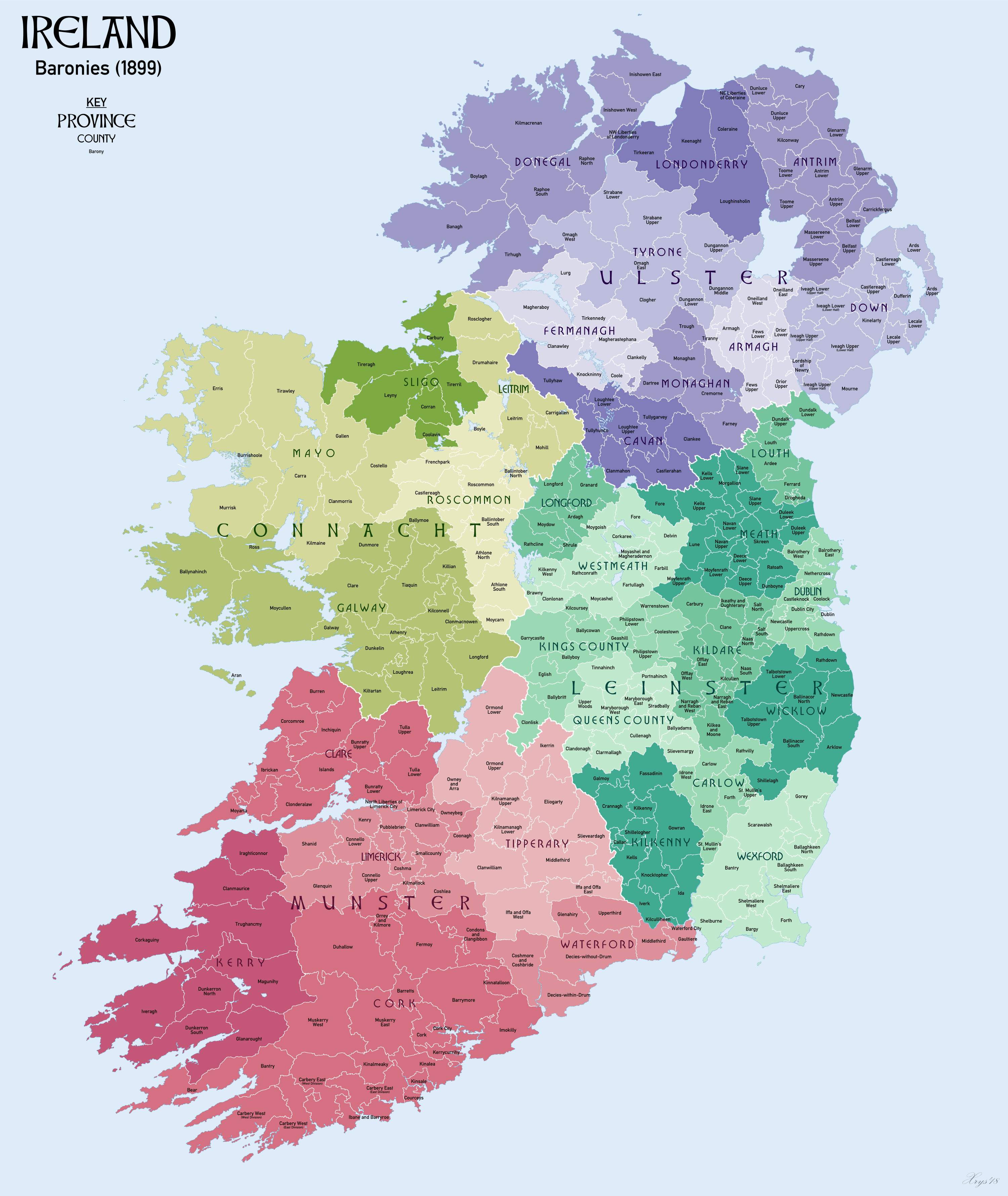
Barony (Ireland)
In Ireland, a barony (, plural ) is a historical subdivision of a counties of Ireland, county, analogous to the hundred (county subdivision), hundreds into which the counties of England were divided. Baronies were created during the Tudor reconquest of Ireland, replacing the earlier cantreds formed after the original Norman invasion of Ireland, Norman invasion.Mac Cotter 2005, pp.327–330 Some early baronies were later subdivided into half baronies with the same standing as full baronies. Baronies were mainly cadastre, cadastral rather than administrative units. They acquired modest local taxation and spending functions in the 19th century before being superseded by the Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898. Subsequent adjustments of county boundaries mean that some baronies now straddle two counties. The final catalogue of baronies numbered 331, with an average area of ; each county was divided, on average, into 10 or 11 baronies. Creation The island of Ireland was "shired" i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toutatis
Teutates (spelled variously Toutatis, Totatis, Totates) is a Celtic god attested in literary and epigraphic sources. His name, which is derived from a proto-Celtic word meaning "tribe", suggests he was a national god, tribal deity. The Roman poet Lucan's epic ''Pharsalia'' mentions Teutates, Esus, and Taranis as gods to whom the Gauls sacrificed humans. This rare mention of Celtic gods under their native names in a Latin text has been the subject of much comment. Almost as often commented on are Commenta Bernensia and Adnotationes Super Lucanum, the scholia to Lucan's poem (early medieval, but relying on earlier sources) which tell us the nature of these sacrifices: in particular, that victims of Teutates were immersed headfirst into a small barrel and drowned. This sacrifice has been compared with a poorly understood ritual depicted on the Gundestrup cauldron, some motifs in Irish mythology, and the death of the bog body known as the Lindow Man. Teutates appears in a number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osraige
Osraige (Old Irish) or Osraighe (Classical Irish), Osraí (Modern Irish), anglicized as Ossory, was a medieval Irish kingdom comprising what is now County Kilkenny and western County Laois, corresponding to the Diocese of Ossory. The home of the Osraige people, it existed from around the first century until the Norman invasion of Ireland in the 12th century. It was ruled by the Dál Birn dynasty, whose medieval descendants assumed the surname Mac Giolla Phádraig. According to tradition, Osraige was founded by Óengus Osrithe in the 1st century and was originally within the province of Leinster. In the 5th century, the Corcu Loígde of Munster displaced the Dál Birn and brought Osraige under Munster's direct control. The Dál Birn returned to power in the 7th century, though Osraige remained nominally part of Munster until 859, when it achieved formal independence under the powerful king Cerball mac Dúnlainge. Osraige's rulers remained major players in Irish politics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dál Riata
Dál Riata or Dál Riada (also Dalriada) () was a Gaels, Gaelic Monarchy, kingdom that encompassed the Inner Hebrides, western seaboard of Scotland and north-eastern Ireland, on each side of the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel. At its height in the 6th and 7th centuries, it covered what is now Argyll ("Coast of the Gaels") in Scotland and part of County Antrim in Northern Ireland.Clancy, Thomas Owen, "Philosopher King: Nechtan mac Der Ilei," SHR 83 (2004): 135–149 After a period of expansion, Dál Riata eventually became associated with the Gaelic Kingdom of Alba.''Oxford Companion to Scottish History'' pp. 161–162, edited by Michael Lynch, Oxford University Press. . In Argyll, it consisted of four main clan, kindreds or tribes, each with their own chief: the Cenél nGabráin (based in Kintyre), the Cenél nÓengusa (based on Islay), the Loarn mac Eirc, Cenél Loairn (who gave their name to the district of Lorne, Scotland, Lorn) and the Cenél Comgai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Irish
Old Irish, also called Old Gaelic (, Ogham, Ogham script: ᚌᚑᚔᚇᚓᚂᚉ; ; ; or ), is the oldest form of the Goidelic languages, Goidelic/Gaelic language for which there are extensive written texts. It was used from 600 to 900. The main contemporary texts are dated 700–850; by 900 the language had already transitioned into early Middle Irish. Some Old Irish texts date from the 10th century, although these are presumably copies of texts written at an earlier time. Old Irish is forebear to Modern Irish, Manx language, Manx and Scottish Gaelic. Old Irish is known for having a particularly complex system of morphology (linguistics), morphology and especially of allomorphy (more or less unpredictable variations in stems and suffixes in differing circumstances), as well as a complex phonology, sound system involving grammatically significant Irish initial mutations, consonant mutations to the initial consonant of a word. Apparently,It is difficult to know for sure, giv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
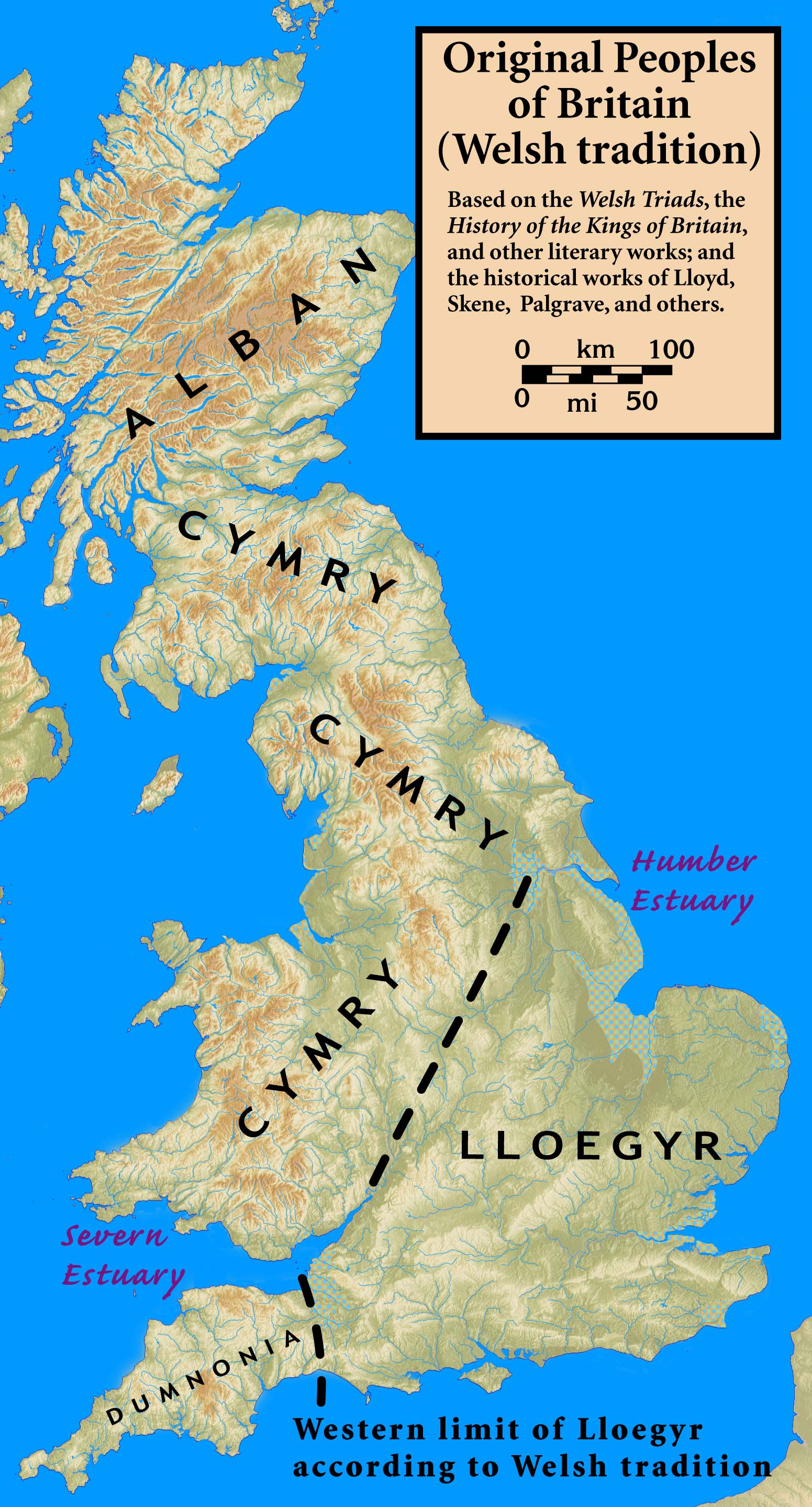
Alba
''Alba'' ( , ) is the Scottish Gaelic name for Scotland. It is also, in English-language historiography, used to refer to the polity of Picts and Scots united in the ninth century as the Kingdom of Alba, until it developed into the Kingdom of Scotland of the late Middle Ages following the absorption of Strathclyde and English-speaking Lothian in the 12th century. It is cognate with the Irish term ' (gen. ', dat. ') and the Manx term ', the two other Goidelic Insular Celtic languages, as well as contemporary words used in Cornish (') and Welsh ('), both of which are Brythonic Insular Celtic languages. The third surviving Brythonic language, Breton, instead uses ', meaning 'country of the Scots'. In the past, these terms were names for Great Britain as a whole, related to the Brythonic name Albion. Etymology The term first appears in classical texts as ' or ' (in Ptolemy's writings in Greek), and later as ' in Latin documents. Historically, the term refers t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |