|
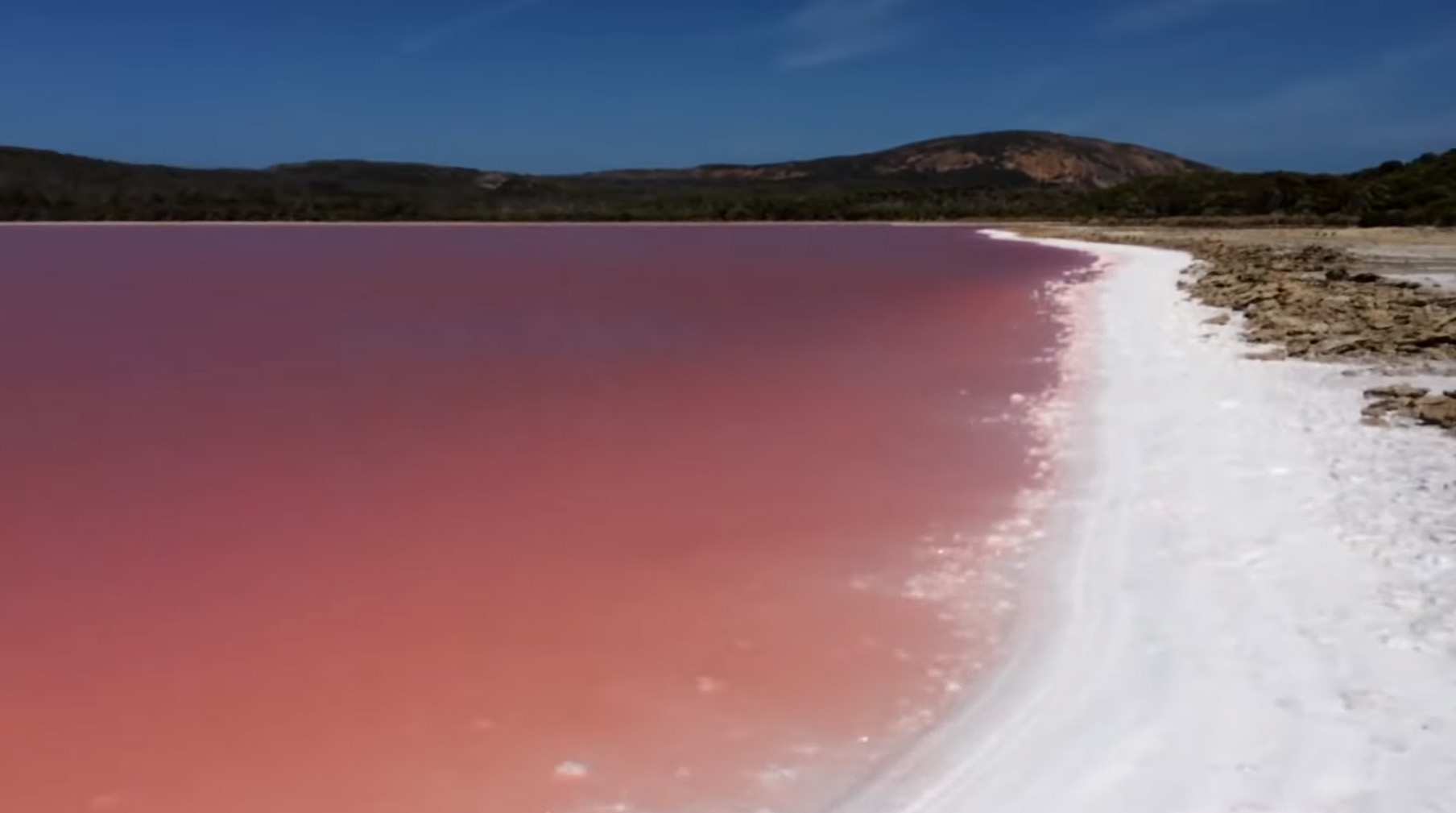
Tuz Gölü
Lake Tuz ( meaning 'Salt Lake) is the second largest lake in Turkey with its surface area and one of the largest hypersaline lakes in the world. It is located in the Central Anatolia Region, northeast of Konya, south-southeast of Ankara and northwest of Aksaray. In recent years, Lake Tuz has become a hotspot for tourists. In October 2021, Lake Tuz temporarily dried up completely due to climate change. Geography The lake, occupying a tectonic depression in the central plateau of Turkey, is fed by two major streams, groundwater, and surface water, but has no outlet. Brackish marshes have formed where channels and streams enter the lake. Arable fields surround the lake, except in the south and southwest, where there is an extensive seasonally flooded salt-steppe. For most of the year, it is very shallow (approx.). During winter part of the salt is dissolved in the fresh water that is introduced to the lake by precipitation and surface runoff (to 324‰ salinity). During the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
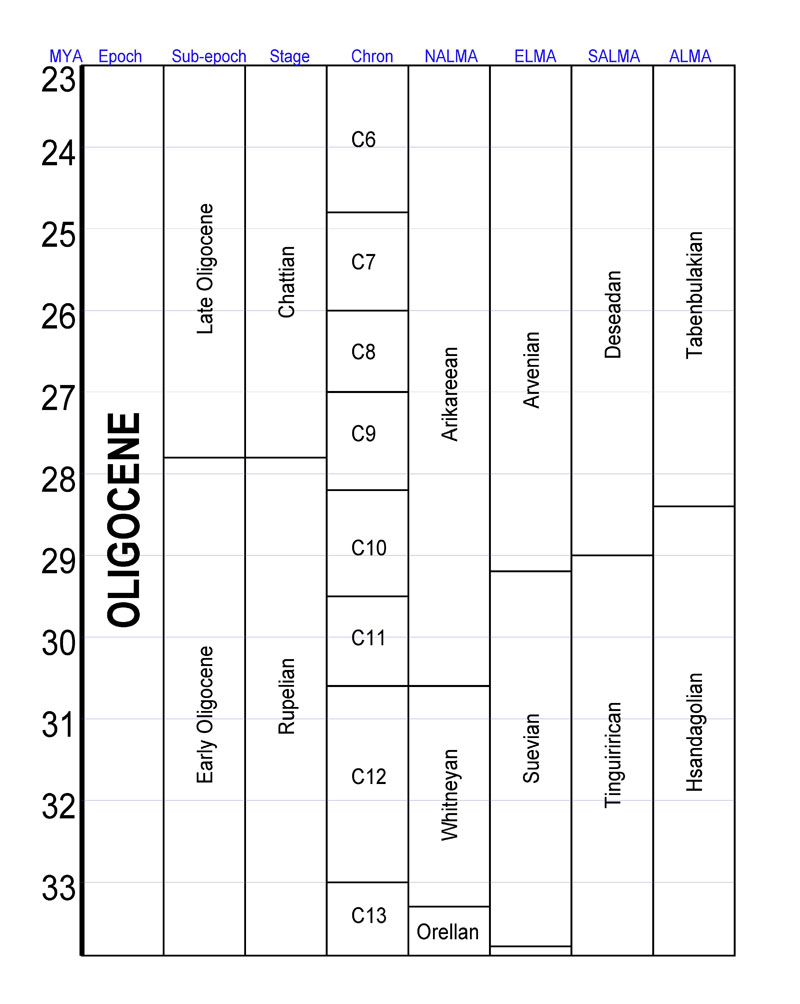
Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from Ancient Greek (''olígos'') 'few' and (''kainós'') 'new', and refers to the sparsity of Neontology, extant forms of Mollusca, molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taurus Mountains
The Taurus Mountains (Turkish language, Turkish: ''Toros Dağları'' or ''Toroslar,'' Greek language, Greek'':'' Ταύρος) are a mountain range, mountain complex in southern Turkey, separating the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coastal region from the central Anatolia#Anatolian plateau, Anatolian Plateau. The system extends along a curve from Lake Eğirdir in the west to the upper reaches of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers in the east. It is a part of the Alpide belt in Eurasia. Etymology The mountain range under the current name was mentioned in The Histories (Polybius), ''The Histories'' by Polybius as Ταῦρος (''Taûros''). Heinrich Kiepert writes in ''Lehrbuch der alten Geographie'' that the name was borrowed into Ancient Greek from the Semitic languages, Semitic (Old Aramaic) root wikt:טורא, טורא (''ṭūrā''), meaning "mountain". Geography The Taurus Mountains are divided into three chains from west to east as follows; * Western Taurus (Batı Torosla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karapınar
Karapınar, formerly known as Barta is a municipality and district of Konya Province, Turkey. Its area is 2,623 km2, and its population is 50,323 (2022). Volcanic Karapınar Field is located nearby. Composition There are 42 neighbourhoods in Karapınar District: * Adalet * Akçayazı * Akören * Alaaddin * Apak * Çetmi * Çiğil * Cumhuriyet * Fatih * Fevzipaşa * Gaziosmanpaşa * Hacı İsa * Hacı Ömerli * Hankapı * Hasanoba * Hotamış * İpekçi * İslik * İsmetpaşa * Kale * Karakışla * Kayacık * Kayalı * Kazanhüyüğü * Kesmez * Küçükaşlama * Küllü * Ortaoba * Oymalı * Pınarbaşı * Reşadiye * Sandıklı * Sazlıpınar * Selimiye * Türüdiye * Ulus * Yağmapınar * Yeni * Yenikuyu * Yeşilyurt * Yunus Emre * Zafer Climate Karapınar has a cold semi-arid climate (Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Bernd Köppen (1951–2014), German pianist and composer * Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Çumra
Çumra is a municipality and district of Konya Province, Turkey. Its area is 2,089 km2, and its population is 67,690 (2022). Geography The town of Çumra is at an altitude of 1,020 m. It is an important stop on the Istanbul to Baghdad railway. It is central to the 500 km²/120,000 acre Çumra irrigation zone, in the Konya Plain, that was established in 1912. Climate Çumra's climate is classified as cold semi-arid (Köppen: ''BSk''). The town experiences hot, dry summers and chilly, frequently snowy winters. History Neolithic (c. 8000 BC) archaeological discoveries have been found at Çatalhöyük. In the 12th century the Konya plain experienced its second great cultural period, when the city became the capital of the Seljuk Turks. Archaeological findings In 2019, a farmer near the site of Türkmen-Karahöyük, a Bronze and Iron Age mounded settlement discovered a stone stele commissioned by Hartapu to commemorate his victory over Phrygia written in Luwian Hierog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kulu, Konya
Kulu is a municipality and district of Konya Province, Turkey. Its area is 2,234 km2, and its population is 51,612 (2022). Kulu is situated approximately 110 km from Ankara Ankara is the capital city of Turkey and List of national capitals by area, the largest capital by area in the world. Located in the Central Anatolia Region, central part of Anatolia, the city has a population of 5,290,822 in its urban center ( ... and 150 km from the city of Konya. With a substantial Swedish-Turkish community, not few of whom are from this region, Kulu hosts around 100,000 visitors from Europe in the summer. Swedish Prime Minister Fredrik Reinfeldt visited the city once. History The modern Kulu district lies on the ancient Galatian city of Drya. Composition There are 46 neighbourhoods in Kulu District: Turkey Civil Admini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humid Continental Climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers, and cold (sometimes severely cold in the northern areas) and snowy winters. Precipitation is usually distributed throughout the year, but often these regions do have dry seasons. The definition of this climate in terms of temperature is as follows: the mean temperature of the coldest month must be below or depending on the isotherm, and there must be at least four months whose mean temperatures are at or above . In addition, the location in question must not be semi-arid or arid. The cooler ''Dfb'', ''Dwb'', and ''Dsb'' subtypes are also known as hemiboreal climates. Although amount of snowfall is not a factor used in defining the humid continental climate, snow during the winter in this type of climate is almost a guarantee, either intermitte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-arid Climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-arid climates, depending on variables such as temperature, and they give rise to different biomes. Defining attributes of semi-arid climates A more precise definition is given by the Köppen climate classification, which treats steppe climates (''BSh'' and ''BSk'') as intermediates between desert climates (BW) and humid climates (A, C, D) in ecological characteristics and agricultural potential. Semi-arid climates tend to support short, thorny or scrubby vegetation and are usually dominated by either grasses or shrubs as they usually cannot support forests. To determine if a location has a semi-arid climate, the precipitation threshold must first be determined. The method used to find the precipitation threshold (in millimeters): * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SALT LAKE
A salt lake or saline lake is a landlocked body of water that has a concentration of salts (typically sodium chloride) and other dissolved minerals significantly higher than most lakes (often defined as at least three grams of salt per liter). In some cases, salt lakes have a higher concentration of salt than sea water; such lakes can also be termed hypersaline lake, and may also be pink lakes on account of their color. An alkalic salt lake that has a high content of carbonate is sometimes termed a soda lake. Salt lakes are classified according to salinity levels. The formation of these lakes is influenced by processes such as evaporation and deposition. Salt lakes face serious conservation challenges due to climate change, pollution and water diversion. Classification The primary method of classification for salt lakes involves assessing the chemical composition of the water within the lakes, specifically its salinity, pH, and the dominant ions present. Subsaline Sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kırşehir
Kırşehir, historically known as Mocissus or Mokissos () and Justinianopolis () in ancient times, is a city in Turkey. It is the seat of Kırşehir Province and Kırşehir District.İl Belediyesi Turkey Civil Administration Departments Inventory. Retrieved 1 March 2023. Its population is 162,989 (2023). History  The history of Kırşehir dates back to the Hittites. During the period of the Hittites, the basin of Kırşehir was known as the country of "Ahiyuva", meaning "the Land of the Achaeans", as the Greeks were known to the Hittites. This basin also took the name Cappadocia at the time of the Roman Empire, Romans and ...
The history of Kırşehir dates back to the Hittites. During the period of the Hittites, the basin of Kırşehir was known as the country of "Ahiyuva", meaning "the Land of the Achaeans", as the Greeks were known to the Hittites. This basin also took the name Cappadocia at the time of the Roman Empire, Romans and ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Lake
A salt lake or saline lake is a landlocked body of water that has a concentration of salts (typically sodium chloride) and other dissolved minerals significantly higher than most lakes (often defined as at least three grams of salt per liter). In some cases, salt lakes have a higher concentration of salt than sea water; such lakes can also be termed hypersaline lake, and may also be pink lakes on account of their color. An alkalic salt lake that has a high content of carbonate is sometimes termed a soda lake. Salt lakes are classified according to salinity levels. The formation of these lakes is influenced by processes such as evaporation and deposition. Salt lakes face serious conservation challenges due to climate change, pollution and water diversion. Classification The primary method of classification for salt lakes involves assessing the chemical composition of the water within the lakes, specifically its salinity, pH, and the dominant ions present. Subsaline Sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene followed the Oligocene and preceded the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by distinct global events but by regionally defined transitions from the warmer Oligocene to the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, Afro-Arabia collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Oceans, and allowing the interchange of fauna between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans and Ape, hominoids into Eurasia. During the late Miocene, the conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |