|
Tokhta
Tokhta (also spelled Toqta, Toktu, Tokhtai, Tochtu or Tokhtogha; died ) was Khan of the Golden Horde from 1291 to 1312. He was a son of Mengu-Timur and a great-grandson of Batu Khan. His name "Tokhtokh" means "hold/holding" in the Mongolian language. Early reign under Nogai Nogai Khan orchestrated a palace coup that ended with the ousting of Talabuga and his execution. Tokhta became khan in 1291 and at first he was subordinate to Nogai. However, Tokhta eventually united his supporters against Nogai and he challenged Nogai's authority in 1297, leading to a civil war. In 1299, Nogai finally defeated Nogai and stabilized the Golden Horde. Tokhta wanted to eliminate the Russian princes' semi-independence and the Russian princes grew increasing restive. As a form of submission, military service was used by the khans, but Russian auxiliary troops were only used in rare attacks in Poland and Hungary, as well as in military campaigns in the Caucasus. Russian troops remained effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
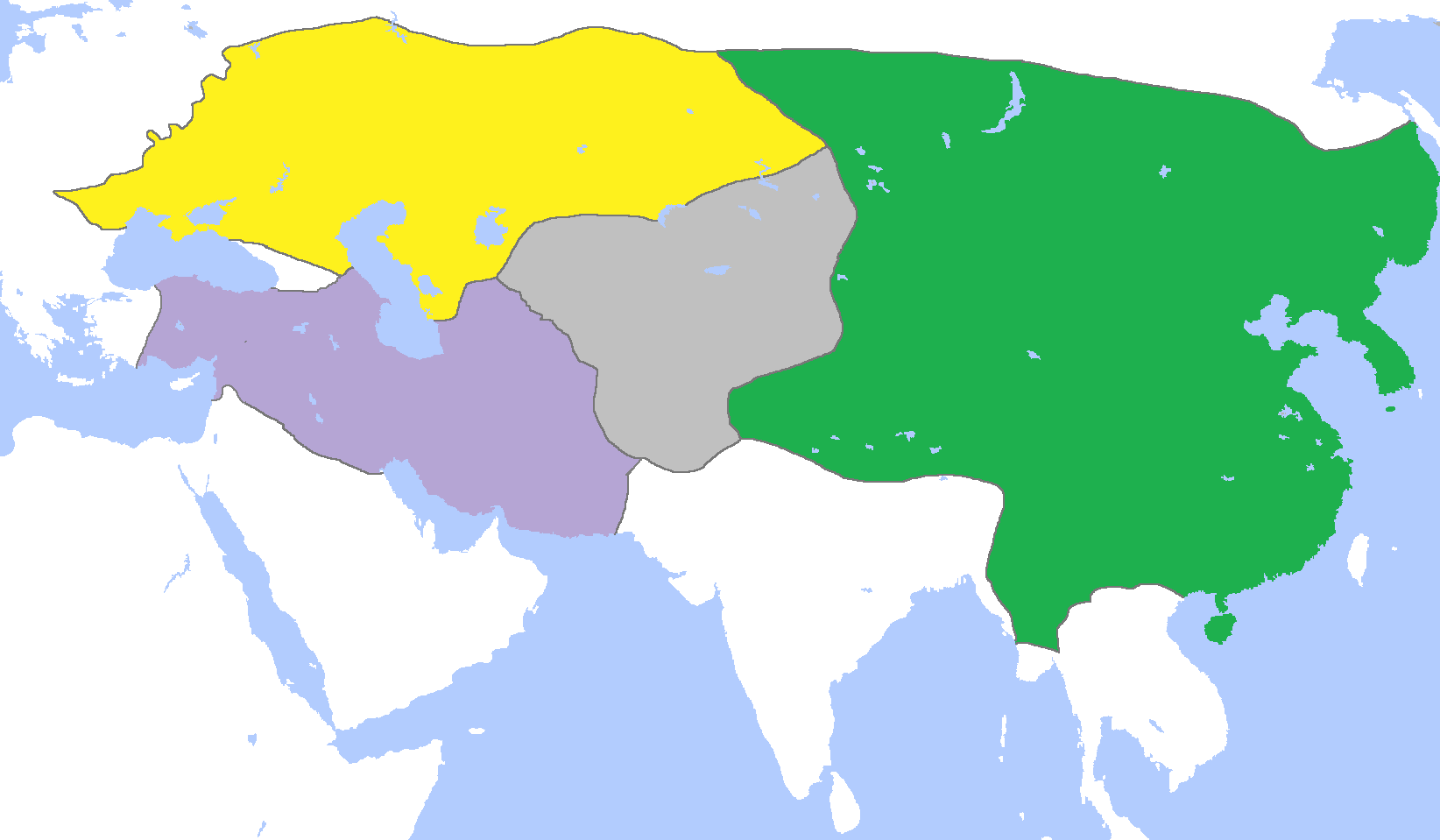
Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as ''Ulug Ulus'' ( in Turkic) was originally a Mongols, Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the division of the Mongol Empire after 1259, it became a functionally separate khanate. It is also known as the Kipchak Khanate or the Ulus of Jochi, and replaced the earlier, less organized Cuman–Kipchak confederation. After the death of Batu Khan (the founder of the Blue Horde) in 1255, his dynasty flourished for a full century, until 1359, though the intrigues of Nogai Khan, Nogai instigated a partial civil war in the late 1290s. The Horde's military power peaked during the reign of Özbeg Khan (1312–1341), who adopted Islam. The territory of the Golden Horde at its peak extended from Siberia and Central Asia to parts of Eastern Europe from the Ural Mountains, Urals to the Danube in the west, and from the Black Sea to the Caspian Sea in the south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
List Of Khans Of The Golden Horde
This is a complete list of khans of the Orda (organization), Ulus of Jochi, better known by its later Russian designation as the Golden Horde, in its right (west) wing and left (east) wing divisions known problematically as the Blue Horde and White Horde, and of its main successor state during a period of disintegration, known as the Great Horde. Khans of the Blue Horde are listed as the principal rulers of the Golden Horde, although many late rulers of the Golden Horde originated from the subordinate White Horde. Following the general convention, the list encompasses the period from the death of Genghis Khan in 1227 to the sack of Sarai (city), Sarai by the Crimean Khanate in 1502. The chronological and genealogical information is often incomplete and contradictory; annotation can be found in the secondary lists in the second part of the article, and in the individual articles on specific monarchs. Secondary list with short biographies The following is a detailed annotated list ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nogai Khan
Nogai, or Noğay ( Kypchak and Turki: نوغای; also spelled Nogay, Nogaj, Nohai, Nokhai, Noqai, Ngoche, Noche, Kara Nokhai, and Isa Nogai; died 1299/1300) was a general and kingmaker of the Golden Horde. His great grandfather was Jochi, son of Genghis Khan. Though he never formally ruled the Golden Horde himself, he was effectively the co-ruler of the state alongside whatever khan was in power at the time and had unrestricted control over the portions west of the Dnieper. At his height, Nogai was one of the most powerful men in Europe and widely thought of as the Horde's true head. The Russian chroniclers gave him the title of tsar, and the Franciscan missionaries in the Crimea spoke of him as a co-emperor. Nogai was also a notable convert to Islam. Name French historian Paul Pelliot wrote that Nokhai meant "dog". Although in the Mongolian language, "nokhoi" (in Mongolian script: , ''nokhai'') literally means a "dog", it does not necessarily mean a particularly negative and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Khongirad
The Khongirad (; ; ; ) was one of the major divisions of the Mongol tribes. Their homeland was located in the vicinity of Hulun Lake, Lake Hulun in Inner Mongolia and Khalkha River in Mongolia,M. Sanjdorj, History of the Mongolian People's Republic, Volume I, 1966 where they maintained close ties with the ruling dynasties of northern China. Because the various Hongirad clans never united under a single leader, the tribe never rose to great military glory. Their greatest fame comes from being the primary consort clan of the ruling house of Genghis Khan's Mongol Empire. Genghis Khan's mother (Hoelun), great grandmother, and first wife were all Khongirads, as were many subsequent Mongol Empress and princesses. During the Yuan dynasty they were given the title Lu Wang ("Prince of Lu"; ), and a few Khongirads migrated west into the territory of modern Uzbekistan and Turkistan Region where they became governors of Khwarazm and were known as the Sufi dynasty. After a brief period as in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Talabuga
Talabuga Khan, also known as Tolibuqa (, ; died 1291), was Khan of the Golden Horde from 1287 to 1291. He ruled a large, independent empire and one of the four successor states of the continent-sized Mongol Empire. He was the son of Tartu, great-grandson of Batu Khan, and great-great-great-grandson of Genghis Khan. Military career Early Military Campaigns As a young Mongol prince, Talabuga led men in the Mongol invasion of Lithuania under the overall command of Burundai in 1258-1259, a campaign in which Talabuga distinguished himself. This Mongol invasion of Lithuania is generally regarded by historians as a Mongol victory, with Lithuanian lands described as "devastated" following the incursion. A year later, Talabuga led the second Mongol invasion of Poland alongside Nogai Khan, both again under the overall command of Burundai. Nogai had devised a plan for the second Mongol invasion of Hungary, and in 1285 Talabuga joined him for this raid. As a rule, the Galician a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Onggirat
The Khongirad (; ; ; ) was one of the major divisions of the Mongol tribes. Their homeland was located in the vicinity of Lake Hulun in Inner Mongolia and Khalkha River in Mongolia,M. Sanjdorj, History of the Mongolian People's Republic, Volume I, 1966 where they maintained close ties with the ruling dynasties of northern China. Because the various Hongirad clans never united under a single leader, the tribe never rose to great military glory. Their greatest fame comes from being the primary consort clan of the ruling house of Genghis Khan's Mongol Empire. Genghis Khan's mother ( Hoelun), great grandmother, and first wife were all Khongirads, as were many subsequent Mongol Empress and princesses. During the Yuan dynasty they were given the title Lu Wang ("Prince of Lu"; ), and a few Khongirads migrated west into the territory of modern Uzbekistan and Turkistan Region where they became governors of Khwarazm and were known as the Sufi dynasty. After a brief period as independen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ilkhan
Il Khan (also ''il-khan'', ''ilkhan'', ''elkhan'', etc.), in Turkic languages and Mongolian, is a title of leadership. It combines the title ''khan'' with the prefix ''el/il'', from the word ''ulus'' – 'tribe, clan', 'the people', 'nation', 'homeland', 'state', 'tribal union', etc. Meaning The exact meaning depends on context: *Khan of the nation. The earliest mention of a similar title in this meaning, namely "Illig Qaghan", refers to Bumin Qaghan and dates to 552 CE. (In fact, Nikolai Gumilyov transcribes Bumin's title as "ilkhan".) *More recently, the tribal chief that heads both branches of the Bakhtiari people, under whom several ''khans'' operate (20th century CE). In the context of the Hulaguid dynasty, commonly known as the Ilkhanate, the title ''Ilkhan'' was borne by the descendants of Hulagu and later other Borjigin princes in Persia, starting from c. 1259-1265. Two interpretations have been proposed: *'submissive', 'peaceable', 'obedient', or 'subservient' khan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chingisid
The Chinggisids were the descendants of Genghis Khan, also known as Chinggis Khan, and his first wife Börte. The dynasty, which evolved from Genghis Khan's own Borjigin tribe, ruled the Mongol Empire and its successor states. The "Chinggisid principle"—that only descendants of Genghis Khan and Börte could be legitimate rulers of the Mongol or post-Mongol world—would be an important concept for centuries, until the fall of Khiva and Bukhara, the last states ruled by Chinggisid monarchs, in 1920. The Borjigin lineage, descendants of Kaidu, an early Mongol leader, were initially one of many clans inhabiting the Mongol heartland. Genghis Khan was born , son of a Borjigit warrior named Yesügei, a member of the Qiyat sub-clan; over the next decades, he subjugated or killed all potential rivals, Borjigit or not. By the time that Genghis established the Mongol Empire in 1206, the only remaining Borjigit were the descendants of Yesügei. They formed the ( 'Golden Family')—the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are linked by 438 bridges. The islands are in the shallow Venetian Lagoon, an enclosed bay lying between the mouths of the Po River, Po and the Piave River, Piave rivers (more exactly between the Brenta (river), Brenta and the Sile (river), Sile). As of 2025, 249,466 people resided in greater Venice or the Comune of Venice, of whom about 51,000 live in the historical island city of Venice (''centro storico'') and the rest on the mainland (''terraferma''). Together with the cities of Padua, Italy, Padua and Treviso, Italy, Treviso, Venice is included in the Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area (PATREVE), which is considered a statistical metropolitan area, with a total population of 2.6 million. The name is derived from the ancient Adr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Genoa
Genoa ( ; ; ) is a city in and the capital of the Italian region of Liguria, and the sixth-largest city in Italy. As of 2025, 563,947 people live within the city's administrative limits. While its metropolitan city has 818,651 inhabitants, more than 1.5 million people live in the wider metropolitan area stretching along the Italian Riviera. On the Gulf of Genoa in the Ligurian Sea, Genoa has historically been one of the most important ports on the Mediterranean: it is the busiest city in Italy and in the Mediterranean Sea and twelfth-busiest in the European Union. Genoa was the capital of one of the most powerful maritime republics for over seven centuries, from the 11th century to 1797. Particularly from the 12th century to the 15th century, the city played a leading role in the history of commerce and trade in Europe, becoming one of the largest naval powers of the continent and considered among the wealthiest cities in the world. It was also nicknamed ''la S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Khan (title)
Khan (, , ) is a historic Turkic peoples, Turkic and Proto-Mongols, Mongolic title originating among nomadic tribes in the Eurasian Steppe#Divisions, Central and Eastern Eurasian Steppe to refer to a king. It first appears among the Rouran and then the Göktürks as a variant of khagan (sovereign, emperor) and implied a subordinate ruler. In the Seljuk Empire, Seljük Empire, it was the highest noble title, ranking above malik (king) and emir (prince). In the Mongol Empire it signified the ruler of a Orda (organization), horde (''ulus''), while the ruler of all the Mongols was the khagan or great khan. It is a title commonly used to signify the head of a Pashtun Pashtun tribes, tribe or clan. The title subsequently declined in importance. During the Safavid Iran, Safavid and Qajar Iran, Qajar dynasty it was the title of an army general high noble rank who was ruling a province, and in Mughal Empire, Mughal India it was a high noble rank restricted to courtiers. After the downfal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ghazan
Mahmud Ghazan (5 November 1271 – 11 May 1304) (, Ghazan Khan, sometimes westernized as Casanus was the seventh ruler of the Mongol Empire's Ilkhanate division in modern-day Iran from 1295 to 1304. He was the son of Arghun, grandson of Abaqa Khan and great-grandson of Hulegu Khan, continuing a long line of rulers who were direct descendants of Genghis Khan. Considered the most prominent of the Ilkhans, he is perhaps best known for converting to Islam and meeting Imam Ibn Taymiyya in 1295 when he took the throne, marking a turning point for the dominant religion of the Mongols in West Asia: Iran, Iraq, Anatolia, and the South Caucasus. One of his many principal wives was Kököchin, a Mongol princess (originally betrothed to Ghazan's father Arghun before his death) sent by his great-uncle Kublai Khan. Military conflicts during Ghazan's reign included war with the Mamluk Sultanate for control of Syria and battles with the Turko-Mongol Chagatai Khanate. Ghazan also pursued dipl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |