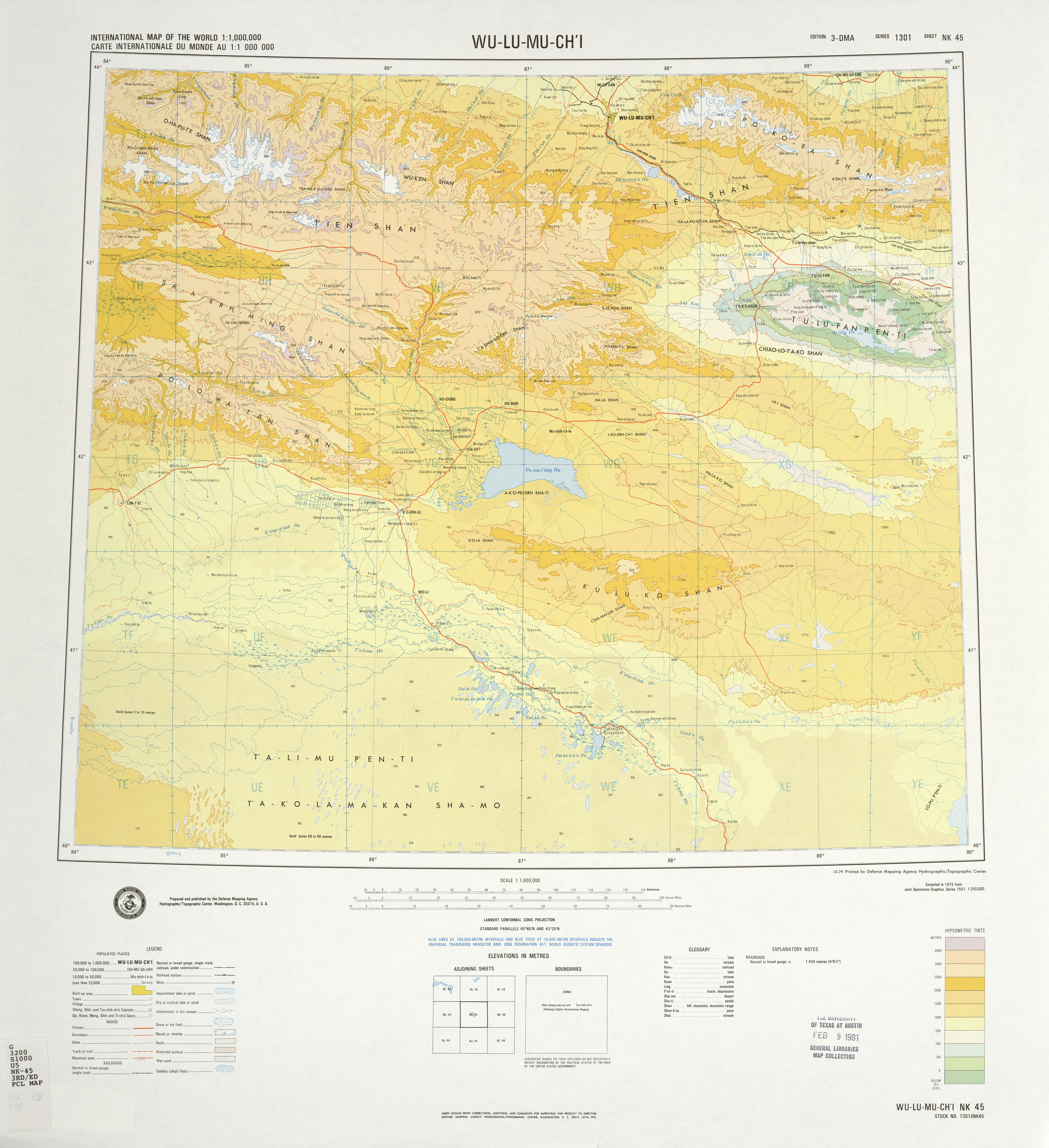
|
Turpan Depression
The Turpan Depression or Turfan Depression, is a fault-bounded trough located around and south of the city-oasis of Turpan, in the Xinjiang Autonomous Region in far Western China, about southeast of the regional capital Ürümqi. It includes Lake Ayding, , the second or third lowest depression on Earth. By some measures, it is also the hottest and driest area in China during the summer. Geology and relief The Turpan Basin is a fault-bounded trough located in the eastern part of the Tian Shan. It covers an area of . The surrounding mountain ranges are: the central Tian Shan in the west, the Bogda Shan in the north-west, the Haerlike Shan in the north-west, and the Jueluotage Shan in the south. Beyond the surrounding mountain ranges lie the Junggar Basin in the north and the Tarim Basin in the south. Some geographers also use the term Turpan-Hami Basin, which is understood as including the Turpan Depression along with the Hami Depression (located to the east of the Turpan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bogda Shan
The Bogda Shan (; zh, s=博格达山, t=博格達山, p=Bógédá shān) range is part of the Eastern Tian Shan mountains and located in Xinjiang, some 60 km east of Ürümqi Ürümqi, , is the capital of the Xinjiang, Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in Northwestern China. With a census population of 4 million in 2020, Ürümqi is the second-largest city in China's northwestern interior after Xi'an, also the .... The topography of the area gradually increases from north to south. The elevation is between 1380 and 5445 m, with the largest relative relief up to 4065 m. The highest elevation is Bogda Peak, at 5,445 m. Administratively, the range forms the border between Dabancheng District to the south and Fukang City and Jimsar County to the north. In all three units, irrigated agriculture is based on the water flowing in streams that starts in the Bogda Shan. References Biosphere reserves of China Mountain ranges of Xinjiang Mountain ranges of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hami City
Hami ( zh, c=哈密) or Kumul () is a prefecture-level city in eastern Xinjiang, China. It is well known for sweet Hami melons. In early 2016, the former Hami county-level city merged with Hami Prefecture to form the Hami prefecture-level city with the county-level city becoming Yizhou District. Since the Han dynasty, Hami has been known for its production of agricultural products and raw resources. History Origins and names Cumuḍa (sometimes ''Cimuda'' or ''Cunuda'') is the oldest known endonym of Hami, when it was founded by a people known in Han Chinese sources as the '' Xiao Yuezhi'' ("Lesser Yuezhi"), during the 1st millennium BCE. The oldest attested Chinese name is "" ( zh, labels=no, p=Kūnmò). By the time of the Han dynasty, it was referred to in Chinese as "" ( zh, labels=no, p=Yīwú) or "" ( zh, labels=no, p=Yīwúlú). Under the Tang dynasty, it was also known as , . The name I-gou, I-gu, Igu, &c. sometimes encountered in European discussion of Hami was a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium radioactive decay, radioactively decays, usually by emitting an alpha particle. The half-life of this decay varies between 159,200 and 4.5 billion years for different isotopes of uranium, isotopes, making them useful for dating the age of the Earth. The most common isotopes in natural uranium are uranium-238 (which has 146 neutrons and accounts for over 99% of uranium on Earth) and uranium-235 (which has 143 neutrons). Uranium has the highest atomic weight of the primordial nuclide, primordially occurring elements. Its density is about 70% higher than that of lead and slightly lower than that of gold or tungsten. It occurs naturally in low concentrations of a few Parts-per notation#Parts-per expressions, parts per million in soil, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Elevation Extremes By Country
The following sortable table lists land surface elevation extremes by country or dependent territory. Topographic elevation is the vertical distance above the reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface. Table National elevation ranges Of all countries, Lesotho has the world's highest low point at . Other countries with high low points include Rwanda and Andorra . Countries with very low high points include Maldives , Tuvalu, and the Marshall Islands . These island countries also have the smallest range between their lowest (sea level) and highest points, and are very sensitive to changes in sea level. The highest and lowest points in China constitute the greatest elevation range within any single country at . The elevation ranges are also great in Nepal , Pakistan , and India . Monaco's elevation range is among the greatest relative to surface area. Within its 2.02 km2 territory, there is a differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ayding Lake
Aydingkol ( Uyghur: , , ), Aydingkul (Mongol) or Ayding () is a lake in the Turpan Depression, Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, PR China. At 154 m below sea level, it is the lowest point in China. This lake is now totally dried, and very muddy and salty. History In ancient times, Ayding Lake was known as ''juéluòwǎn'' (觉洛浣). The Uyghur derived name ''Aydingköl'' means "moon lake", due to the lake having a layer of white salt along its edge, giving the appearance of a shining moon. Geography The lake is located in the south hinterland of the Turpan Depression, approximately 35 kilometres away from the city of Turpan. From east to west, the lake spans 40 kilometres; the north-south span is 8 kilometres; and the total area of the lake is 200 square kilometres. The lake was formed from the formation of an orogeny of the Himalayas 249 million years ago, and once held approximately 5 million square kilometres of inland sea, which at one time surged up and became vastly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flaming Mountains
The Flaming Mountains () or Huoyan Mountains, are barren, eroded, red sandstone hills in the Tian Shan of Xinjiang. They lie near the northern rim of the Taklamakan Desert and east of the city of Turpan. Their striking gullies and trenches caused by erosion of the red sandstone bedrock give the mountains a flaming appearance at certain times of the day. The mountains are approximately ''probably'' long and wide, crossing the Turpan Depression from east to west. The average height of the Flaming Mountains is , with some peaks reaching over . The mountain climate is harsh, with summer temperatures often rising extremely high. One of the largest thermometers in China is on display adjacent to the mountain, tracking the surrounding ground temperatures. It is a popular tourist spot. A number of important palaeontological remains have been found in the area, see e.g. Lianmuqin Formation and Subashi Formation. Silk route In ancient times, the merchant traders traversing the Sil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenozoic
The Cenozoic Era ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterized by the dominance of mammals, insects, birds and angiosperms (flowering plants). It is the latest of three geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon, preceded by the Mesozoic and Paleozoic. The Cenozoic started with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, when many species, including the non-avian dinosaurs, became extinct in an event attributed by most experts to the impact of a large asteroid or other celestial body, the Chicxulub impactor. The Cenozoic is also known as the Age of Mammals because the terrestrial animals that dominated both hemispheres were mammalsthe eutherians ( placentals) in the Northern Hemisphere and the metatherians (marsupials, now mainly restricted to Australia and to some extent South America) in the Southern Hemisphere. The extinction of many groups allowed mammals and birds to greatly diversify so that large m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Plate
The Indian plate (or India plate) is or was a minor tectonic plate straddling the equator in the Eastern Hemisphere. Originally a part of the ancient continent of Gondwana, the Indian plate broke away from the other fragments of Gondwana and began moving north, carrying Insular India with it. It was once fused with the adjacent Australian plate to form a single Indo-Australian plate, but recent studies suggest that India and Australia may have been separate plates for at least 3 million years. The Indian plate includes most of modern South Asia (the Indian subcontinent) and a portion of the basin under the Indian Ocean, including parts of South China, western Indonesia, and extending up to but not including Ladakh, Kohistan, and Balochistan in Pakistan. Plate movements Until roughly , the Indian plate formed part of the supercontinent, Gondwana, together with modern Africa, Australia, Antarctica, and South America. Gondwana fragmented as these continents drifted apa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angaran Craton
Siberia, also known as Siberian Craton, Angaraland (or simply Angara) and Angarida, is an ancient craton in the heart of Siberia. Today forming the Central Siberian Plateau, it formed an independent landmass prior to its fusion into Pangea during the Late Carboniferous-Permian. The Verkhoyansk Sea, a passive continental margin, was fringing the Siberian Craton to the east in what is now the East Siberian Lowland. Angaraland was named in the 1880s by Austrian geologist Eduard Suess who erroneously believed that in the Paleozoic Era there were two large continents in the Northern Hemisphere: "Atlantis", which was North America connected to Europe via a peninsula (Greenland and Iceland), and "Angara-land", which would have been eastern Asia, named after the Angara River in Siberia. Precambrian history About 2.5 billion years ago (in the Siderian Period), Siberia was part of a continent called Arctica, along with the Canadian Shield. Around 1.1 billion years ago (in the Stenian Peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |