|
Turbo-compound Engines
A turbo-compound engine is a reciprocating engine that employs a turbine to recover energy from the exhaust gases. Instead of using that energy to drive a turbocharger as found in many high-power aircraft engines, the energy is instead sent to the output shaft to increase the total power delivered by the engine. The turbine is usually mechanically connected to the crankshaft, as on the Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone, but electric and hydraulic power recovery systems have been investigated as well. As this recovery process does not increase fuel consumption, it has the effect of reducing the specific fuel consumption (shaft engine), specific fuel consumption, the ratio of fuel use to power. Turbo-compounding was used for commercial airliners and similar long-range, long-endurance roles before the introduction of turbojet engines. Examples using the Duplex-Cyclone include the Douglas DC-7B and Lockheed L-1049 Super Constellation, while other designs did not see production use. Conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napier Nomad
The Napier Nomad is a British diesel engine, diesel aircraft engine designed and built by Napier & Son in 1949. They combined a piston engine with a turbine to recover energy from the exhaust and thereby improve fuel efficiency, fuel economy. Two versions were tested, the complex Nomad I which used two propellers, each driven by mechanically independent stages, and the Nomad II, using the turbo-compound principle which coupled the two parts to drive a single propeller. The Nomad II had the lowest specific fuel consumption (shaft engine), specific fuel consumption figures seen up to that time. Despite this the Nomad project was cancelled in 1955 having spent £5.1 million on development, as most interest had passed to turboprop designs. Design and development In 1945 the Air Ministry asked for proposals for a new class engine with good fuel economy. Curtiss-Wright was designing an engine of this sort of power known as the turbo-compound engine, but Sir Harry Ricardo, one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolls-Royce Crecy
The Rolls-Royce Crecy was a British experimental Two-stroke engine, two-stroke, 90-degree, V12 engine, V12, liquid-cooled Aircraft engine, aero-engine of 1,593.4 Cubic inch, cu.in (26.11 Litre, L) Engine displacement, capacity, featuring sleeve valves and Fuel injection, direct petrol injection. Initially intended for a high-speed "sprint" interceptor fighter, the Crecy was later seen as an economical high-altitude long-range powerplant. Developed between 1941 and 1946, it was among the most advanced two-stroke aero-engines ever built. The engine never reached flight trials and the project was cancelled in December 1945, overtaken by the progress of jet engine development. The engine was named after the Battle of Crécy, after Rolls-Royce chose battles as the theme for naming their two-stroke aero engines. Rolls-Royce did not develop any other engines of this type. Design and development Origins Henry Tizard, Sir Henry Tizard, Chairman of the Aeronautical Research Committee (A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daimler Trucks North America
Daimler Truck North America LLC (formerly Freightliner Corporation) is an automotive industry manufacturer of commercial vehicles headquartered in Portland, Oregon, and LLC of the German multinational Daimler Truck AG. On October 1, 2021, Daimler AG stockholders approved a spinoff of the truck division. Brands * Alliance Parts * Detroit Diesel * Freightliner Trucks * Freightliner Custom Chassis Corporation * Freightliner SelecTrucks *Thomas Built Buses * Western Star Trucks * Demand Detroit * Sterling Trucks Fuso Trucks America, while mostly owned by Daimler Truck, currently operates separately from Daimler Trucks North America. History Early years *1896- Gottlieb Daimler creates the first truck. *1923- First diesel truck: Benz *1926- Daimler and Benz merge. *1942- Leland James founds the Freightliner Corporation. *1947- Freightliner opens its first truck plant in Portland, Oregon. *1950- Hyster Company is the first private carrier to order a Freightliner truck. *195 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formula One Engines
This article gives an outline of Formula One engines, also called Formula One power units since the hybrid era starting in 2014. Since its inception in 1947, Formula One has used a variety of engine Formula One regulations, regulations. ''Formulae'' limiting engine capacity had been used in Grand Prix racing on a regular basis since after World War I. The engine formulae are divided according to #Engine regulation progression by era, era. Characteristics Formula One currently uses 1.6 litre four-stroke turbocharged 90 degree V6 engine, V6 overhead camshaft engine#Double overhead camshaft, double-overhead camshaft (DOHC) reciprocating engines. They were introduced in 2014 and have been developed over the subsequent seasons. Mostly from the 2023 season, specifications on Formula One engines, including the software used to control them and the maximum per-engine price to F1 teams of €15,000,000, have been frozen until the end of 2025, when the completely new 2026 spec will c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formula One
Formula One (F1) is the highest class of worldwide racing for open-wheel single-seater formula Auto racing, racing cars sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The FIA Formula One World Championship has been one of the world's premier forms of motorsport since its 1950 Formula One season, inaugural running in 1950 and is often considered to be the pinnacle of motorsport. The word ''Formula racing, formula'' in the name refers to Formula One regulations, the set of rules all participant cars must follow. A Formula One season consists of a series of races, known as List of Formula One Grands Prix, Grands Prix. Grands Prix take place in multiple countries and continents on either purpose-built List of Formula One circuits, circuits or closed roads. A List of Formula One World Championship points scoring systems, points scoring system is used at Grands Prix to determine two annual World Championships: List of Formula One World Drivers' Champions, one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scania AB
Scania AB ( , ), stylised SCANIA in its products, is a major Sweden, Swedish manufacturer headquartered in Södertälje, focusing on commercial vehicles—specifically heavy lorries, trucks and buses. It also manufactures diesel engines for heavy vehicles as well as Marine propulsion, marine and general industrial applications. Scania was formed in 1911 through the merger of Södertälje-based Vabis and Malmö-based Maskinfabriks-aktiebolaget Scania. Since 1912, the company headquarters have been based in Södertälje after the merger. Today, Scania has production facilities in Sweden, France, the Netherlands, Thailand, China, India, Argentina, Brazil, Poland and Finland. In addition, there are assembly plants in ten countries in Africa, Asia and Europe. Scania's sales and service organisation and finance companies are worldwide. In 2022, the company employed approximately 56,927 people around the world. Scania was listed on the NASDAQ OMX Stockholm stock exchange from 1996 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detroit Diesel
Detroit Diesel Corporation (DDC) is an American diesel engine manufacturer headquartered in Detroit, Michigan. It is a subsidiary of Daimler Truck North America, which is itself a wholly owned subsidiary of the multinational Daimler Truck AG. The company manufactures heavy-duty engines and chassis components for the on-highway and vocational commercial truck markets. Detroit Diesel has built more than 5 million engines since 1938, more than 1 million of which are still in operation worldwide. Detroit Diesel's product line includes engines, axles, transmissions, and a Virtual Technician service. Detroit engines, transmissions, and axles are used in several models of truck manufactured by Daimler Truck North America. Divisions Detroit Diesel consists of manufacturing operations of axles, transmissions and diesel engines for on-highway only, which is owned by Daimler Truck AG. The former off-highway division was sold to MTU Friedrichshafen in 2006 and subsequently purchased by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turboprop
A turboprop is a Gas turbine, gas turbine engine that drives an aircraft Propeller (aeronautics), propeller. A turboprop consists of an intake, reduction drive, reduction gearbox, gas compressor, compressor, combustor, turbine, and a propelling nozzle. Air enters the intake and is compressed by the compressor. Fuel is then added to the compressed air in the combustor, where the Fuel mixture, fuel-air mixture then Combustion, combusts. The hot combustion gases expand through the turbine stages, generating power at the point of exhaust. Some of the power generated by the turbine is used to drive the compressor and electric generator. The gases are then exhausted from the turbine. In contrast to a turbojet or turbofan, the engine's exhaust gases do not provide enough power to create significant thrust, since almost all of the engine's power is used to drive the propeller. Technological aspects Exhaust thrust in a turboprop is sacrificed in favor of shaft power, which is obtaine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allison V-1710
The Allison V-1710 aircraft engine designed and produced by the Allison Engine Company was the most common United States, US-developed V12 engine, V-12 Internal combustion engine cooling, liquid-cooled engine in service during World War II. Versions with a turbocharger gave excellent performance at high altitude in the twin-engined Lockheed P-38 Lightning, and turbo-superchargers were fitted to experimental single-engined fighters with similar results. The United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) preference for turbochargers early in the V-1710's development program meant that less effort was spent on developing suitable mechanically driven centrifugal superchargers for the Allison V-12 design, as other V-12 designs from friendly nations like the British Rolls-Royce Merlin were already using. When smaller-dimensioned or lower-cost versions of the V-1710 were desired, they generally had poor performance at higher altitudes. Design and development The Allison Engine Company, Allis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolls-Royce Griffon
The Rolls-Royce Griffon is a British 37-litre (2,240 cubic inch, cu in) Engine displacement, capacity, 60-degree V12 engine, V-12, liquid-cooled Aircraft engine, aero engine designed and built by Rolls-Royce Limited. In keeping with company convention, the Griffon was named after a bird of prey, in this case the griffon vulture. Design work on the Griffon started in 1938 at the request of the Fleet Air Arm, for use in new aircraft designs such as the Fairey Firefly. In 1939 it was also decided that the engine could be adapted for use in the Supermarine Spitfire (Griffon powered variants), Spitfire. Development was stopped temporarily to concentrate efforts on the smaller Rolls-Royce Merlin, Merlin and the 24-cylinder Rolls-Royce Vulture, Vulture; the engine did not go into production until the early 1940s. The Griffon was the last in the line of V-12 aero engines to be produced by Rolls-Royce with production ceasing in 1955. Griffon engines remain in Royal Air Force servic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
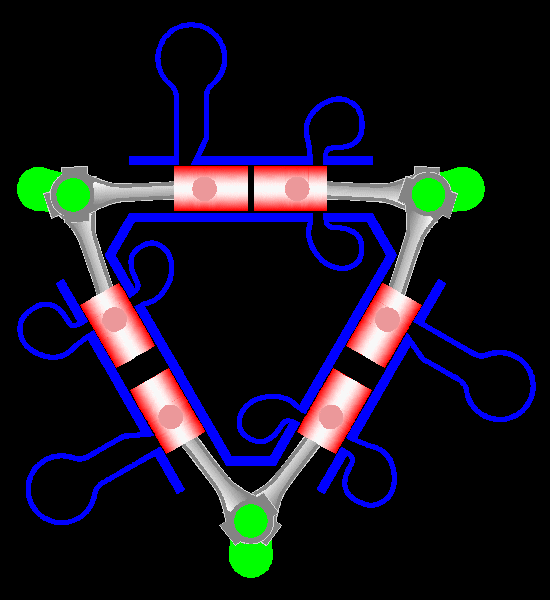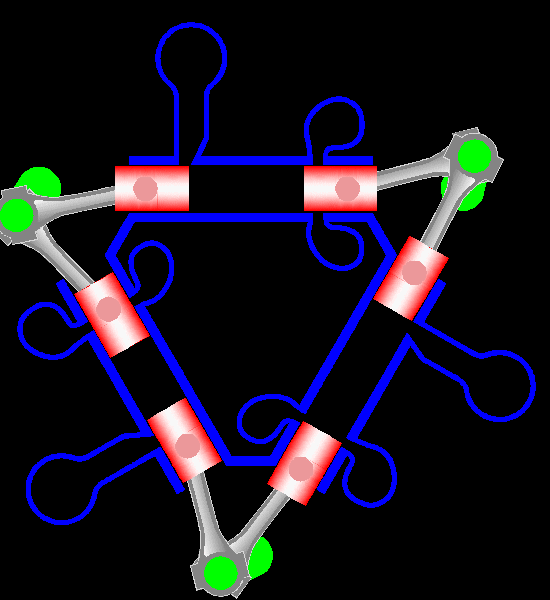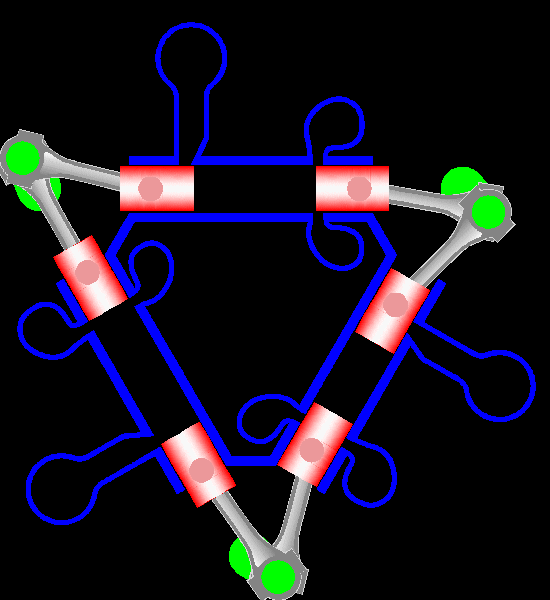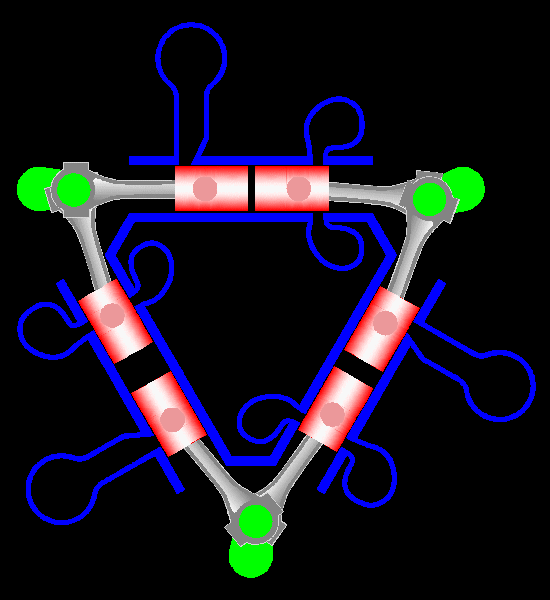
Napier Deltic
The Napier Deltic engine is a British opposed-piston valveless, supercharged uniflow scavenged, two-stroke diesel engine used in marine and locomotive applications, designed and produced by D. Napier & Son. Unusually, the cylinders were disposed in a three-bank triangle, with a crankshaft at each corner of the triangle. The term Deltic (meaning "in the form of the Greek letter (capital) delta") is used to refer to both the Deltic E.130 opposed-piston, high-speed diesel engine and the locomotives produced by English Electric using these engines, including its demonstrator locomotive named ''DELTIC'' and the production version for British Railways, which designated these as the Class 55. A single, half-sized, turbocharged Deltic power unit also featured in the English Electric-built Type 2 locomotive, designated as the Class 23. Both locomotive and engine became better known as the "Baby Deltic". History and design The Deltic story began in 1943 when the British Admiral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |