|
Truso
Truso was a Viking Age port of trade (emporium) set up by the Scandinavians at the banks of the Nogat delta branch of the Vistula River, close to a bay (the modern Drużno lake), where it emptied into the shallow and brackish Vistula Lagoon. This sizeable lagoon is separated from the Gdańsk Bay by the Vistula Spit at the southern Baltic Sea coast. In the 9th century, the merchant Wulfstan of Hedeby travelled to Truso in the service of the English King Alfred the Great and wrote his account of the place at a prominent location of the Amber Road, which attracted merchants from central and southern Europe, who supplied the markets in the Mediterranean and the Middle East with the highly valued commodity. The account of the voyage to the town of Truso in the land of the ''Pruzzens'' around the year 890 by Wulfstan of Hedeby has been included in Alfred the Great's translation of Orosius' ''Histories''. Moreover, Wulfstan named Truso as being near ''Estmere'' (which is his re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drużno
Drużno (; , ) is a body of water historically considered a lake in northern Poland on the east side of the Vistula delta, near the city of Elbląg. As it is currently not deep enough to qualify as a lake hydrologically and receives some periodic inflow of sea water from the Vistula Lagoon along the Elbląg River, some suggest that it be termed an estuary reservoir. A village of recent origin also called Drużno is situated near the lake. The German name ''Drausensee'', in earlier records called ''Drusensee'', is connected to the ancient trade city of Truso, which stood within the lands now occupied by Elbląg. The lake is greatly reduced from its original size partly due to large building expansion of housing in the last few decades, but mainly because of the natural death of the lake by sedimentation. The lake is the site of a nature reserve, one of the 13 sites in Poland protected under the Ramsar convention. An old mention of the name is as a place named ''Truso'' in the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elbląg
Elbląg (; ; ) is a city in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, in northern Poland, located in the eastern edge of the Żuławy region with 127,390 inhabitants, as of December 2021. It is the capital of Elbląg County. Elbląg is one of the oldest cities in the province. Its history dates back to 1237, when the Teutonic Order constructed their fortified stronghold on the banks of a nearby river. The castle subsequently served as the official seat of the Teutonic Order Masters. Elbląg became part of the Hanseatic League, which contributed much to the city's wealth. Through the Hanseatic League, the city was linked to other major ports like Gdańsk, Lübeck and Amsterdam. Elbląg joined Poland in 1454 and after the defeat of the Teutonic Knights in the Thirteen Years’ War was recognized as part of Poland in 1466. It then flourished and turned into a significant trading point, but its growth was eventually hindered by the Second Northern War and the Swedish Deluge. The city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
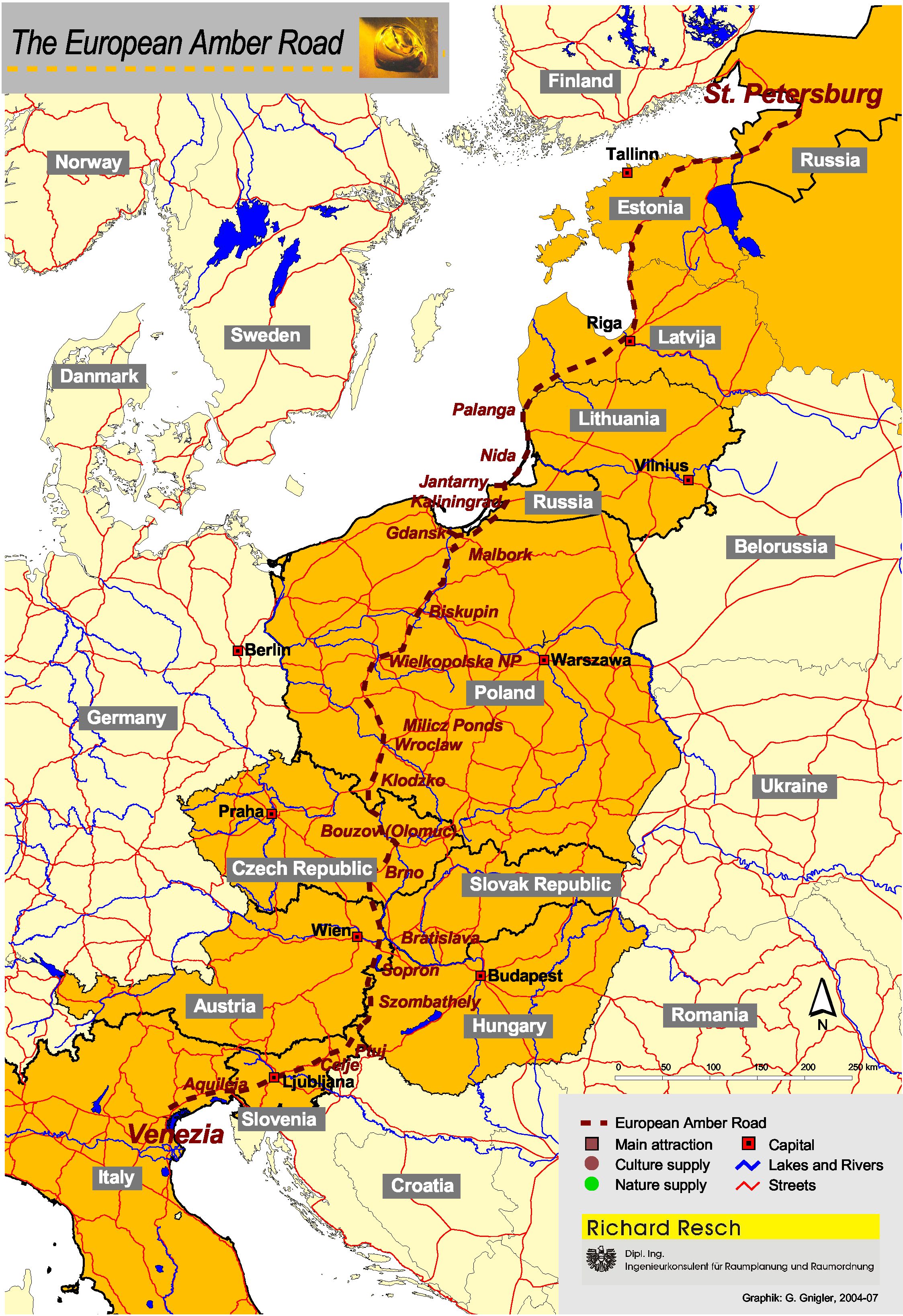
Amber Road
The Amber Road was an ancient trade route for the transfer of amber from coastal areas of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea to the Mediterranean Sea. Prehistoric trade routes between Northern and Southern Europe were defined by the amber trade. As an important commodity, sometimes dubbed "the gold of the north", amber was transported from the North Sea and Baltic Sea coasts overland by way of the Vistula and Dnieper rivers to Italy, Greece, the Black Sea, Syria and Egypt over a period of thousands of years. Antiquity The oldest trade in amber started from Sicily. The Sicilian amber trade was directed to Greece, North Africa and Spain. Sicilian amber was also discovered in Mycenae by the archaeologist Heinrich Schliemann, and it appeared in sites in southern Spain and Portugal. Its distribution is similar to that of ivory, so it is possible that amber from Sicily reached the Iberian Peninsula through contacts with North Africa. After a decline in the consumption and trade of amb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viking Age
The Viking Age (about ) was the period during the Middle Ages when Norsemen known as Vikings undertook large-scale raiding, colonising, conquest, and trading throughout Europe and reached North America. The Viking Age applies not only to their homeland of Scandinavia but also to any place significantly settled by North Germanic peoples, Scandinavians during the period. Although few of the Scandinavians of the Viking Age were Vikings in the sense of being engaged in piracy, they are often referred to as ''Vikings'' as well as ''Norsemen''. Voyaging by sea from their homelands in Denmark, Norway, and Sweden, the Norse people settled in the Viking activity in the British Isles, British Isles, History of Ireland (800–1169), Ireland, the Faroe Islands, Settlement of Iceland, Iceland, Norse settlements in Greenland, Greenland, History of Normandy, Normandy, and the Baltic Sea, Baltic coast and along the Trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks, Dnieper and Volga trade rout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wulfstan Of Hedeby
Wulfstan of Hedeby was a late ninth-century traveller and trader. His travel accounts, as well as those of another trader, Ohthere of Hålogaland, were included in the ''Old English Orosius''. It is unclear if Wulfstan was England, English or indeed if he was from Hedeby, in what is now northern Germany near the Schleswig, Schleswig-Holstein, city of Schleswig but in the 9th century was Danish. According to this account, Wulfstan undertook a journey by sea from Hedeby to the Old Prussians, Prussian trading centre of Truso around the year 880. He names the lands the coasts he passes. This may be the earliest recorded use of the word "Denmark" (''Danemearcan''). The text of Wulfstan is also one of the earliest attestments of unique traditions and customs of Western Balts – Old Prussians, Prussians, called Aesti, and their land called Witland in his text. The purpose of this travel remains unclear; one hypothesis is that King Alfred was interested in having allies against Viking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiskiauten
Kaup is a hill on the bank of the Curonian Lagoon, immediately north of the village of Mokhovoye, Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia. It is a large early medieval burial site with Norse grave goods. Kaup has been viewed by historians as an important early medieval emporium and a likely starting point of the Amber Road to the south. The original name of this medieval settlement is uncertain. It is also the birthplace of Baltic chieftain Caupo, who descended from Swedish Varangian tradesmen. History Archaeological excavations, undertaken in 1899 and 1932, when the area was a part of East Prussia, and in 1979, during Soviet times, suggest that a major center of Old Prussians sprang up there in the early 9th century. Kaup may have been its name, because the place-name is cognate to Old Prussian (and Germanic) terms for "purchase". Marija Gimbutas describes it as the gateway for the traffic leading to the east via the lower Nemunas basin into the lands of the Curonians, Lithuanians, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred The Great
Alfred the Great ( ; – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who both died when Alfred was young. Three of Alfred's brothers, Æthelbald, King of Wessex, Æthelbald, Æthelberht, King of Wessex, Æthelberht and Æthelred I of Wessex, Æthelred, reigned in turn before him. Under Alfred's rule, considerable administrative and military reforms were introduced, prompting lasting change in England. After ascending the throne, Alfred spent several years fighting Viking invasions. He won a decisive victory in the Battle of Edington in 878 and made an agreement with the Vikings, dividing England between Anglo-Saxon territory and the Viking-ruled Danelaw, composed of Scandinavian York, the north-east Midlands and East Anglia. Alfred also oversaw the conversion of Viking leader Guthrum to Christianity. He defended his kingdom again ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the world's largest brackish water basin. The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 10°E to 30°E longitude. It is a Continental shelf#Shelf seas, shelf sea and marginal sea of the Atlantic with limited water exchange between the two, making it an inland sea. The Baltic Sea drains through the Danish straits into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, Great Belt and Little Belt. It includes the Gulf of Bothnia (divided into the Bothnian Bay and the Bothnian Sea), the Gulf of Finland, the Gulf of Riga and the Bay of Gdańsk. The "Baltic Proper" is bordered on its northern edge, at latitude 60°N, by Åland and the Gulf of Bothnia, on its northeastern edge by the Gulf of Finland, on its eastern edge by the Gulf of Riga, and in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia. The Alpine arch extends from Nice on the western Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean to Trieste on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Vienna at the beginning of the Pannonian Basin. The mountains were formed over tens of millions of years as the African and Eurasian tectonic plates collided. Extreme shortening caused by the event resulted in marine sedimentary rocks rising by thrust fault, thrusting and Fold (geology), folding into high mountain peaks such as Mont Blanc and the Matterhorn. Mont Blanc spans the French–Italian border, and at is the highest mountain in the Alps. The Alpine region area contains 82 peaks higher than List of Alpine four-thousanders, . The altitude and size of the range affect the climate in Europe; in the mountain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia (country), Georgia, Romania, Russia, Turkey, and Ukraine. The Black Sea is Inflow (hydrology), supplied by major rivers, principally the Danube, Dnieper and Dniester. Consequently, while six countries have a coastline on the sea, its drainage basin includes parts of 24 countries in Europe. The Black Sea, not including the Sea of Azov, covers , has a maximum depth of , and a volume of . Most of its coasts ascend rapidly. These rises are the Pontic Mountains to the south, bar the southwest-facing peninsulas, the Caucasus Mountains to the east, and the Crimean Mountains to the mid-north. In the west, the coast is generally small floodplains below foothills such as the Strandzha; Cape Emine, a dwindling of the east end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hedeby
Hedeby (, Old Norse: ''Heiðabýr'', German: ''Haithabu'') was an important Danish Viking Age (8th to the 11th centuries) trading settlement near the southern end of the Jutland Peninsula, now in the Schleswig-Flensburg district of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. Around 965, chronicler Ibrahim ibn Yaqub visited Hedeby and described it as "a very large city at the very end of the world's ocean." Due to its unique position between the Frankish Empire and the Danish Kingdom, the settlement developed as a trading centre at the head of a narrow, navigable inlet known as the Schlei, which connects to the Baltic Sea. The location was favorable because there is a short portage of less than 15 km to the Treene River, which flows into the Eider with its North Sea estuary, making it a convenient place where goods and ships could be pulled on a corduroy road overland for an almost uninterrupted seaway between the Baltic and the North Sea and avoid a dangerous and time-consuming ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vineta
Vineta (sometimes ''Wineta'') is the name of a legendary city at the southern coast of the Baltic Sea. The legend evolved around traditions about the Medieval emporium called Jumne, Jomsborg, Julin or similar names by the chronicles, and with which Vineta is sometimes identified. Legend There are several Vineta legends. All of them portray the Vinetans as having an excessive, voluptuous or blasphemous way of life and then being punished in a flood that took the city to the bottom of the Baltic. In some variants of the myth, the city or parts thereof reappear on certain days or can be seen from a boat, making the warning conveyed by the myth more tangible for the audience. Primary sources * About 965, Ibrahim ibn Jaqub wrote in Arabic letters about this city. The transcription might be ''Weltaba'', which corresponds to modern Polish "Wełtawa" meaning roughly a place among waves. * 1075/80, Adam of Bremen wrote about an emporium on an island in the Oder estuary, east of his Dioce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |