|
Tremarctinae
The Tremarctinae or short-faced bears is a subfamily of Ursidae that contains one living representative, the spectacled bear (''Tremarctos ornatus'') of South America, and several extinct species from four genera: the Florida spectacled bear (''Tremarctos floridanus''), the North American giant short-faced bears '' Arctodus'' (''A. pristinus'' and ''A. simus''), the South American giant short-faced bear ''Arctotherium'' (including ''A. angustidens'', ''A. vetustum'', ''A. bonariense'', ''A. wingei'', and ''A. tarijense)'' as well as '' Plionarctos'' ''(P. edensis and P. harroldorum),'' which is thought to be ancestral to the other three genera. Of these, the giant short-faced bears ('' Arctodus simus'' and '' Arctotherium angustidens'') may have been the largest ever carnivorans in the Americas. The group is thought to have originated in eastern North America, and then invaded South America as part of the Great American Interchange. Most short-faced bears became extinct at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctotherium
''Arctotherium'' ("bear beast") is an extinct genus of the Pleistocene Tremarctinae, short-faced bears endemic to Central America, Central and South America. ''Arctotherium'' migrated from North America to South America during the Great American Interchange, following the formation of the Isthmus of Panama during the late Pliocene. Evolution Tremarctinae ''Arctotherium'' is part of the Tremarctinae subfamily of bears, otherwise known as the Tremarctinae, short faced bears, which also includes ''Arctodus'' (North American short faced bears) and ''Tremarctos'' (the Tremarctos floridanus, Floridian and modern spectacled bear). Tremarctinae originate with their common ancestor, ''Plionarctos,'' in the Hemphillian, Middle Hemphillian (earliest Late Miocene, ~10 Ma) of North America; ''Plionarctos'' is last recorded in the Blancan, early Blancan (Early Pliocene, ~3.3 Ma). Around the Late Miocene, Miocene-Zanclean, Pliocene boundary (~5 Ma) Tremarctinae, Tremarctines, along with other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctodus
''Arctodus'' is an extinct genus of short-faced bear that inhabited North America during the Pleistocene (~2.6 Year#mya, Mya until 12,800 years ago). There are two recognized species: the lesser short-faced bear (''Arctodus pristinus'') and the giant short-faced bear (''Arctodus simus''). Of these species, ''A. simus'' was larger, is known from more complete remains, and is considered one of the best known members of North America's extinct Ice Age megafauna. ''A. pristinus'' was largely restricted to the Early Pleistocene of the eastern United States, whereas ''A. simus'' had a broader range, with most finds being from the Late Pleistocene of the United States, Mexico and Canada. ''A. simus'' evolved from ''A. pristinus'', but both species likely overlapped in the Middle Pleistocene. Both species are relatively rare in the fossil record. Today considered to be an enormous omnivore, ''Arctodus simus'' is believed to be one of the largest known terrestrial carnivorans that has ever e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectacled Bear
The spectacled bear (''Tremarctos ornatus''), also known as the South American bear, Andean bear, Andean short-faced bear or mountain bear and locally as jukumari ( Aymara and Quechua), ukumari ( Quechua) or ukuku, is a species of bear native to the Andes Mountains in northern and western South America. It is the only living species of bear native to South America, and the last remaining short-faced bear (subfamily Tremarctinae). Unlike other omnivorous bears, the diet of the spectacled bear is mostly herbivorous. The species is classified as Vulnerable by the IUCN because of habitat loss. Taxonomy ''Tremarctos ornatus'' is commonly referred to in English as the "spectacled bear", a reference to the light colouring on its chest, neck and face, which may resemble spectacles in some individuals, or the "Andean bear" for its distribution along the Andes. The root ''trem''- comes from a Greek word meaning "hole"; ''arctos'' is the Greek word for "bear". ''Tremarctos'' is a refere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ursidae
Bears are carnivoran mammals of the family (biology), family Ursidae (). They are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans. Although only eight species of bears are extant, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats throughout most of the Northern Hemisphere and partially in the Southern Hemisphere. Bears are found on the continents of North America, South America, and Eurasia. Common characteristics of modern bears include large bodies with stocky legs, long snouts, small rounded ears, shaggy hair, plantigrade paws with five nonretractile claws, and short tails. While the polar bear is mostly carnivorous, and the giant panda is mostly herbivorous, the remaining six species are omnivorous with varying diets. With the exception of courtship display, courting individuals and mothers with their young, bears are typically solitary animals. They may be diurnality, diurnal or nocturnal and have an excellent sense of smell. Despite their heavy build and awk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great American Interchange
The Great American Biotic Interchange (commonly abbreviated as GABI), also known as the Great American Interchange and the Great American Faunal Interchange, was an important late Cenozoic paleozoogeographic biotic interchange event in which land and freshwater fauna (animals), fauna migrated from North America to South America via Central America and vice versa, as the volcanic Isthmus of Panama rose up from the sea floor, forming a land bridge between the previously separated continents. Although earlier dispersals had occurred, probably over water, the migration accelerated dramatically about 2.7 million years (Ma (unit), Ma) ago during the Piacenzian age. It resulted from the joining of the Neotropical realm, Neotropic (roughly South American) and Nearctic realm, Nearctic (roughly North American) biogeographic realms definitively to form the Americas. The interchange is visible from observation of both biostratigraphy and nature (neontology). Its most dramatic effect is on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tremarctos Floridanus
''Tremarctos floridanus'' is an extinct species of bear in the family Ursidae, subfamily Tremarctinae. ''T. floridanus'' became extinct at the end of the last ice age, 11,000 years ago. Its fossils have been found throughout the Southeastern United States, in northeastern Mexico, and in Belize from the Rancholabrean epoch (250,000–11,000 years ago), and from earlier epochs at some sites in western North America. Names ''Tremarctos floridanus'' is called the Florida spectacled bear, Florida cave bear, or rarely Florida short-faced bear. Description ''T. floridanus'' is presumed to closely resemble its modern relative that shares the same genus, the spectacled bear (''Tremarctos ornatus'') found in the Andes Mountains of South America. Intermediate in size between a modern American black bear and grizzly bear, it was noticeably larger than its South American relation though still much smaller than the fellow Tremarctinae bear ''Arctodus''. ''Arctodus'' was a contemporary of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tremarctos
''Tremarctos'' is a genus of the monophyletic bear subfamily Tremarctinae, endemic to Americas from the Pliocene to recent. The northern species, the Florida short-faced bear, became extinct 11,000 years ago.B. Kurten & E. Anderson (1980): Pleistocene mammals of North America, pp 1-442. Columbia University Press The sole living ''Tremarctos'' species is the South American spectacled bear. ''Tremarctos'' is also the only living genus under the Tremarctinae subfamily, with the other genera, '' Plionarctos, Arctodus,'' and ''Arctotherium'' all being extinct. Species * †''Tremarctos floridanus'' - Florida short-faced bear * '' Tremarctos ornatus'' - spectacled bear Habitat ''Tremarctos floridanus'' bears lived in the southern parts of North America. ''Tremarctos ornatus'' however lives in South America, such as in the Andes Mountains of Peru. They also live in countries like Bolivia and Venezuela. ''Tremarctos orantus'' is the only species of bear to live in South America. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plionarctos
''Plionarctos'' is an extinct genus of short-faced bear endemic to North America from the Miocene to the Pliocene. Taxonomy Described by Childs Frick in 1926, ''Plionarctos'' is the oldest known genus within the subfamily of the short-faced bears (Tremarctinae), and is believed to be ancestral to ''Arctodus'', ''Arctotherium'' and ''Tremarctos''. A new species, ''P. harroldum'', was described in 2001 from the White Bluffs Fauna in Washington from remains previously attributed to '' Ursus cf. abstrusus''. ''P. edensis'' is thought to be ancestral to ''P. harroldorum''. Description ''Plionarctos'' is thought to have weighed around the size of a smaller spectacled bear (60-150kg), and a skull length of 20cm. Postcranial skeletons of ''Plionarctos'' are unknown. Diagnostics Unlike other tremarctine bears, ''Plionarctos'' did not posses a premasseteric fossa. Although tooth sizes are similar, they also be differentiated from ''Tremarctos'' by the slightly shorter M2 molar. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
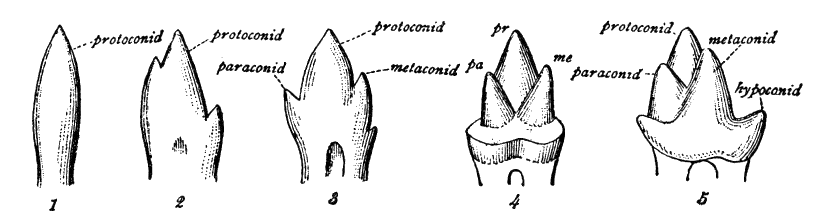
Trigonid
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across the mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies among individuals and populations, and in many cases the tooth is missing. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandibular) molars. They are: maxillary first molar, maxillary second molar, maxillary third molar, man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ursinae
Ursinae is a subfamily of Ursidae (bears) named by Swainson (1835). It was assigned to Ursidae by Bjork (1970), Hunt (1998), and Jin et al. (2007). Classification The genera '' Melursus'' and '' Helarctos'' are sometimes also included in ''Ursus''. The Asiatic black bear and the polar bear used to be placed in their own genera, ''Selenarctos'' and ''Thalarctos''; these are now placed at subgenus rank. * Subfamily Ursinae Fischer de Waldheim, 1817 ** †'' Aurorarctos'' Jiangzuo & Flynn, 2020 *** †''Aurorarctos tirawa'' Jiangzuo & Flynn, 2020 ** '' Helarctos'' Horsfield, 1825 *** ''Helarctos malayanus'' ( Raffles, 1821) – sun bear *** †'' Helarctos sinomalayanus'' (Thenius, 1947) ** '' Melursus'' Meyer, 1793 ***''Melursus ursinus'' ( Shaw, 1791) – sloth bear *** †'' Melursus theobaldi'' ( Lydekker, 1884) ** †'' Protarctos'' Kretzoi, 1945 *** †''Protarctos abstrusus'' (Bjork, 1970) *** †''Protarctos boeckhi'' ( Schlosser, 1899) *** †''Protarctos ruscinens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |