|
Torlakian Dialect
Torlakian, or Torlak, is a group of transitional South Slavic dialects spoken across southeastern Serbia, southern and eastern Kosovo, northwestern and northeastern North Macedonia, and northwestern Bulgaria. Torlakian, together with Bulgarian and Macedonian, falls into the Balkan Slavic linguistic area, which is part of the broader Balkan sprachbund. Torlakian is not standardized, and its subdialects vary significantly in some features. Yugoslav linguists traditionally classified it as an old Shtokavian dialect or as a fourth supradialect of Serbo-Croatian along with Shtokavian, Chakavian, and Kajkavian. Bulgarian scholars classify it as a Western Bulgarian dialect, in which case it is referred to as a Transitional Bulgarian dialect. According to UNESCO's list of endangered languages, Torlakian is a vulnerable distinct language."Torlak" at In Bulgarian common speech, the Torlakian dialects are traditionally referred to as ("U-dialects"), referencing their reflex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg , national_motto = , image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg , national_anthem = () , image_map = , map_caption = Location of Serbia (green) and the claimed but uncontrolled territory of Kosovo (light green) in Europe (dark grey) , image_map2 = , capital = Belgrade , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = Serbian language, Serbian , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2022 , religion = , religion_year = 2022 , demonym = Serbs, Serbian , government_type = Unitary parliamentary republic , leader_title1 = President of Serbia, President , leader_name1 = Aleksandar Vučić , leader_title2 = Prime Minister of Serbia, Prime Minister , leader_name2 = Đuro Macut , leader_title3 = Pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Serbia (region)
Southern Serbia () or sometimes referred to as South Serbia, Southeastern Serbia, Southern Pomoravlje, South of Central Serbia, historically known as New Territories, is a historical and geographical region in Republic of Serbia which most often refers to the territories of Nišava, Toplica, Jablanica, Pčinja and Pirot Districts. This region occupies about 14,000 square kilometers and is home to about 877.000 people. More than a quarter of the population in the region lives in the city of Niš. People from Southern Serbia are commonly known as Southerners. Southern Serbia is not an official subdivision of Serbia, nor are its borders precisely defined. The region is characterized by the South Morava river, which flows almost entirely through Southern Serbia and which has historically connected the peoples who lived in its basin. The region is defined by a common history and culture. Term Today, Southern Serbia is a region in the south of the Republic of Serbia, and over tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motoki Nomachi
Motoki Nomachi (野町 素己; born 1976) is a professor in the Slavic-Eurasian Research Center at Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan. He specializes in Slavic linguistics and general linguistics, and is an expert on Slavic microlanguages. Biography Nomachi was born and raised in Tokyo. He earned his BA in 2000, his MA in Slavic languages and literatures in 2002, and his PhD in 2008, all from the University of Tokyo. In 2002–2003 he continued his education and did research at the University of Belgrade in Serbia. Subsequently, in 2003–2005, he did research and taught Japanese language and culture at the University of Warsaw in Poland. On 1 May 2008 he was employed as associate professor in the Slavic Research Center. Since 2010 Nomachi has acted as General Editor of one of the Center's periodicals, namely, '' Acta Slavica Iaponica''. Edited volumes *(co-edited by Tomasz Kamusella and Catherine Gibson) ''Central Europe through the lens of language and politics: on the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western South Slavic
The South Slavic languages are one of three branches of the Slavic languages. There are approximately 30 million speakers, mainly in the Balkans. These are separated geographically from speakers of the other two Slavic branches (West and East) by a belt of German, Hungarian and Romanian speakers. History The first South Slavic language to be written (also the first attested Slavic language) was the variety of the Eastern South Slavic spoken in Thessaloniki, now called Old Church Slavonic, in the ninth century. It is retained as a liturgical language in Slavic Orthodox churches in the form of various local Church Slavonic traditions. Classification The South Slavic languages constitute a dialect continuum. Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian, and Montenegrin constitute a single dialect within this continuum. *South Slavic ** Eastern South Slavic *** Bulgarian *** Macedonian *** Old Church Slavonic (extinct) ** Transitional South Slavic *** Torlakian ** *** Slovene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International security, security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It has 194 Member states of UNESCO, member states and 12 associate members, as well as partners in the Non-governmental organization, non-governmental, Intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental and private sector. Headquartered in Paris, France, UNESCO has 53 regional field offices and 199 National Commissions for UNESCO, national commissions. UNESCO was founded in 1945 as the successor to the League of Nations' International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation.English summary). UNESCO's founding mission, which was shaped by the events of World War II, is to advance peace, sustainable development and human rights by facilitating collaboratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transitional Bulgarian Dialects
The Transitional Bulgarian dialects are a group of Bulgarian dialects, whose speakers are located west of the yat boundary and are part of the Western Bulgarian dialects. As they have most of the typical characteristics of the North-Western Bulgarian dialects, they are sometimes classified as belonging to this subgroup under the name of Extreme North-Western dialects. On Bulgarian territory, the Transitional dialects occupy a narrow strip of land along the Bulgarian border with Serbia, including the regions of Tran, Breznik, Godech, Chiprovtsi and Belogradchik. They also cross the border to include the dialects or subdialects of the Bulgarian minority in the Western Outlands (the regions of Tsaribrod and Bosilegrad). The Transitional dialects are part of the Torlak dialectal group also spoken in southeastern Serbia and North Macedonia and are part of the gradual transition from Bulgarian to Serbian. The Bulgarian Transitional dialects and the Serbian Prizren-Timok di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Bulgarian Dialects
Bulgarian (; , ) is an Eastern South Slavic language spoken in Southeast Europe, primarily in Bulgaria. It is the language of the Bulgarians. Along with the closely related Macedonian language (collectively forming the East South Slavic languages), it is a member of the Balkan sprachbund and South Slavic dialect continuum of the Indo-European language family. The two languages have several characteristics that set them apart from all other Slavic languages, including the elimination of case declension, the development of a suffixed definite article, and the lack of a verb infinitive. They retain and have further developed the Proto-Slavic verb system (albeit analytically). One such major development is the innovation of evidential verb forms to encode for the source of information: witnessed, inferred, or reported. It is the official language of Bulgaria, and since 2007 has been among the official languages of the European Union. It is also spoken by the Bulgarian hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kajkavian
Kajkavian is a South Slavic languages, South Slavic supradialect or language spoken primarily by Croats in much of Central Croatia and Gorski Kotar. It is part of the South Slavic dialect continuum, being transitional to the supradialects of Čakavian, Štokavian and the Slovene language. There are differing opinions over whether Kajkavian is best considered a dialect of the Serbo-Croatian language or a fully-fledged language of its own, as it is only partially mutually intelligible with either Čakavian or Štokavian and bears more similarities to Slovene language, Slovene; it is transitional to and fully Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible with Prekmurje Slovene and the dialects in Styria (Slovenia), Slovenian Lower Styria's region of Prlekija in terms of phonology and vocabulary. Outside Croatia's northernmost regions, Kajkavian is also spoken in Austrian Burgenland and a number of enclaves in Hungary along the Austrian and Croatian border and in Romania. Name Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chakavian
Chakavian or Čakavian (, , , proper name: or own name: ''čokovski, čakavski, čekavski'') is a South Slavic supradialect or language spoken by Croats along the Adriatic coast, in the historical regions of Dalmatia, Istria, Croatian Littoral and parts of coastal and southern Central Croatia (now collectively referred to as Adriatic Croatia or Littoral Croatia), as well as by the Burgenland Croats as Burgenland Croatian in southeastern Austria, northwestern Hungary and southwestern Slovakia as well as few municipalities in southern Slovenia on the border with Croatia. Chakavian represents the basis for early literary standards in Croatia, and until the modern age was simply known and understood, along with the Kajkavian and Shtokavian idioms in Croatia, as the Croatian language (''hrvatski jezik''). Legal and liturgical to literary texts until the 16th century, including literary work by "the father of Croatian literature" Marko Marulić and the first Croatian dictionar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbo-Croatian
Serbo-Croatian ( / ), also known as Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS), is a South Slavic language and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Montenegro. It is a pluricentric language with four mutually intelligible Standard language, standard varieties, namely Serbian language, Serbian, Croatian language, Croatian, Bosnian language, Bosnian, and Montenegrin language, Montenegrin. South Slavic languages historically formed a dialect continuum. The region's turbulent history, particularly due to the expansion of the Ottoman Empire, led to a complex dialectal and religious mosaic. Due to population migrations, Shtokavian became the most widespread supradialect in the western Balkans, encroaching westward into the area previously dominated by Chakavian and Kajkavian. Bosniaks, Croats, and Serbs differ in religion and were historically often part of different cultural spheres, although large portions of these populations lived side by side und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
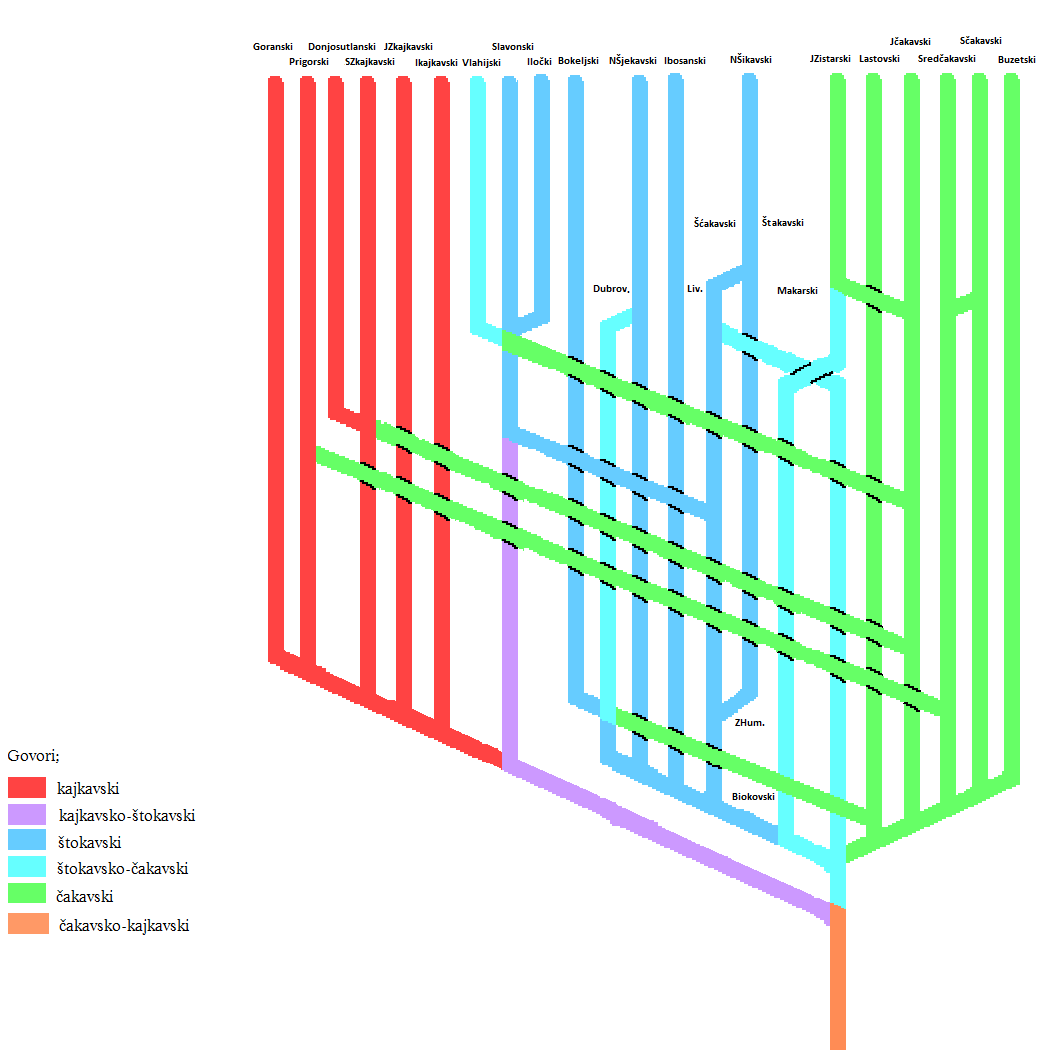
Supradialect
Supradialect (from Latin , "above", and Ancient Greek , "discourse") is a linguistic term designating a dialectological category between the levels of language and dialect. It is used in two distinctive contexts, describing structural or functional relations within a particular language. As a structural category, supradialects designate the first level of dialectological subdivision within a language, as for example in the pluricentric Serbo-Croatian language, which is divided into three basic supradialects (Shtokavian, Kajkavian and Chakavian Chakavian or Čakavian (, , , proper name: or own name: ''čokovski, čakavski, čekavski'') is a South Slavic supradialect or language spoken by Croats along the Adriatic coast, in the historical regions of Dalmatia, Istria, Croatian L ...), with each of them being further divided into several dialects. As a functional category, supradialect designates a predominant dialectal form within a particular language, referring to the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |