|
Trebava
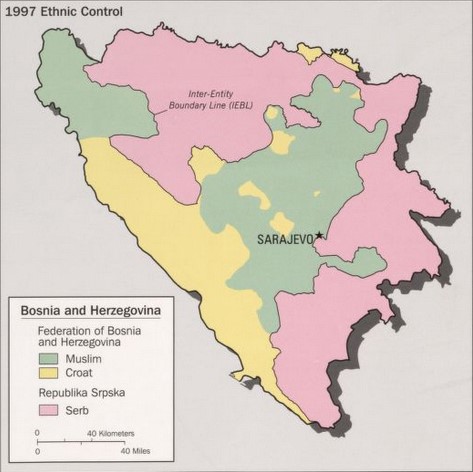
Trebava (Serbian Cyrillic: Требава/Требавац) is a mountain of Republika Srpska, located in northeastern Bosnia-Herzegovinabr>It is situated in an area of irrevocable importance for the Serbs of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbs of the Bosnian region, with historical and religious attachment to the Serbian national continuum, and in particular it was the site of ancient pagan rituals conducted by the polytheistic Old Slavs who lived there before their spiritual transformation into monotheistic Serbian Eastern Orthodoxy. The national conversion of the previously paynim Early South Slavs to Christianity effectively served as the ''bona fide'' genesis of the whole Serbian nation as it is understood in the modern context, and with Trebava's Christian holy sites reflecting this, the area manages to hold significance both for the Orthodox promulgation of the Serbs and their pagan past. Trebava sits next to the border with the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, a form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pogled S Trebave
Pogled may refer to: In Montenegro: * Pogled (mountain peak), a mountain peak in Kosovo, Serbia, and Montenegro In Serbia: * Pogled, Arilje, a settlement in the Municipality of Arilje In Slovenia: * Pogled, Moravče, a settlement in the Municipality of Moravče * Pogled, Apače, a settlement in the Municipality of Apače {{geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bona Fide
In human interactions, good faith () is a sincere intention to be fair, open, and honest, regardless of the outcome of the interaction. Some Latin phrases have lost their literal meaning over centuries, but that is not the case with , which is still widely used and interchangeable with its generally accepted modern-day English translation of ''good faith''. It is an important concept within law and business. The opposed concepts are bad faith, (duplicity) and perfidy (pretense). is a Latin phrase meaning "good faith". Its ablative case is , meaning "in good faith", which is often used in English as an adjective to mean "genuine". While may be translated as "faith", it embraces a range of meanings within a core concept of "reliability", in the sense of a trust between two parties for the potentiality of a relationship. For the ancient Romans, ''bona fides'' was to be assumed by both sides, with implied responsibilities and both legal and religious consequences if broken ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbo-Croatian
Serbo-Croatian ( / ), also known as Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS), is a South Slavic language and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Montenegro. It is a pluricentric language with four mutually intelligible Standard language, standard varieties, namely Serbian language, Serbian, Croatian language, Croatian, Bosnian language, Bosnian, and Montenegrin language, Montenegrin. South Slavic languages historically formed a dialect continuum. The region's turbulent history, particularly due to the expansion of the Ottoman Empire, led to a complex dialectal and religious mosaic. Due to population migrations, Shtokavian became the most widespread supradialect in the western Balkans, encroaching westward into the area previously dominated by Chakavian and Kajkavian. Bosniaks, Croats, and Serbs differ in religion and were historically often part of different cultural spheres, although large portions of these populations lived side by side und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Church Slavonic
Old Church Slavonic or Old Slavonic ( ) is the first Slavic languages, Slavic literary language and the oldest extant written Slavonic language attested in literary sources. It belongs to the South Slavic languages, South Slavic subgroup of the Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family and remains the liturgical language of many Christian Orthodox churches. Historians credit the 9th-century Byzantine Empire, Byzantine missionaries Saints Cyril and Methodius with Standard language, standardizing the language and undertaking the task of translating the Gospels and necessary Eastern Orthodox worship#Liturgical books, liturgical books into it as part of the Christianization of the Slavs. It is thought to have been based primarily on the dialect of the 9th-century Sclaveni, Byzantine Slavs living in the Thessalonica (theme), Province of Thessalonica (in present-day Greece). Old Church Slavonic played an important rol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banja Luka
Banja Luka ( sr-Cyrl, Бања Лука, ) or Banjaluka ( sr-Cyrl, Бањалука, ) is the List of cities in Bosnia and Herzegovina, second largest city in Bosnia and Herzegovina and the largest city in Republika Srpska. Banja Luka is the traditional centre of the densely forested Bosanska Krajina region of northwestern Bosnia (region), Bosnia. , the city proper has a population of 138,963, while its administrative area comprises a total of 185,042 inhabitants. The city is home to the University of Banja Luka and University Clinical Center of the Republika Srpska, as well as numerous entity and state institutions for Republika Srpska and Bosnia and Herzegovina, respectively. The city lies on the Vrbas (river), Vrbas river and is well known in the countries of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, former Yugoslavia for being full of tree-lined avenues, boulevards, gardens, and parks. Banja Luka was designated European city of sport in 2018. Name The name ''Banja Luka' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarajevo
Sarajevo ( ), ; ''see Names of European cities in different languages (Q–T)#S, names in other languages'' is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Bosnia and Herzegovina, largest city of Bosnia and Herzegovina, with a population of 275,524 in its administrative limits. The Sarajevo metropolitan area with its surrounding municipalities has a population of 592,714 people. Located within the greater Sarajevo valley of Bosnia (region), Bosnia, it is surrounded by the Dinaric Alps and situated along the Miljacka River in the heart of the Balkans, a region of Southeastern Europe. Sarajevo is the political, financial, social, and cultural centre of Bosnia and Herzegovina and a prominent centre of culture in the Balkans. It exerts region-wide influence in entertainment, media, fashion, and the arts. Due to its long history of religious and cultural diversity, Sarajevo is sometimes called the "Jerusalem of Europe" or "Jerusalem of the Balkans". It is one of a few major Europea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federation Of Bosnia And Herzegovina
The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (Serbo-Croatian: ''Federacija Bosne i Hercegovine'' / ''Федерација Босне и Херцеговине'') is one of the two Political divisions of Bosnia and Herzegovina, entities composing Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being Republika Srpska. The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina consists of ten autonomous Cantons of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, cantons with their own governments and legislatures. The Federation was created by the 1994 Washington Agreement (1994), Washington Agreement, which ended the Croat–Bosniak War within the Bosnian War, and established a constituent assembly that continued its work until October 1996. The Federation has a Sarajevo, capital, Government of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, government, president, parliament, customs and police departments and two postal systems. It occupies about half of the land of Bosnia and Herzegovina. From 1996 until 2005 it had its own a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sclaveni
The ' (in Latin language, Latin) or ' (Sclaveni#Terminology, various forms in Greek language, Greek) were Early Slavs, early Slavic tribes that raided, invaded and settled in the Balkans in the Early Middle Ages and eventually became one of the progenitors of modern South Slavs. They were mentioned by early Byzantine Empire, Byzantine chroniclers as Barbarians in the Byzantine Empire, barbarians having appeared at the Byzantine borders along with the Antes (people), Antes (East Slavs), another Slavic group. The Sclaveni were differentiated from the Antes and Wends (West Slavs); however, they were described as kin. Eventually, most South Slavic tribes accepted Byzantine Empire, Byzantine or Francia, Frankish suzerainty, and came under their cultural influences and Chalcedonian Christianity. The term was widely used as a general catch-all term until the emergence of separate tribal names by the 10th century. Customs The Sclaveni had similar if not identical customs and culture to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbian Cyrillic Alphabet
The Serbian Cyrillic alphabet (, ), also known as the Serbian script, (, ), is a standardized variation of the Cyrillic script used to write the Serbian language. It originated in medieval Serbia and was significantly reformed in the 19th century by the Serbian philologist and linguist Vuk Karadžić. The Serbian Cyrillic alphabet is one of the two official scripts used to write modern standard Serbian, the other being Gaj's Latin alphabet. Karadžić based his reform on the earlier 18th-century Slavonic-Serbian script. Following the principle of "write as you speak and read as it is written" (''piši kao što govoriš, čitaj kao što je napisano''), he removed obsolete letters, eliminated redundant representations of iotated vowels, and introduced the letter from the Latin script. He also created new letters for sounds unique to Serbian phonology. Around the same time, Ljudevit Gaj led the standardization of the Latin script for use in western South Slavic languages, appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paynim
Paganism (, later 'civilian') is a term first used in the fourth century by Early Christianity, early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Christianity, Judaism, and Samaritanism. In the time of the Roman Empire, individuals fell into the pagan class either because they were increasingly rural and provincial relative to the Christian population, or because they were not ''milites Christi'' (soldiers of Christ).J. J. O'Donnell (1977)''Paganus'': Evolution and Use, ''Classical Folia'', 31: 163–69. Alternative terms used in Christian texts were ''hellene'', ''gentile'', and ''wikt:heathen, heathen''. Ritual sacrifice was an integral part of ancient Classical mythology, Greco-Roman religion and was regarded as an indication of whether a person was pagan or Christian. Paganism has broadly connoted the "religion of the peasantry". During and after the Middle Ages, the term ''paganism'' was applied to any non-Christian reli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |