|
Trichophyton Rubrum
''Trichophyton rubrum'' is a dermatophytic fungus in the phylum Ascomycota. It is an exclusively clonal, anthropophilic saprotroph that colonizes the upper layers of dead skin, and is the most common cause of athlete's foot, fungal infection of nail, jock itch, and ringworm worldwide. ''Trichophyton rubrum'' was first described by in 1845 and is currently considered to be a complex of species that comprises multiple, geographically patterned morphotypes, several of which have been formally described as distinct taxa, including ''T. raubitschekii'', ''T. gourvilii'', ''T. megninii'' and ''T. soudanense''. Growth and morphology Typical isolates of ''T. rubrum'' are white and cottony on the surface. The colony underside is usually red, although some isolates appear more yellowish and others more brownish. ''Trichophyton rubrum'' grows slowly in culture with sparse production of teardrop or peg-shaped microconidia laterally on fertile hyphae. Macroconidia, when present, are smoot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatophyte
Dermatophyte (from Greek '' derma'' "skin" ( GEN ''dermatos'') and ''phyton'' "plant") is a common label for a group of fungus of '' Arthrodermataceae'' that commonly causes skin disease in animals and humans. Traditionally, these anamorphic (asexual or imperfect fungi) mold genera are: '' Microsporum'', '' Epidermophyton'' and ''Trichophyton''. There are about 40 species in these three genera. Species capable of reproducing sexually belong in the teleomorphic genus Arthroderma, of the Ascomycota (see Teleomorph, anamorph and holomorph for more information on this type of fungal life cycle). As of 2019 a total of nine genera are identified and new phylogenetic taxonomy has been proposed. Dermatophytes cause infections of the skin, hair, and nails, obtaining nutrients from keratinized material. The organisms colonize the keratin tissues causing inflammation as the host responds to metabolic byproducts. Colonies of dermatophytes are usually restricted to the nonliving cornifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
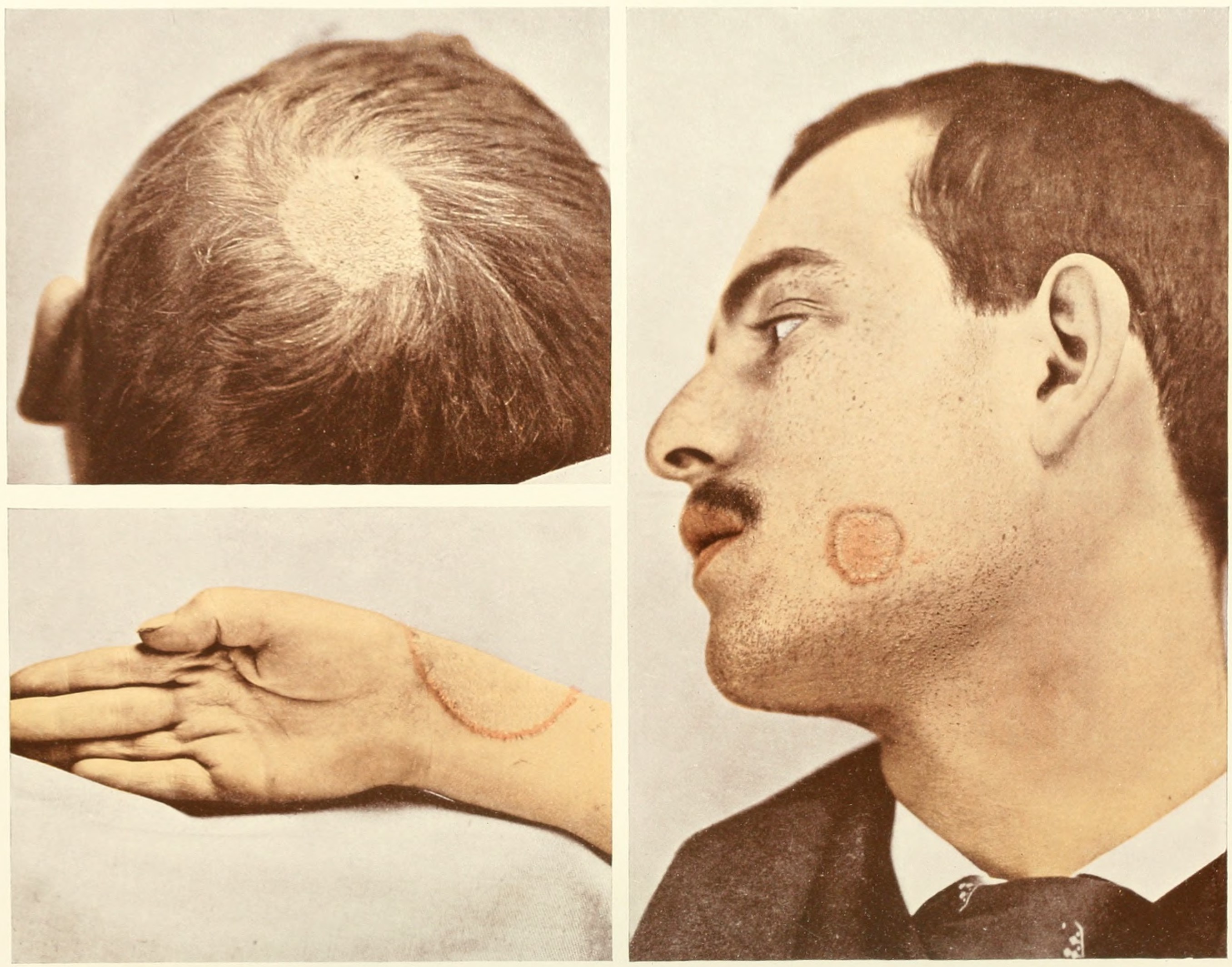
Tinea Unguium
Dermatophytosis, also known as tinea and ringworm, is a fungal infection of the skin (a dermatomycosis), that may affect skin, hair, and nails. Typically it results in a red, itchy, scaly, circular rash. Hair loss may occur in the area affected. Symptoms begin four to fourteen days after exposure. The types of dermatophytosis are typically named for area of the body that they affect. Multiple areas can be affected at a given time. About 40 types of fungus can cause dermatophytosis. They are typically of the '' Trichophyton'', '' Microsporum'', or '' Epidermophyton'' type. Risk factors include using public showers, contact sports such as wrestling, excessive sweating, contact with animals, obesity, and poor immune function. Ringworm can spread from other animals or between people. Diagnosis is often based on the appearance and symptoms. It may be confirmed by either culturing or looking at a skin scraping under a microscope. Prevention is by keeping the skin dry, not w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoophilic
Zoophily, or zoogamy, is a form of pollination whereby pollen is transferred by animals, usually by invertebrates but in some cases vertebrates, particularly birds and bats, but also by other animals. Zoophilous species frequently have evolved mechanisms to make themselves more appealing to the particular type of pollinator, e.g. brightly colored or scented flowers, nectar, and appealing shapes and patterns. These plant-animal relationships are often mutually beneficial because of the food source provided in exchange for pollination. Pollination is defined as the transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma. There are many vectors for pollination, including abiotic (wind and water) and biotic (animal). There are benefits and costs associated with any vector. For instance, using animal pollination is beneficial because the process is more directed and often results in pollination. At the same time it is costly for the plant to produce rewards, such as nectar, to attract anim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunula (anatomy)
The lunula (: lunulae; ) is the crescent-shaped whitish area of the bed of a fingernail or toenail. In humans, it appears by week 14 of gestation, and has a primary structural role in defining the free edge of the distal nail plate (the part of the nail that grows outward). Appearance The lunula is located at the end of the nail that is closest to the skin of the finger, but it still lies under the nail. It is not actually white but only appears so when it is seen through the nail. Outlining the nail matrix, the lunula is a very delicate part of the nail structure. If one damages the lunula, the nail will be permanently deformed. Even when the totality of the nail is removed, the lunula remains in place and is similar in appearance to another smaller fingernail embedded in the nail bed. In most cases, it is half-moon-shaped and has unique histologic features. Examinations concluded that the lunula is an area of loose dermis with lesser developed collagen bundles. It appears w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moccasin Foot
Athlete's foot, known medically as ''tinea pedis'', is a common skin infection of the feet caused by a fungus. Signs and symptoms often include itching, scaling, cracking and redness. In rare cases the skin may blister. Athlete's foot fungus may infect any part of the foot, but most often grows between the toes. The next most common area is the bottom of the foot. The same fungus may also affect the nails or the hands. It is a member of the group of diseases known as ''tinea''. Athlete's foot is caused by a number of different funguses, including species of ''Trichophyton'', '' Epidermophyton'', and ''Microsporum''. The condition is typically acquired by coming into contact with infected skin, or fungus in the environment. Common places where the funguses can survive are around swimming pools and in locker rooms. They may also be spread from other animals. Usually diagnosis is made based on signs and symptoms; however, it can be confirmed either by culture or seeing hyphae u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Id Reaction
ID or its variants may refer to: * Identity document, a document used to verify a person's identity * Identifier, a symbol which uniquely identifies an object or record People * I. D. Ffraid (1814–1875), Welsh poet and Calvinistic Methodist minister * I. D. McMaster (1923–2004), American assistant district attorney * I. D. Serebryakov (1917–1998), Russian lexicographer and translator Places * İd or Narman, a town in Turkey * Idaho, US (postal abbreviation ID) * Indonesia, ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 country code "ID" ** Indonesian language, ISO 639-1 language code "ID" Arts, entertainment, and media Music * The Id (band), an English new wave/synthpop band * New:ID, an upcoming Filipino boy band Albums * ''I.D.'' (album), a 1989 album by The Wailers Band * ''ID'' (Michael Patrick Kelly album), a 2017 studio album by Michael Patrick Kelly * ''Id'' (Siddharta album), 1999 * '' d' (Veil of Maya album), 2010 * ''ID'', an album by Anna Maria Jopek * ''The Id'' (album), a 2001 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cells
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: CD8+ "killer" (cytotoxic) and CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presence of the cell surface proteins CD8 or CD4.) CD8+ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphocytes
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), and innate lymphoid cells (ILCs; "innate T cell-like" cells involved in mucosal immunity and homeostasis), of which natural killer cells are an important subtype (which functions in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity). They are the main type of cell found in lymph, which prompted the name "lymphocyte" (with ''cyte'' meaning cell). Lymphocytes make up between 18% and 42% of circulating white blood cells. Types The three major types of lymphocyte are T cells, B cells and natural killer (NK) cells. They can also be classified as small lymphocytes and large lymphocytes based on their size and appearance. Lymphocytes can be identified by their large nucleus. T cells and B cells T cells (thymus cells) and B cells ( bone marrow- or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cushing Syndrome
Cushing's syndrome is a collection of signs and symptoms due to prolonged exposure to glucocorticoids such as cortisol. Signs and symptoms may include high blood pressure, abdominal obesity but with thin arms and legs, reddish stretch marks, a round red face due to facial plethora, a fat lump between the shoulders, weak muscles, weak bones, acne, and fragile skin that heals poorly. Women may have more hair and irregular menstruation or loss of menses, with the exact mechanisms of why still unknown. Occasionally there may be changes in mood, headaches, and a chronic feeling of tiredness. Cushing's syndrome is caused by either excessive cortisol-like medication, such as prednisone, or a tumor that either produces or results in the production of excessive cortisol by the adrenal glands. Cases due to a pituitary adenoma are known as Cushing's disease, which is the second most common cause of Cushing's syndrome after medication. A number of other tumors, often referred to as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granuloma
A granuloma is an aggregation of macrophages (along with other cells) that forms in response to chronic inflammation. This occurs when the immune system attempts to isolate foreign substances that it is otherwise unable to eliminate. Such substances include infectious organisms including bacteria and fungi, as well as other materials such as foreign objects, keratin, and suture fragments. Definition In pathology, a granuloma is an organized collection of macrophages. In medical practice, doctors occasionally use the term ''granuloma'' in its more literal meaning: "a small nodule". Since a small nodule can represent any tissue from a harmless nevus to a malignant tumor, this use of the term is not very specific. Examples of this use of the term ''granuloma'' are the lesions known as vocal cord granuloma (known as contact granuloma), pyogenic granuloma, and intubation granuloma, all of which are examples of granulation tissue, not granulomas. "Pulmonary hyalinizing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folliculitis
Folliculitis is the infection and inflammation of one or more hair follicles. The condition may occur anywhere on hair-covered skin. The rash may appear as pimples that come to white tips on the face, chest, back, arms, legs, buttocks, or head. Although acne can often involve superficial infection and inflammation of some hair follicles, the condition of those follicles is usually not called folliculitis, as that term is usually reserved for the separate set of disease entities comprising infected and inflamed hair follicles with causes other than acne. Signs and symptoms * Rash (reddened skin area) * Itching skin * Pimples or pustules located around a hair or follicle; may be confused with chicken pox ** May crust over ** Typically occur on neck, armpit, or groin ** May present as genital lesions * Spreading from leg to arm to body through improper treatment with antibiotics File:Sebaceaous Hyperplasia Chronic folliculits Right Mid Chest.jpg, Chronic folliculitis surroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoscytalidium Dimidiatum
''Neoscytalidium dimidiatum'' was first described in 1933 as ''Hendersonula toruloidea'' from diseased orchard trees in Egypt. Decades later, it was determined to be a causative agent of human dermatomycosis-like infections and foot infections predominantly in tropical areas; however the fungus is considered to be widespread. A newer name, ''Scytalidium dimidiatum'', was applied to a synanamorph of ''Nattrassia mangiferae'', otherwise known as ''Neofusicoccum mangiferae''. Substantial confusion has arisen in the literature on this fungus resulting from the use of multiple different names including ''Torula dimidiata'', ''Fusicoccum dimidiatum'', ''Scytalidium dimidiatum'', and ''Hendersonula toruloidea''. Additionally, ''Scytalidium lignicola'' and ''Scytalidium lignicolum'' are often considered earlier names of ''N. dimidiatum''. History and taxonomy In 1933, British mycologist Dr. Rolland Marshall Nattrass described an arthroconidial asexual fungus that he named ''H. toruloidea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |