|
Tonga Language (Mozambique)
The Tonga language of Mozambique, or ''Gitonga'' (spelled ''Guitonga'' in Portuguese) is a Bantu language The Bantu languages (English: , Proto-Bantu language, Proto-Bantu: *bantʊ̀), or Ntu languages are a language family of about 600 languages of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern, East Africa, Eastern and Southeast Africa, South ... spoken along the southern coast of the country. Often thought to be closest to Chopi to its south, the two languages have only a 44% lexical similarity. References External links''Christian hymns, together with some of the Psalms of David in the language of the Ba Tonga, as spoken in the district of Inhambane, east Africa'' (1901) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mozambique
Mozambique, officially the Republic of Mozambique, is a country located in Southeast Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi and Zambia to the northwest, Zimbabwe to the west, and Eswatini and South Africa to the south and southwest. The sovereign state is separated from the Comoros, Mayotte, and Madagascar by the Mozambique Channel to the east. The capital and largest city is Maputo. Between the 7th and 11th centuries, a series of Swahili port towns developed on that area, which contributed to the development of a distinct Swahili culture and dialect. In the late medieval period, these towns were frequented by traders from Somalia, Ethiopia, Egypt, Arabia, Persia, and India. The voyage of Vasco da Gama in 1498 marked the arrival of the Portuguese Empire, Portuguese, who began a gradual process of colonisation and settlement in 1505. After over four centuries of Portuguese Mozambique, Portuguese rule, Mozambique Mozambican War of Indepen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic–Congo Languages
The Atlantic–Congo languages make up the largest demonstrated family of languages in Africa. They have characteristic noun class systems and form the core of the Niger–Congo family hypothesis. They comprise all of Niger–Congo apart from Mande, Dogon, Ijoid, Siamou, Kru, the Katla and Rashad languages (previously classified as Kordofanian), and perhaps some or all of the Ubangian languages. Hans Gunther Mukanovsky's "Western Nigritic" corresponded roughly to modern Atlantic–Congo. In the infobox, the languages which appear to be the most divergent are placed at the top. The Atlantic branch is defined in the narrow sense (as Senegambian), while the former Atlantic branches Mel and the isolates Sua, Gola and Limba are split out as primary branches; they are mentioned next to each other because there is no published evidence to move them; Volta–Congo is intact apart from Senufo and Kru. ''Glottolog'', based primarily on Güldemann (2018), has a more limi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
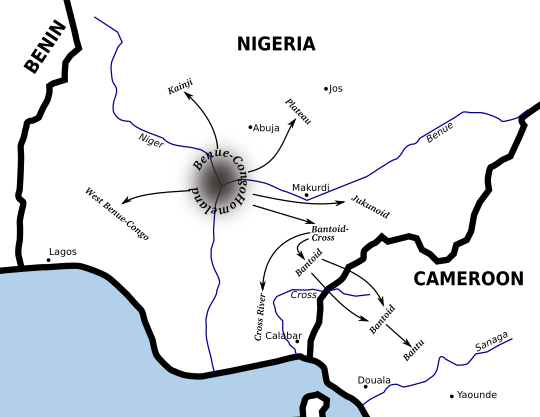
Benue–Congo Languages
Benue–Congo (sometimes called East Benue–Congo) is a major branch of the Volta-Congo languages which covers most of Sub-Saharan Africa. Subdivisions Central Nigerian (or Platoid) contains the Plateau languages, Plateau, Jukunoid languages, Jukunoid and Kainji languages, Kainji families, and Bantoid–Cross combines the Bantoid languages, Bantoid and Cross River languages, Cross River groups. Bantoid is only a collective term for every subfamily of Bantoid–Cross except Cross River, and this is no longer seen as forming a valid branch, however one of the subfamilies, Southern Bantoid, is still considered valid. It is Southern Bantoid which contains the Bantu languages, which are spoken across most of Sub-Saharan Africa. This makes Benue–Congo one of the largest subdivisions of the Niger–Congo language family, both in number of languages, of which ''Ethnologue'' counts 976 (2017), and in speakers, numbering perhaps 350 million. Benue–Congo also includes a few minor Languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bantoid Languages
Bantoid is a major branch of the Benue–Congo language family. It consists of the Northern Bantoid languages and the Southern Bantoid languages, a division which also includes the Bantu languages that constitute the overwhelming majority and after which Bantoid is named. History The term "Bantoid" was first used by Krause in 1895 for languages that showed resemblances in vocabulary to Bantu. Joseph Greenberg, in his 1963 ''The Languages of Africa'', defined Bantoid as the group to which Bantu belongs together with its closest relatives; this is the sense in which the term is still used today. However, according to Roger Blench, the Bantoid languages probably do not actually form a coherent group. Internal classification A proposal that divided Bantoid into Northern Bantoid languages, North Bantoid and Southern Bantoid languages, South Bantoid was introduced by Williamson. In this proposal, the Mambiloid and Dakoid languages (and later Tikar language, Tikar) are grouped together ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bantu Languages
The Bantu languages (English: , Proto-Bantu language, Proto-Bantu: *bantʊ̀), or Ntu languages are a language family of about 600 languages of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern, East Africa, Eastern and Southeast Africa, Southeast Africa. They form the largest branch of the Southern Bantoid languages. The total number of Bantu languages is estimated at between 440 and 680 distinct languages, depending on the definition of Dialect#Dialect or language, "language" versus "dialect"."Guthrie (1967–71) names some 440 Bantu 'varieties', Grimes (2000) has 501 (minus a few 'extinct' or 'almost extinct'), Bastin ''et al.'' (1999) have 542, Maho (this volume) has some 660, and Mann ''et al.'' (1987) have ''c.'' 680." Derek Nurse, 2006, "Bantu Languages", in the ''Encyclopedia of Language and Linguistics'', p. 2:Ethnologue report for Southern Bantoid" lists a total of 535 languages. The count includes 13 Mbam languages, which are not always included under "Narrow Bantu". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Bantu
The Southern Bantu or siNtu languages are a large group of Bantu languages, largely validated in Janson (1991/92).Tore Janson (1991-92) "Southern Bantu and Makua", ''Sprache und Geschichte in Afrika'' (''SUGIA'') Vol. 12/13: 63-106, Rüdiger Köppe Verlag, Cologn/ref> They are nearly synonymous with Guthrie's '' Guthrie classification of Bantu languages, Bantu zone S'', apart from the debated exclusion of Shona and inclusion of Makhuwa. They include all of the major Bantu languages of South Africa, Botswana, Lesotho, Eswatini, and Mozambique, with outliers such as Lozi in Zambia and Namibia, and Ngoni in Zambia, Tanzania and Malawi. Languages Language groups are followed by their code in the Guthrie classification. Makhuwa languages are included in this tree. *Southern Bantu languages ** Makua (P30) *** Makhuwa *** Koti *** Sakati (Nathembo) *** Lomwe *** Chuwabu *** Moniga ** Chopi (S60) *** Chopi *** Guitonga **Nguni languages (S40) ***Zunda ****Xhosa **** Zulu ****Ndebe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bantu Language
The Bantu languages (English: , Proto-Bantu language, Proto-Bantu: *bantʊ̀), or Ntu languages are a language family of about 600 languages of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern, East Africa, Eastern and Southeast Africa, Southeast Africa. They form the largest branch of the Southern Bantoid languages. The total number of Bantu languages is estimated at between 440 and 680 distinct languages, depending on the definition of Dialect#Dialect or language, "language" versus "dialect"."Guthrie (1967–71) names some 440 Bantu 'varieties', Grimes (2000) has 501 (minus a few 'extinct' or 'almost extinct'), Bastin ''et al.'' (1999) have 542, Maho (this volume) has some 660, and Mann ''et al.'' (1987) have ''c.'' 680." Derek Nurse, 2006, "Bantu Languages", in the ''Encyclopedia of Language and Linguistics'', p. 2:Ethnologue report for Southern Bantoid" lists a total of 535 languages. The count includes 13 Mbam languages, which are not always included under "Narrow Bantu". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chopi Language
Chopi, (also spelled ''Copi, Tschopi,'' and ''Txopi)'', is a Bantu language spoken along the southern coast of Mozambique Mozambique, officially the Republic of Mozambique, is a country located in Southeast Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi and Zambia to the northwest, Zimbabwe to the west, and Eswatini and South Afr .... Maho (2009) lists the possibly extinct Lenge dialect as a distinct language. Phonology Consonants *Sounds /t͡sᶲ, t͡sᶲʰ, d͡zᵝ, ⁿd͡zᵝ/, are typically heard as labial-alveolar affricates ͡sᶲ, p͡sᶲʰ, b͡zᵝ, ᵐb͡zᵝ however in recent years there has been a shift in pronunciation having them pronounced purely as alveolar. *Consonants when preceding /j, w/ are always either palatalized ʲor labialized ʷ */ɟ/ may also be heard as an implosive �in free variation. */v/ may also be heard as an affricate ͡vin free variation. Vowels * Nasalized vowel sounds ��may be heard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Bantu Languages
The Southern Bantu or siNtu languages are a large group of Bantu languages, largely validated in Janson (1991/92).Tore Janson (1991-92) "Southern Bantu and Makua", ''Sprache und Geschichte in Afrika'' (''SUGIA'') Vol. 12/13: 63-106, Rüdiger Köppe Verlag, Cologn/ref> They are nearly synonymous with Guthrie's '' Guthrie classification of Bantu languages, Bantu zone S'', apart from the debated exclusion of Shona and inclusion of Makhuwa. They include all of the major Bantu languages of South Africa, Botswana, Lesotho, Eswatini, and Mozambique, with outliers such as Lozi in Zambia and Namibia, and Ngoni in Zambia, Tanzania and Malawi. Languages Language groups are followed by their code in the Guthrie classification. Makhuwa languages are included in this tree. *Southern Bantu languages ** Makua (P30) *** Makhuwa *** Koti *** Sakati (Nathembo) *** Lomwe *** Chuwabu *** Moniga ** Chopi (S60) *** Chopi *** Guitonga **Nguni languages (S40) ***Zunda **** Xhosa **** Zulu ****Ndeb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |