|
Turkic Tribes
The Turkic languages, Turkic term ''oğuz'' or ''oğur'' (in z-Turkic, z- and r-Turkic, respectively) is a historical term for "military division, clan, or tribe" among the Turkic peoples. With the Mongol invasions of 1206–21, the Turkic Khanate, khaganates were replaced by Mongolic peoples, Mongol or hybrid Turco-Mongol confederations, where the corresponding military division came to be known as ''Orda (organization), orda''. Background The 8th-century Orkhon inscriptions, Kul Tigin stela has the earliest instance of the term in Old Turkic epigraphy: ''Toquz Oghuz'', the "nine tribes". Later the word appears often for two largely separate groups of the Turkic migration in the early medieval period, namely: *Onogurs, Onogur ("ten tribes") *Utigurs *Kutrigurs *Uyghur Khaganate, Uyghur *Saragurs The stem ''uq-, oq-'' "kin, tribe" is from a Proto-Turkic ''*uk''. The Old Turkic word has often been connected with ''oq'' "arrow"; Pohl (2002) in explanation of this connection add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic Languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of more than 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and West Asia. The Turkic languages originated in a region of East Asia spanning from Mongolia to Northwest China, where Proto-Turkic language, Proto-Turkic is thought to have been spoken, from where they Turkic migration, expanded to Central Asia and farther west during the first millennium. They are characterized as a dialect continuum. Turkic languages are spoken by some 200 million people. The Turkic language with the greatest number of speakers is Turkish language, Turkish, spoken mainly in Anatolia and the Balkans; its native speakers account for about 38% of all Turkic speakers, followed by Uzbek language, Uzbek. Characteristic features such as vowel harmony, agglutination, subject-object-verb order, and lack of grammatical gender, are almost universal within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
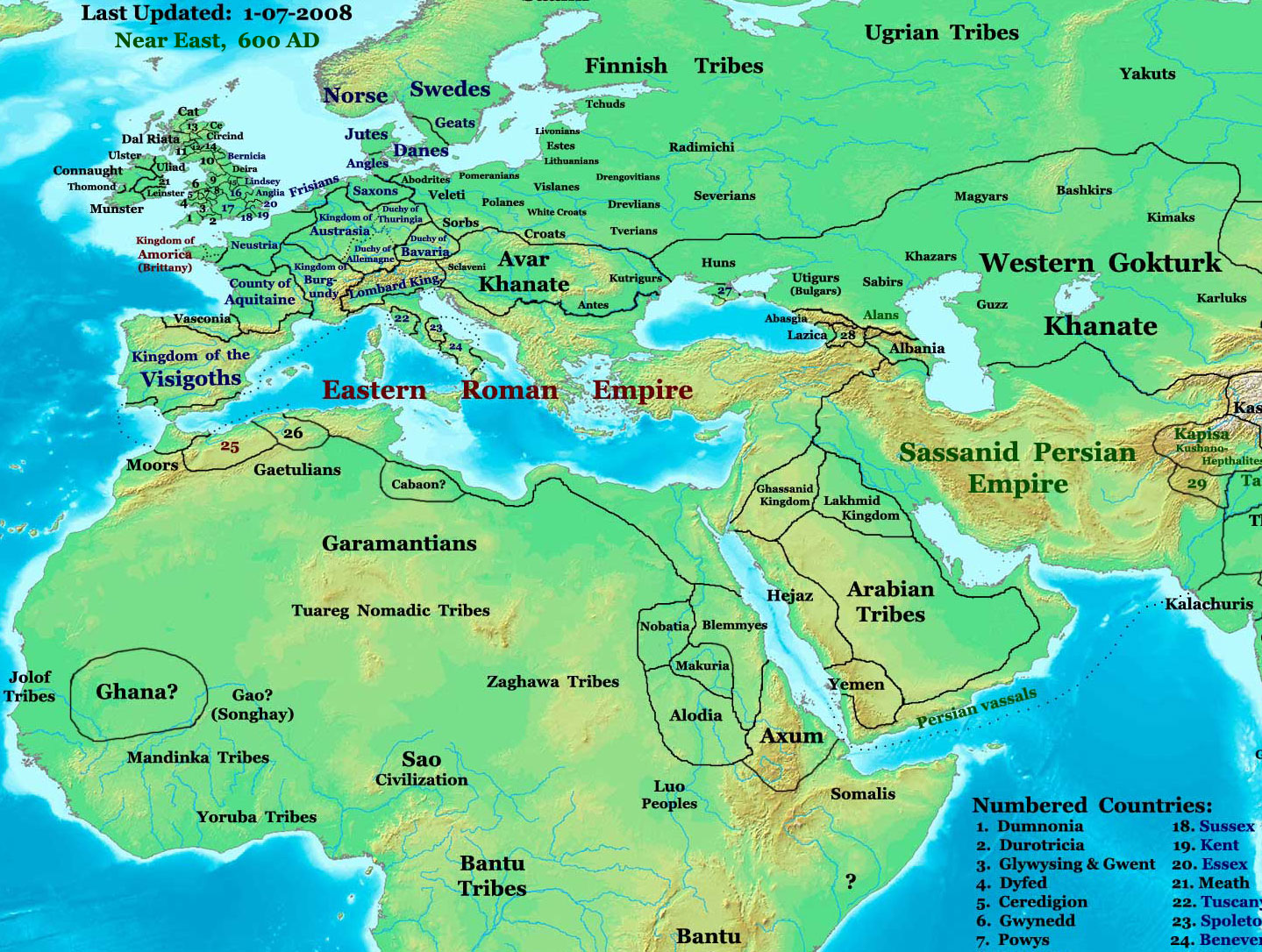
Kutrigurs
The Kutrigurs were a Turkic nomadic equestrian tribe who flourished on the Pontic–Caspian steppe in the 6th century AD. To their east were the similar Utigurs and both possibly were closely related to the Bulgars. They warred with the Byzantine Empire and the Utigurs. Towards the end of the 6th century they were absorbed by the Pannonian Avars under pressure from the Türks. Etymology The name ''Kutrigur'', also recorded as ''Kwrtrgr'', ''Κουτρίγουροι'', ''Κουτούργουροι'', ''Κοτρίγουροι'', ''Κοτρίγοροι'', ''Κουτρίγοροι'', ''Κοτράγηροι'', ''Κουτράγουροι'', ''Κοτριαγήροι'', has been suggested as a metathecized form of Turkic ''*Toqur- Oğur'', with ''*quturoğur'' meaning "nine Oğur (tribes)". David Marshall Lang derived it from Turkic ''kötrügür'' (conspicuous, eminent, renowned). Few scholars support theories deriving the Kutrigurs from the Guti/Quti and the Utigurs from the Ud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of Nomad, nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese historiography, Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 BC, founded the Xiongnu Empire. After overthrowing their previous overlords, the Yuezhi, the Xiongnu became the dominant power on the steppes of East Asia, centred on the Mongolian Plateau. The Xiongnu were also active in areas now part of Siberia, Inner Mongolia, Gansu and Xinjiang. Their relations with the Chinese dynasties to the south-east were complex—alternating between various periods of peace, war, and subjugation. Ultimately, the Xiongnu were defeated by the Han dynasty in a Han–Xiongnu Wars, centuries-long conflict, which led to the confederation splitting in two, and forcible resettlement of large numbers of Xiongnu within Han borders. During the Sixteen Kingdoms era, listed as one of the "Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th centuries AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part of Scythia at the time. By 370 AD, the Huns had arrived on the Volga, causing the westwards movement of Goths and Alans. By 430, they had established a vast, but short-lived, empire on the Danubian frontier of the Roman empire in Europe. Either under Hunnic hegemony, or fleeing from it, several central and eastern European peoples established kingdoms in the region, including not only Goths and Alans, but also Vandals, Gepids, Heruli, Suebians and Rugians. The Huns, especially under their King Attila, made frequent and devastating raids into the Eastern Roman Empire. In 451, they invaded the Western Roman province of Gaul, where they fought a combined army of Romans and Visigoths at the Battle of the Catalaunian Fields, and in 452, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oghuz Turks
The Oghuz Turks ( Middle Turkic: , ) were a western Turkic people who spoke the Oghuz branch of the Turkic language family. In the 8th century, they formed a tribal confederation conventionally named the Oghuz Yabgu State in Central Asia. Today, much of the populations of Turkey, Azerbaijan and Turkmenistan are descendants of Oghuz Turks. The term Oghuz was gradually supplanted by the terms Turkmen and Turcoman ( or ''Türkmân'') by the 13th century.Lewis, G. ''The Book of Dede Korkut''. Penguin Books, 1974, p. 10. The Oghuz confederation migrated westward from the Jeti-su area after a conflict with the Karluk allies of the Uyghurs. In the 9th century, the Oghuz from the Aral steppes drove Pechenegs westward from the Emba and Ural River region. In the 10th century, the Oghuz inhabited the steppe of the rivers Sari-su, Turgai and Emba north of Lake Balkhash in modern-day Kazakhstan. They embraced Islam and adapted their traditions and institutions to the Islam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oghurs
The Onoghurs, Onoğurs, or Oğurs (Ὀνόγουροι, Οὔρωγοι, Οὔγωροι; Onογurs, Ογurs; "ten tribes", "tribes") were a group of Turkic nomadic equestrians who flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region between the 5th and 7th centuries, and spoke an Oghuric language. Etymology The name ''Onoğur'' is widely thought to derive from ''On-Oğur'' "ten Oğurs (tribes)". Modern scholars consider Turkic terms for tribe ''oğuz'' and ''oğur'' to be derived from Turkic ''*og/uq'', meaning "kinship or being akin to". The terms initially were not the same, as ''oq/ogsiz'' meant "arrow", while ''oğul'' meant "offspring, child, son", ''oğuš/uğuš'' was "tribe, clan", and the verb ''oğša-/oqša'' meant "to be like, resemble". The modern name of "Hungary" (see name of Hungary) is usually believed to be derived from On-Oğur (> (H)Ungari). Language The Onoghuric or Oghuric languages are a branch of the Turkic languages. Some scholars suggest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnogenesis
Ethnogenesis (; ) is the formation and development of an ethnic group. This can originate by group self-identification or by outside identification. The term ''ethnogenesis'' was originally a mid-19th-century neologism that was later introduced into 20th-century academic anthropology. In that context, it refers to the observable phenomenon of the emergence of new social groups that are identified as having a cohesive identity, i.e., an "ethnic group" in anthropological terms. Relevant social sciences not only observe this phenomenon but also search for explanations for its causes. The term ''ethnogeny'' is also used as a variant of ''ethnogenesis''. Passive or active ethnogenesis Ethnogenesis can occur passively or actively. A passive ethnogenesis is an unintended outcome, which involves the spontaneous emergence of various markers of group identity through processes such as the group's interaction with unique elements of their physical environment, cultural divisions (such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomadic Empire
Nomadic empires, sometimes also called steppe empires, Central or Inner Asian empires, were the empires erected by the bow-wielding, horse-riding, nomadic people in the Eurasian Steppe, from classical antiquity (Scythia) to the early modern era ( Dzungars). They are the most prominent example of non- sedentary polities. Some nomadic empires consolidated by establishing a capital city inside a conquered sedentary state and then exploiting the existing bureaucrats and commercial resources of that non-nomadic society. In such a scenario, the originally nomadic dynasty may become culturally assimilated to the culture of the occupied nation before it is ultimately overthrown. Ibn Khaldun (1332–1406) described a similar cycle on a smaller scale in 1377 in his Asabiyyah theory. Historians of the early medieval period may refer to these polities as "khanates" (after ''Khan (title), khan'', the title of their rulers). After the Mongol conquests of the 13th century the term Orda (orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Édouard Chavannes
Émmanuel-Édouard Chavannes (5 October 1865 – 29 January 1918) was a French sinologist and expert on Chinese history and religion, and is best known for his translations of major segments of Sima Qian's ''Records of the Grand Historian'', the work's first ever translation into a Western language. Chavannes was a prolific and influential scholar, and was one of the most accomplished Sinologists of the modern era notwithstanding his relatively early death at age 52 in 1918. A successor of 19th century French sinologists Jean-Pierre Abel-Rémusat and Stanislas Julien, Chavannes was largely responsible for the development of Sinology and Chinese scholarship into a respected field in the realm of French scholarship. Life and career Édouard Chavannes was born on 5 October 1865 in Lyon, France. As a youth he studied at the ''lycée'' in Lyon, where, like most students of his era, his education focused mainly on the Latin and Greek classics. Chavannes was then sent to Par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shad (prince)
Shad () was a state office in the early Central Asian Turkic states, roughly equivalent to governor. "Shad" could only be an appointee over a vassal tribe, where he represented interests of the preeminent Kagan. The name of this tribe was included in his title. For example, Tardu-shad could only be a Shad over Tardu tribe. The title carried autonomy in different degrees, and its links with the central authority of kagan varied from economical and political subordination to superficial political deference. The title ''Shad'' is borrowed from an Iranian source (cf. Sogdian ''’ġšyδ'', Saka ''šao'', Middle Iranian ''šāδ'', Persian ''šāh'' < ''xšāyaθiya'' ‘king’, or Avestan ''xšaēta'' "chief"). The position of Shad was traditionally given to the member of a ruling ( [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saragurs
The Saragurs or Saraguri (, , Šarağurs) were a Turkic nomadic tribe mentioned in the 5th and 6th centuries. They may be the Sulujie (蘇路羯, ''suoluo-kjɐt'') mentioned in the Chinese '' Book of Sui''. They originated from Western Siberia and the Kazakh steppes, from where they were displaced north of the Caucasus by the Sabirs. Around 463 AD, the Akatziri and other tribes that had been part of the Hunnic union were attacked by the Saragurs, one of the first Oghur tribes that entered the Pontic–Caspian steppe as the result of migrations set off in Inner Asia by the Uar attacking the Kidara (a sub-group of the Xiyon). The Akatziri had lived north of the Black Sea, west of Crimea. According to Priscus, in 463 Ernakh and Dengizich sent the representatives of Saragurs, Oghurs (or Urogi, perhaps a Byzantine error for Uyghurs) and Onogurs to the Emperor in Constantinople, and explained they had been driven out of their homeland by the Sabirs, who had been attacked by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uyghur Khaganate
The Uyghur Khaganate (also Uyghur Empire or Uighur Khaganate, self defined as Toquz-Oghuz country; , Tang-era names, with modern Hanyu Pinyin: or ) was a Turkic empire that existed for about a century between the mid 8th and 9th centuries. It was a tribal confederation under the Orkhon Uyghur () nobility, referred to by the Chinese as the ''Jiu Xing'' ("Nine Clans"), a calque of the name '' Toquz Oghuz'' or ''Toquz Tughluq''. History Rise In the mid-5th century, Uyghurs constituted a tribe of the Tiele, which was also under the Turkic Khaganate.Chapter 195, Huihe. Sewikisource/ref> In 657, the Western Turkic Khaganate was defeated by the Tang dynasty, after which the Uyghurs defected to the Tang. Prior to this the Uyghurs had already shown an inclination towards alliances with the Tang when they fought with them against the Tibetan Empire and Turks in 627. In 742, the Uyghurs, Karluks, and Basmyls rebelled against the Second Turkic Khaganate. In 744, the Basmyls capt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |