|
Two-hybrid Screening
Two-hybrid screening (originally known as yeast two-hybrid system or Y2H) is a molecular biology technique used to discover protein–protein interactions (PPIs) and DNA-binding protein#Protein–DNA interactions, protein–DNA interactions by testing for physical interactions (such as binding) between two proteins or a single protein and a DNA molecule, respectively. The premise behind the test is the activation of Upstream and downstream (DNA), downstream reporter gene(s) by the binding of a transcription factor onto an upstream activating sequence (UAS). For two-hybrid screening, the transcription factor is split into two separate fragments, called the DNA-binding domain (DBD or often also abbreviated as BD) and activating domain (AD). The BD is the protein domain, domain responsible for DNA-binding protein, binding to the UAS and the AD is the domain responsible for the activation of Transcription (genetics), transcription. The Y2H is thus a protein-fragment complementation a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two Hybrid Assay
2 (two) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 1 and preceding 3. It is the smallest and the only even prime number. Because it forms the basis of a duality, it has religious and spiritual significance in many cultures. Mathematics The number 2 is the second natural number after 1. Each natural number, including 2, is constructed by succession, that is, by adding 1 to the previous natural number. 2 is the smallest and the only even prime number A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a Product (mathematics), product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime ..., and the first Ramanujan prime. It is also the first superior highly composite number, and the first colossally abundant number. An integer is determined to be Parity (mathematics), even if it is Division (mathematics), divisible by two. When written ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Host Organism
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasitic, a mutualistic, or a commensalist ''guest'' (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include animals playing host to parasitic worms (e.g. nematodes), cells harbouring pathogenic (disease-causing) viruses, or a bean plant hosting mutualistic (helpful) nitrogen-fixing bacteria. More specifically in botany, a host plant supplies food resources to micropredators, which have an evolutionarily stable relationship with their hosts similar to ectoparasitism. The host range is the collection of hosts that an organism can use as a partner. Symbiosis Symbiosis spans a wide variety of possible relationships between organisms, differing in their permanence and their effects on the two parties. If one of the partners in an association is much larger than the other, it is generally known as the host. In parasitism, the parasite benefits a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassette Mutagenesis
Cassette mutagenesis is a type of site-directed mutagenesis that uses a short, double-stranded oligonucleotide sequence (gene cassette) to replace a fragment of target DNA. It uses complementary restriction enzyme digest ends on the target DNA and gene cassette to achieve specificity. It is different from methods that use single oligonucleotide in that a single gene cassette can contain multiple mutations. Unlike many site directed mutagenesis methods, cassette mutagenesis also does not involve primer extension by DNA polymerase. Mechanism First, restriction enzymes are used to cleave near the target sequence on DNA contained in a suitable vector. This step removes the target sequence and everything between the restriction sites. Then, the synthetic double stranded DNA containing the desired mutation and ends that are complementary to the restriction digest ends are ligated in place of the sequence removed. Finally, the resultant construct is sequenced to check that the targ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse Transcription
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to convert RNA genome to DNA, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B virus, hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, by retrotransposon mobile genetic elements to proliferate within the host genome, and by eukaryote, eukaryotic cells to extend the telomeres at the ends of their Chromosome#Eukaryotes, linear chromosomes. The process does not violate the flows of genetic information as described by the classical central dogma of molecular biology, central dogma, but rather expands it to include transfers of information from RNA to DNA. Retroviral RT has three sequential biochemical activities: RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity, ribonuclease H (RNase H), and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity. Collectively, these activities enable the enzyme to convert single-stranded RNA into double-stranded cDNA. In retroviruses and retrotransposons, this cDNA can then inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
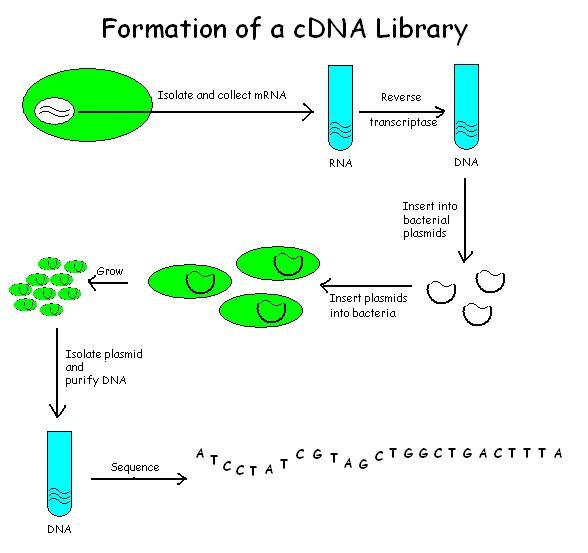
CDNA Library
A cDNA library is a combination of cloned cDNA (complementary DNA) fragments inserted into a collection of host cells, which constitute some portion of the transcriptome of the organism and are stored as a "library". cDNA is produced from fully transcribed mRNA found in the nucleus and therefore contains only the expressed genes of an organism. Similarly, tissue-specific cDNA libraries can be produced. In eukaryotic cells the mature mRNA is already spliced, hence the cDNA produced lacks introns and can be readily expressed in a bacterial cell. While information in cDNA libraries is a powerful and useful tool since gene products are easily identified, the libraries lack information about enhancers, introns, and other regulatory elements found in a genomic DNA library. cDNA Library Construction cDNA is created from a mature mRNA from a eukaryotic cell with the use of reverse transcriptase. In eukaryotes, a poly-(A) tail (consisting of a long sequence of adenine nucleotides) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zif268
EGR-1 (Early growth response protein 1) or NGFI-A (nerve growth factor-induced protein A) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EGR1'' gene. EGR-1 is a mammalian transcription factor. It was also named Krox-24, TIS8, and ZENK. It was originally discovered in mice. Function The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the EGR family of Cys2His2-type zinc finger proteins. It is a nuclear protein and functions as a transcriptional regulator. The products of target genes it activates are required for differentiation and mitogenesis. Studies suggest this is a tumor suppressor gene. It has a distinct pattern of expression in the brain, and its induction has been shown to be associated with neuronal activity. Several studies suggest it has a role in neuronal plasticity. EGR-1 is an important transcription factor in memory formation. It has an essential role in brain neuron epigenetic reprogramming. EGR-1 recruits the TET1 protein that initiates a pathway of DNA demethyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Library (biology)
In molecular biology, a library is a collection of genetic material fragments that are stored and propagated in a population of microbes through the process of molecular cloning. There are different types of DNA libraries, including cDNA libraries (formed from reverse-transcribed RNA), genomic libraries (formed from genomic DNA) and randomized mutant libraries (formed by de novo gene synthesis where alternative nucleotides or codons are incorporated). DNA library technology is a mainstay of current molecular biology, genetic engineering, and protein engineering, and the applications of these libraries depend on the source of the original DNA fragments. There are differences in the cloning vectors and techniques used in library preparation, but in general each DNA fragment is uniquely inserted into a cloning vector and the pool of recombinant DNA molecules is then transferred into a population of bacteria (a Bacterial Artificial Chromosome or BAC library) or yeast such that e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmid
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria and archaea; however plasmids are sometimes present in and eukaryotic organisms as well. Plasmids often carry useful genes, such as those involved in antibiotic resistance, virulence, secondary metabolism and bioremediation. While chromosomes are large and contain all the essential genetic information for living under normal conditions, plasmids are usually very small and contain additional genes for special circumstances. Artificial plasmids are widely used as vectors in molecular cloning, serving to drive the replication of recombinant DNA sequences within host organisms. In the laboratory, plasmids may be introduced into a cell via transformation. Synthetic plasmids are available for procurement over the internet by various vendors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleic Acid
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a pentose, 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). If the sugar is ribose, the polymer is RNA; if the sugar is deoxyribose, a variant of ribose, the polymer is DNA. Nucleic acids are chemical compounds that are found in nature. They carry information in cells and make up genetic material. These acids are very common in all living things, where they create, encode, and store information in every living cell of every outline of life forms, life-form on Earth. In turn, they send and express that information inside and outside the cell nucleus. From the inner workings of the cell to the young of a living thing, they contain and provide information via the nucleic acid sequence. This gives the RNA and DNA their unmistakable 'la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups ( alpha- , beta- , gamma- amino acids, etc.); other categories relate to polarity, ionization, and side-chain group type ( aliphatic, acyclic, aromatic, polar, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino-acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life on Earth and its emergence. Amino acids are formally named by the IUPAC- IUBMB Joint Commi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis, i.e., chemical synthesis occurring in biological contexts, is a term most often referring to multi-step, enzyme-Catalysis, catalyzed processes where chemical substances absorbed as nutrients (or previously converted through biosynthesis) serve as enzyme substrate (chemistry), substrates, with conversion by the living organism either into simpler or more complex Product (chemistry), products. Examples of biosynthetic pathways include those for the production of amino acids, lipid membrane components, and nucleotides, but also for the production of all classes of biological macromolecules, and of acetyl-coenzyme A, adenosine triphosphate, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and other key intermediate and transactional molecules needed for metabolism. Thus, in biosynthesis, any of an array of Chemical compound, compounds, from simple to complex, are converted into other compounds, and so it includes both the catabolism and anabolism (building up and breaking down) of comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of Genetic engineering techniques, technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA is obtained by either isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using recombinant DNA methods or by Artificial gene synthesis, artificially synthesising the DNA. A Vector (molecular biology), construct is usually created and used to insert this DNA into the host organism. The first recombinant DNA molecule was made by Paul Berg in 1972 by combining DNA from the monkey virus SV40 with the Lambda phage, lambda virus. As well as inserting genes, the process can be used to remove, or "Gene knockout, knock out", genes. The new DNA can either be inserted randomly or Gene targeting, targeted to a spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |