|
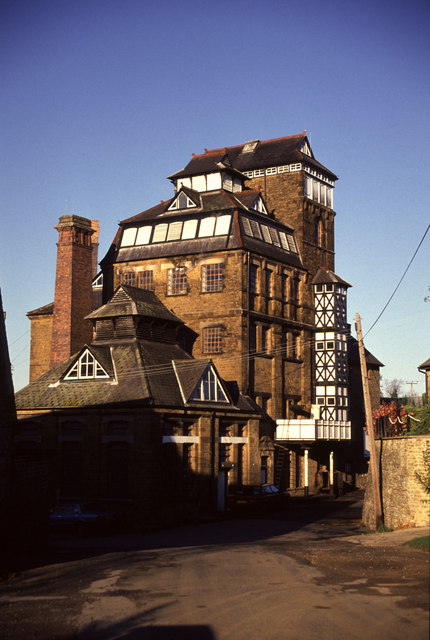
Tower Breweries
A tower brewery is a distinct form of brewery, identified by its external buildings being arranged in the form of a vertical tower. The purpose of a tower brewery is to allow this multi-stage flow process to continue by gravity, rather than lifting or pumping the brew liquor between stages. Once the bulk raw materials, water and barley malt, are first raised to the top of the tower, they can then mostly flow downwards without requiring further pumping. Tower breweries developed in the late Victorian period, the first examples from around 1870, the majority in the 1880s. At this time steam power was available, but not electricity. Powering a single large pumping step was practical, but multiple small pumps around a building would be much less so. The buildings of a tower brewery are arranged as a tower with around six floors. There may be a single tower, but many breweries were less regular, with portions reaching varying heights. Only relatively small areas were needed for the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hook Norton Brewery - Geograph
A hook is a tool consisting of a length of material, typically metal, that contains a portion that is curved/bent back or has a deeply grooved indentation, which serves to grab, latch or in any way attach itself onto another object. The hook's design allows traction forces to be relayed through the curved/indented portion to and from the proximal end of the hook, which is either a straight shaft (known as the hook's ''shank'') or a ring (sometimes called the hook's "''eye''") for attachment to a thread (yarn), thread, rope or chain, providing a reversible attachment between two objects. In many cases, the distal end of the hook is sharply pointed to enable penetration into the target material, providing a firmer anchorage. Some hooks, particularly fish hooks, also have a ''barb'', a backwards-pointed projection near the pointed end that functions as a secondary "mini-hook" to catch and trap surrounding material, ensuring that the hook point cannot be easily pulled back out once e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets, and is contained in large amounts in staple foods such as wheat, potatoes, maize (corn), rice, and cassava (manioc). Pure starch is a white, tasteless and odorless powder that is insoluble in cold water or Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol. It consists of two types of molecules: the linear and helix, helical amylose and the branched amylopectin. Depending on the plant, starch generally contains 20 to 25% amylose and 75 to 80% amylopectin by weight. Glycogen, the energy reserve of animals, is a more highly branched version of amylopectin. In industry, starch is often converted into sugars, for example by malting. These sugars may be fermentation, fermented to produce ethanol in the manufacture of beer, whisky and biofuel. In addition, sugars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
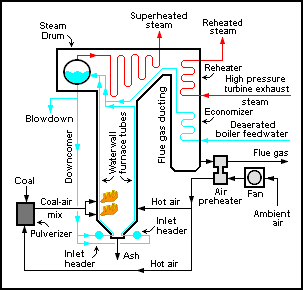
Steam Boiler
file:Dampfkessel für eine Stationärdampfmaschine im Textilmuseum Bocholt.jpg, An industrial boiler, originally used for supplying steam to a stationary steam engine A boiler or steam generator is a device used to create steam by applying heat energy to water. Although the definitions are somewhat flexible, it can be said that older steam generators were commonly termed ''boilers'' and worked at low to medium pressure () but, at pressures above this, it is more usual to speak of a ''steam generator''. A boiler or steam generator is used wherever a source of steam is required. The form and size depends on the application: mobile steam engines such as steam locomotives, portable engines and Traction engine, steam-powered road vehicles typically use a smaller boiler that forms an integral part of the vehicle; stationary steam engines, industrial installations and power stations will usually have a larger separate steam generating facility connected to the point-of-use by piping. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucarne
In general architecture a lucarne is a dormer window. The term is borrowed from , which refers to a dormer window, usually one set into the middle of a roof although it can also apply to a façade lucarne, where the gable of the lucarne is aligned with the face of the wall. This general meaning is also preserved in British use, particularly for small windows into unoccupied attic or spire spaces. Nikolaus Pevsner described it as "a small gabled opening in a roof or a spire". In industrial architecture a lucarne or lucam is a feature of warehouses, mills, factories or the like in which a window, opening or housing high up on an exterior wall supports a hoist above doors on the floors below. The simplest lucarne is no more than the extension of a roof beyond a gable wall, with a ridge timber strong enough to support a hoist. A gin wheel on this beam can provide a simple rope hoist, sufficient to lift a sack of grain. Any greater weights than this are likely to need either a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mash Rake
Mash, MASH, or M*A*S*H may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media * '' M*A*S*H'', an American media franchise ** '' MASH: A Novel About Three Army Doctors'' (Mobile Army Surgical Hospital), 1968, by Richard Hooker ** ''M*A*S*H'' (film), 1970 American black comedy war film ** ''M*A*S*H'' (TV series) (1972–1983), American war comedy drama TV series ** List of ''M*A*S*H'' novels *Mash, the main character of the manga series Mashle Foods and beverages * Mashing and heating grains with water *Mash ingredients, to make alcoholic beverages * Mashed potato (English colloquialism: ''mash'') People * Deborah Mash, American professor of neurology * Lloyd Mash (born 1981), Australian cricketer * Matt Mervis ("Mash"; b. 1998), American baseball player * Mashrafe Mortaza ("Mash"), Bangladeshi cricketer and politician Mathematics and technology * MASH (modulator) (Multi-stAge noise SHaping) * MASH-1 and MASH-2, a hash function * Yahoo! Mash, a social network service Medicine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stationary Steam Engine
Stationary steam engines are fixed steam engines used for pumping or driving mills and factories, and for power generation. They are distinct from locomotive engines used on railways, traction engines for heavy steam haulage on roads, steam cars (and other motor vehicles), agricultural engines used for ploughing or threshing, marine engines, and the steam turbines used as the mechanism of power generation for most nuclear power plants. They were introduced during the 18th century and widely made for the whole of the 19th century and most of the first half of the 20th century, only declining as electricity supply and the internal combustion engine became more widespread. Types of stationary steam engine There are different patterns of stationary steam engines, distinguished by the layout of the cylinders and crankshaft: * Beam engines have a rocking beam providing the connection between the vertical cylinder and crankshaft. * Table engines have the crosshead above the v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Engine, Greenall Whitley Brewery - Geograph
Steam is water vapor, often mixed with air or an aerosol of liquid water droplets. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporization. Saturated or superheated steam is invisible; however, wet steam, a visible mist or aerosol of water droplets, is often referred to as "steam". When liquid water becomes steam, it increases in volume by 1,700 times at standard temperature and pressure; this change in volume can be converted into mechanical work by steam engines such as reciprocating piston type engines and steam turbines, which are a sub-group of steam engines. Piston type steam engines played a central role in the Industrial Revolution and modern steam turbines are used to generate more than 80% of the world's electricity. If liquid water comes in contact with a very hot surface or depressurizes quickly below its vapour pressure, it can create a steam explosion. Types of steam and conversions Steam is trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stillage
A stillage is like a pallet or skid, but with a cage or sides, or some form of support specifically tailored to the material it is intended to carry. Some are designed to be stackable. Stillages are mainly used to transport goods, raise products off the ground, and can help to separate goods in transit without the need to load and unload the product being carried, which saves time and decreases the chance of damage. An example is the use of stillages in glass manufacturing, where they are shaped like an upright "A"; the plate glass leans inward and is strapped to the stillage ready for transport. Stillages are usually manufactured using steel, and are a popular storage and logistic solution in the following fields: engineering, automotive, warehousing, and logistics. For return logistics, demounted stillages, or "post pallets" as they are also often referred to, help to occupy minimal vehicle space, helping to reduce transportation costs. Beverage and alcohol field A stillage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
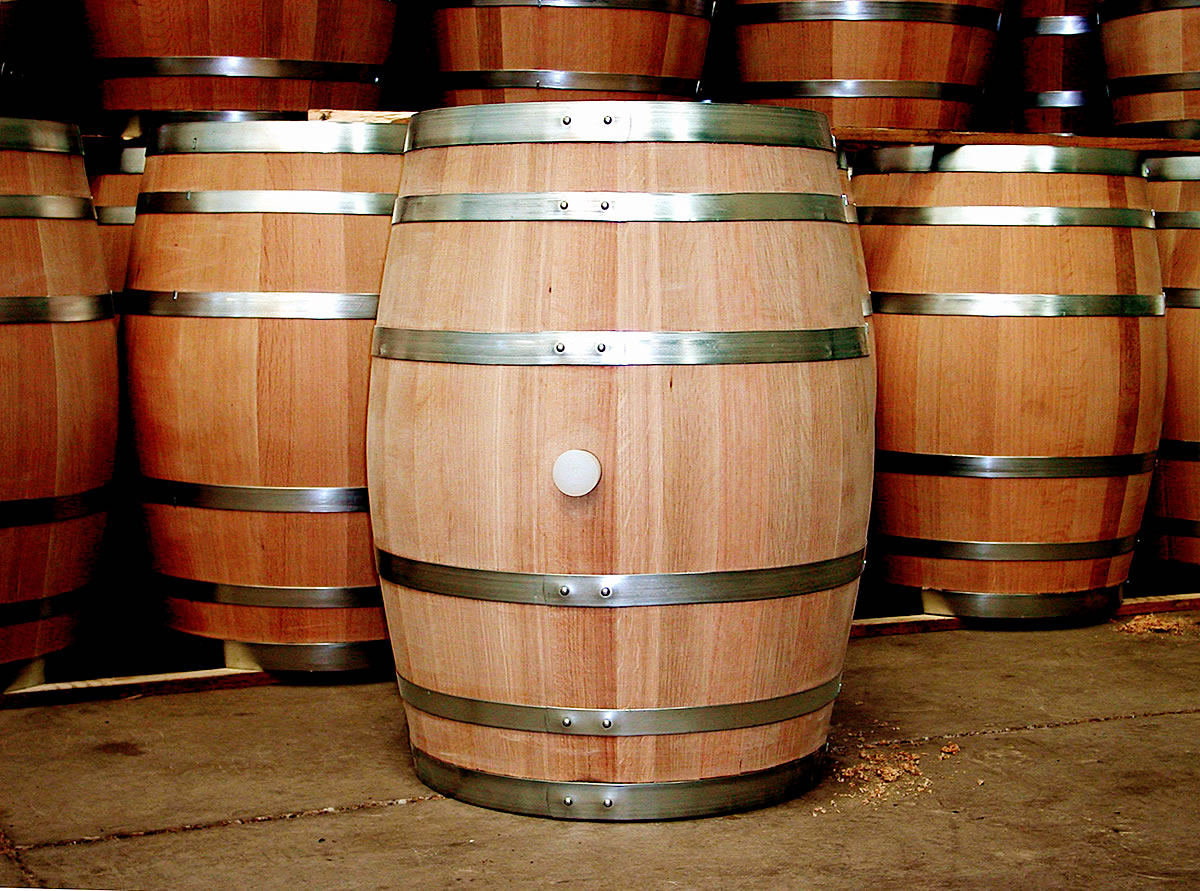
Cask
A barrel or cask is a hollow cylindrical container with a bulging center, longer than it is wide. They are traditionally made of wooden staves and bound by wooden or metal hoops. The word vat is often used for large containers for liquids, usually alcoholic beverages; a small barrel or cask is known as a keg. Barrels have a variety of uses, including storage of liquids such as water, oil, and alcohol. They are also employed to hold maturing beverages such as wine, cognac, armagnac, sherry, port, whiskey, beer, arrack, and sake. Other commodities once stored in wooden casks include gunpowder, meat, fish, paint, honey, nails, and tallow. Modern wooden barrels for wine-making are made of English oak (''Quercus robur''), white oak (''Quercus petraea''), American white oak (''Quercus alba''), more exotic is mizunara oak ('' Quercus crispula''), and recently Oregon oak ('' Quercus garryana'') has been used. Someone who makes traditional wooden barrels is called a coope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brewer's Yeast
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungal microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have been originally isolated from the skin of grapes. It is one of the most intensively studied eukaryotic model organisms in molecular and cell biology, much like ''Escherichia coli'' as the model bacterium. It is the microorganism which causes many common types of fermentation. ''S. cerevisiae'' cells are round to ovoid, 5–10 μm in diameter. It reproduces by budding. Many proteins important in human biology were first discovered by studying their homologs in yeast; these proteins include cell cycle proteins, signaling proteins, and protein-processing enzymes. ''S. cerevisiae'' is currently the only yeast cell known to have Berkeley bodies present, which are involved in particular secretory pathways. Antibodies against ''S. c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hop Back
Brewing is the production of beer by steeping a starch source (commonly cereal grains, the most popular of which is barley) in water and fermenting the resulting sweet liquid with yeast. It may be done in a brewery by a commercial brewer, at home by a homebrewer, or communally. Brewing has taken place since around the 6th millennium BC, and archaeological evidence suggests that emerging civilizations, including ancient Egypt, China, and Mesopotamia, brewed beer. Since the nineteenth century the brewing industry has been part of most western economies. The basic ingredients of beer are water and a fermentable starch source such as malted barley. Most beer is fermented with a brewer's yeast and flavoured with hops. Less widely used starch sources include millet, sorghum and cassava. Secondary sources (adjuncts), such as maize (corn), rice, or sugar, may also be used, sometimes to reduce cost, or to add a feature, such as adding wheat to aid in retaining the foamy head of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hops
Hops are the flowers (also called seed cones or strobiles) of the hop plant ''Humulus lupulus'', a member of the Cannabaceae family of flowering plants. They are used primarily as a bittering, flavouring, and stability agent in beer, to which, in addition to bitterness, they impart floral, fruity, or citrus flavours and aromas. Hops are also used for various purposes in other beverages and herbal medicine. The hops plants have separate female and male plants, and only female plants are used for commercial production. The hop plant is a vigorous climbing herbaceous perennial, usually trained to grow up strings in a field called a hopfield, hop garden (in the South of England), or hop yard (in the West Country and United States) when grown commercially. Many different varieties of hops are grown by farmers around the world, with different types used for particular styles of beer. The first documented use of hops in beer is from the 9th century, though Hildegard of Bingen, 300 y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |