|
Tuimalealiʻifano
Tuimalealiʻifano is one of the four paramount chiefly titles of Samoa, known as the '' tama a ʻāiga''. Samoa's other three paramount chiefs are Malietoa, Mataʻafa and Tupua Tamasese. The seat of the Tuimalealiʻifano title is at Falelatai in the Aʻana district. The current title-holder is Tuimalealiʻifano Vaʻaletoʻa Sualauvi II, who has held the title since 1977 and currently serves as the head of state of Samoa (O le Ao o le Malo). Origins The title is the most recent of the ''tama a ʻāiga'', originating in the mid-nineteenth century with Tuiaana Sualauvi, a nephew of Malietoa Fitisemanu I. Sualauvi was appointed ''Tui Aʻana'' in 1848. By the early 1860s he had also been appointed to the pāpā titles of Gatoaitele and Vaetamasoalii. In 1869, he obtained the support of Fuataga and Tafua of Aleipata and Moeono and Tusa of Falefa and Lufilufi and was appointed ''Tui Ātua'', briefly ascending to the position of ''Tupu Tafaʻifa''. His reign would only last a year unt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuimalealiʻifano Vaʻaletoʻa Sualauvi II
Afioga Tuimalealiʻifano Vaʻaletoʻa Eti Sualauvi II (born 29 April 1947) is a Samoan politician who is the current O le Ao o le Malo (head of state) of Samoa, in office since 2017. Biography He is a great-grandson of one of the Mau movement leaders, Tuimalealiʻifano Faʻaoloiʻi Siʻuaʻana I, and grand-nephew of Tuiaana Tuimalealiʻifano Suatipatipa II, who was the inaugural member of the Council of Deputies in 1962. He was appointed to the title of Tuimalealiʻifano in July 1977, a title formed out of a cadet branch of the Sā Tupua state dynasty and one of the four paramount chiefly titles of Samoa. He is married to Masiofo Faʻamausili Leinafo Tuimalealiʻifano. Early career He worked as a policeman, lawyer and previously was a Samoan Police Chief Inspector and a secondary school teacher. He was a police officer in New Zealand for three years. He also served as a public-defender, public trustee, and barrister and solicitor in the Supreme Court of Samoa. He is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O Le Ao O Le Malo
The Independent State of Samoa ( Samoan for "Chief of the government") is the ceremonial head of state of Samoa. The position is described in Part III of the 1960 Samoan constitution. At the time the constitution was adopted, it was anticipated that future heads of state would be chosen from among the four ''Tama a 'Aiga'' "matai" paramount chiefs in line with customary protocol. This is not a constitutional requirement, so Samoa can be considered a parliamentary republic rather than a constitutional monarchy. The government Press Secretariat describes Head of State as a "ceremonial president". The holder is given the formal style of ''Highness'', as are the heads of the four paramount chiefly dynasties. Members of the Council of Deputies act as deputy heads of state, standing in for the head of state when they are unable to fulfil their duties, such as when the Head of State is either absent or ill. The current O le Ao o le Malo is Tuimalealiʻifano Vaʻaletoʻa Sualauvi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
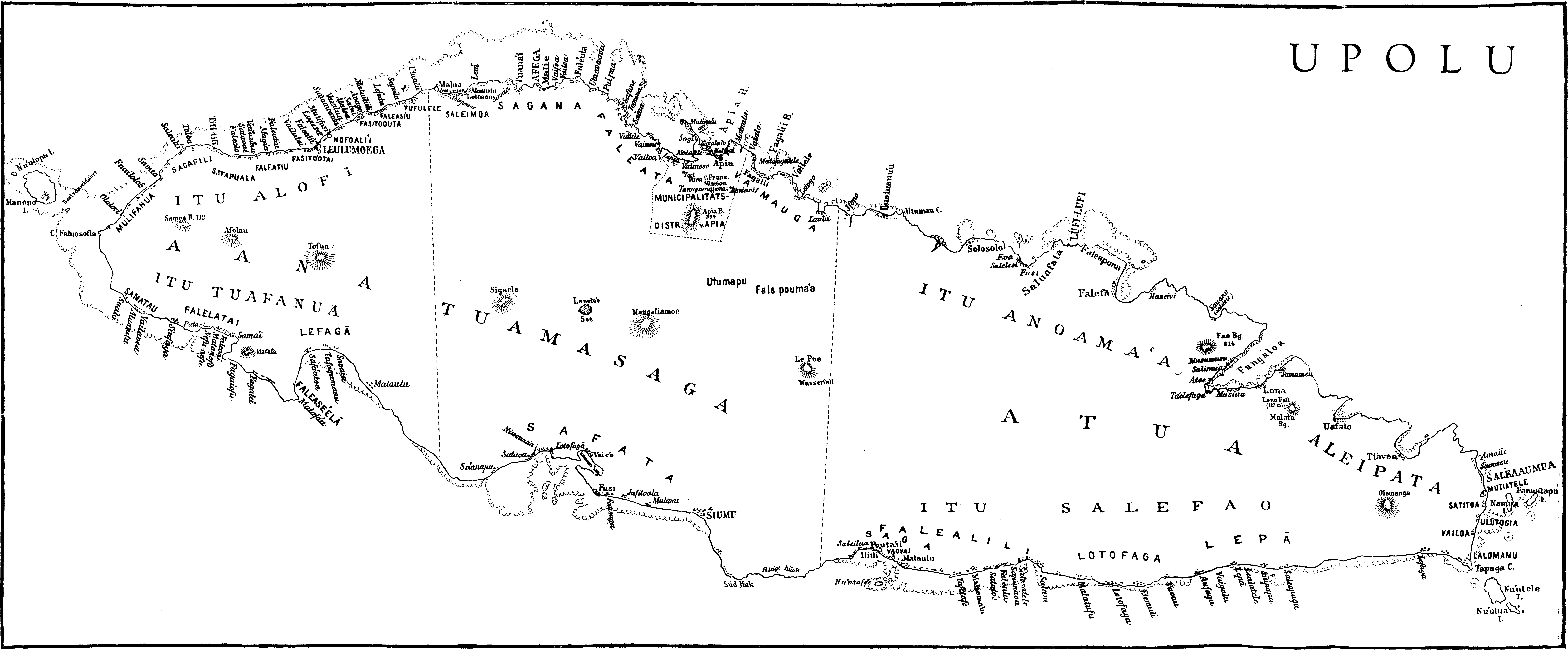
Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa and known until 1997 as Western Samoa, is an island country in Polynesia, part of Oceania, in the South Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main islands (Savai'i and Upolu), two smaller, inhabited islands (Manono Island, Manono and Apolima), and several smaller, uninhabited islands, including the Aleipata Islands (Nuʻutele, Nuʻulua, Fanuatapu and Namua). Samoa is located west of American Samoa, northeast of Tonga, northeast of Fiji, east of Wallis and Futuna, southeast of Tuvalu, south of Tokelau, southwest of Hawaii, and northwest of Niue. The capital and largest city is Apia. The Lapita culture, Lapita people discovered and settled the Samoan Islands around 3,500 years ago. They developed a Samoan language and Culture of Samoa, Samoan cultural identity. Samoa is a Unitary state, unitary Parliamentary system, parliamentary democracy with 11 Districts of Samoa, administrative divisions. It is a sovereign state and a membe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuiaana Tuimalealiʻifano Suatipatipa II
Tuiaana Tuimalealiʻifano Suatipatipa II (1914 – 24 July 1974) was a Western Samoan paramount chief, politician and church elder. For most of the period between 1962 and 1974 he was the only member of the Council of Deputies, whose members serve as deputy to the O le Ao o le Malo. Biography Suatipatipa was born in 1914,Morgan A. Tuimalealiʻifano (2006O Tama a ʻāiga: The Politics of Succession to Sāmoa's Paramount Titlespiiii the son of Tuimalealiʻifano Faʻaoloiʻi Siʻuaʻana I, a member of the anti-colonial Mau movement. He was educated at Marist Brothers schools in Samoa and New Zealand.T.T. Suatipatipa II ''Pacific Islands Monthly'', September 1974, p102 In 1952 he succeeded his father as [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamaʻāiga
(meaning "sons of the families") is a Samoan term used to refer to the four high chiefly titles in the system of the Independent State of Samoathe Malietoa, Mataʻafa, Tupua Tamasese and Tuimalealiʻifano. American Samoa has its own paramount chiefs, known as , who are the sole authority of their districtsthe Leʻiato, Faumuina, Mauga, Tuitele, Fuimaono, Sātele, Letuli, and Tui Manuʻa. History The term first emerged during the ascension of Fuiavailili in the aftermath of King Muagututia's death in the late 17th century. Before affirming his kingship, the powerful orator polities of Lufilufi and Leulumoega had to first verify his royal pedigree by identifying the families and lineages to which he was connected. Having been satisfied, the orator polity declared Fuiavailili was a , owing to his ancestry and links to the great families of Samoa and was subsequently proclaimed king. By the last quarter of the 19th century, the status of the four dominant high chiefly dynastie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faʻamatai
''Faʻamatai'' is the indigenous political ('chiefly') system of Samoa, central to the organization of Samoan society. It is the traditional indigenous form of governance in both Samoas, comprising American Samoa and the Independent State of Samoa. The term comprises the prefix ''faʻa'' ( Samoan for "in the way of") and the word ''matai'' (family name or title). Of central importance in the system are the ''matai'', the holders of family chief titles, and their role in looking after their family. ''Faʻamatai'' is the key socio-political system of governance and way of life ('' faʻa Samoa'') in Samoan culture. Inherent in the ''faʻamatai'' system is the welfare and well-being of the extended family ('' ʻaiga'') and the protection of family property, consisting most importantly of customary land. About 81% (567,000 acres), is under customary ownership, with the rest under the national government (''malo'') as public lands with another 4% freehold. In the Independent Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mataʻafa
Matāʻafa is one of the four paramount ''tama a ʻāiga'' (maximal lineage) titles of Samoa. Tradition versus democracy in the South Pacific: Fiji, Tonga, and Western Samoa by Stephanie Lawson, p. 146 It is one of two such titles originating from the district at the east end of island (the other being of Falefa & Salani) and has its historical seat in the village of Amaile. Prominent holders of the title include [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tupua Tamasese
Tupua Tamasese, formally known as Tupua, is a State (polity), state dynasty and one of the four paramount Fa'amatai, chiefly titles of Samoa, known as the ''Tamaʻāiga, tama a ʻāiga''. It is the titular head of one of Samoa's two great royal families – Sā Tupua, the lineage of King Tupua Fuiavailili, descendant of Salamasina, Queen Salamasina. The current holder of the title is Tui Ātua Tupua Tamasese Efi. "Tupua" refers to Salamasina's descendant, King Tupua Fuiavailili, who was the first to unite both of Salamasina's descent lines in his personage and ascended to the kingship of Samoa in c.1550, upon the death of his adoptive father, King Muagututiʻa. Tupua Fuiavailili was adopted by his aunt, Fenunuʻivao (daughter of Leutele and wife of King Muagututiʻa) and named as the King's successor. Tupua's rise also led to the first usage of the term ''tama a ʻāiga'' by the orator polity of Leulumoega and Lufilufi, in reference to his many genealogical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Louis Stevenson With Tuimalealufano At Vailima, Samoa, Between 1889 And 1894
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of ''Hrōþ, Hruod'' () "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown, godlike" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin.Reaney & Wilson, 1997. ''Dictionary of English Surnames''. Oxford University Press. It is also in use Robert (surname), as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert (name), Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe, the name entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta (given name), Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto (given name), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malietoa
Mālietoa ( ''Mālietoa'') is a state dynasty and one of the four paramount chiefly titles of Samoa. It is the titular head of one of the two great royal families of Samoa: Sā Malietoa. Literally translated as "great warrior", the title's origin comes from the final words of Tu'i Tonga Talakaifaiki as he was fleeing on the beach to his boat, "''Mālie toa, mālie tau''" ("Great warrior, bravely you have fought"). The Malietoa title is currently held by HH Malietoa Faamausili Moli and HH Malietoa Bob Ainuu Afamasaga based on Samoa's Lands and Titles Court Decision of August 17, 2018. HH Malietoa Faamausili Moli is a member of Samoa’s Council of Deputies and eligible for the Head of State and his co-heir Malietoa Bob Ainuu Afamasaga is the heir to Samoa's traditional monarch Kingship or Tafaifa to glorify Jehovah's Name and His Kingdom with its King Jesus Christ globally. History In early Polynesian history the Tu'i Tonga dynasty from Tu'i Tonga 'Aho'eitutupu'a supreme rule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aʻana
Aana is a district of Samoa. It is on the western third of Upolu island, with a small exclave (Satuimalufilufi village) surrounded by Aiga-i-le-Tai. It has an area of 193 km2 and a population (2016 Census) of 23,265. The main centre is Leulumoega. Overview The Aana District comprises approximately 18 villages from Faleasiu in the North to Matautu in the South. The district encompasses the western portion of Upolu except for the extreme Western promontory, belonging to Aiga i le Tai district. Traditionally the northern part of the district was known as 'Itu Alofi', (Gathering side or Assembly side), as the Northern villages held a lot of the political power in historical times, whilst the Southern side was known as 'Itu Tufanua', (the backward side or the uncivilised side). It is a common occurrence in Samoa that the northern areas of both Upolu and Savaii usually held a lot of the political power especially as many of the principal villages being located in the Northern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |