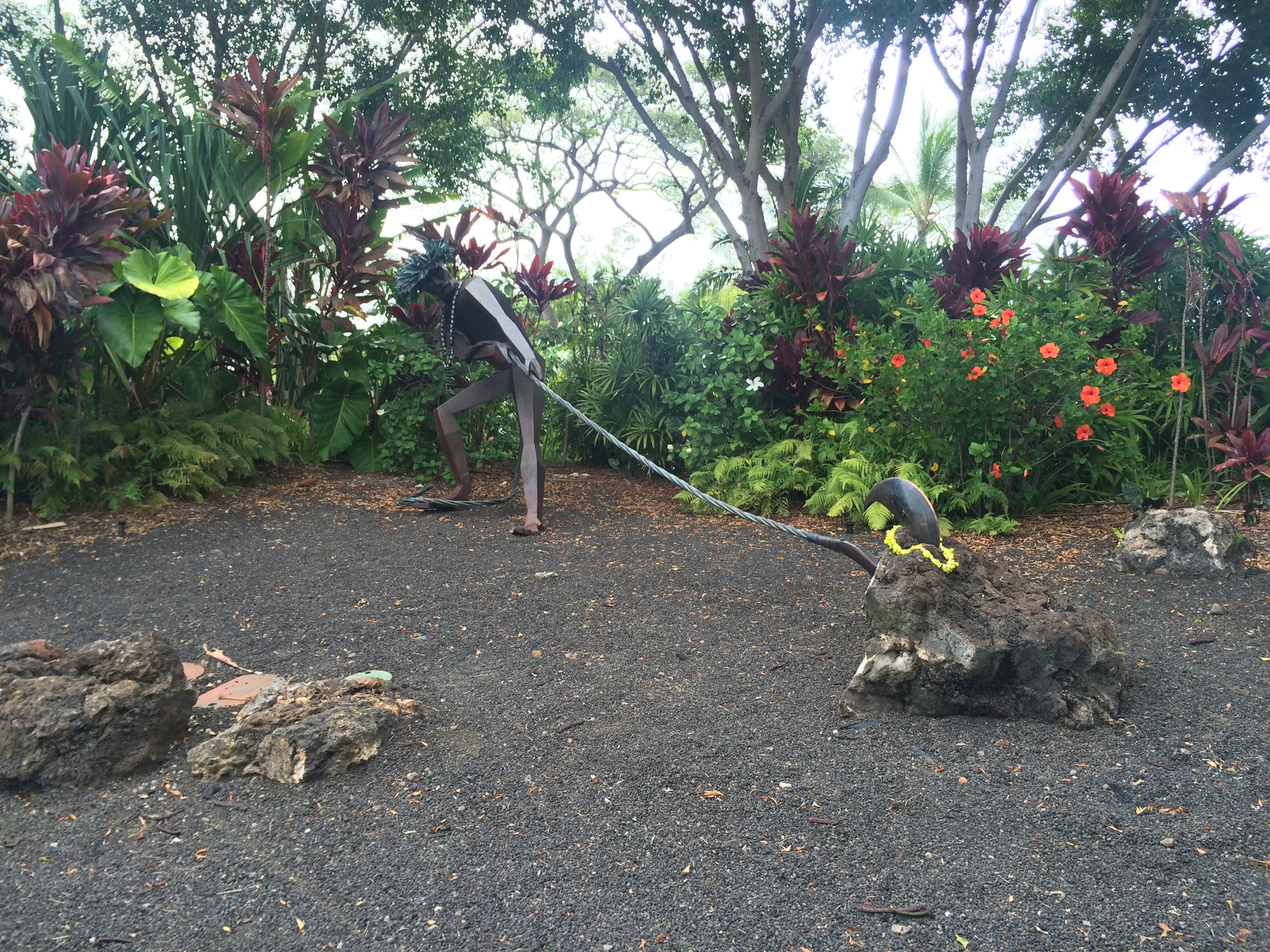|
Tiʻitiʻi
In Samoan legend, the mythological figure Tiitii Atalaga appears in legends very similar to those recounting the tales of the demigod Māui, found in other island cultures. In one such legend, which is almost identical to the New Zealand fire myth of Māui Tikitiki-a-Taranga, he succeeds in bringing fire to the people of Samoa after a battle with the earthquake god, Mafuiʻe. During the battle, Ti'iti'i breaks off one of Mafui'e's arms, forcing him to agree to teach him of how fire had been concealed by the gods in certain trees during the making of the world. The people of Samoa were thankful to Ti'iti'i for breaking off Mafui'e's arm, as they believed that he was less able to create large earthquakes as a result. In Polynesian spellings, 't' and 'k' are linguistically linked, and in speech, the 'k' sound is typically used in place of the 't' sound. Likewise, the apostrophe can be used to replace either sounds. Thus, the Samoan ''Ti'iti'i'' is comparable to the Gilbert Islands' '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māui (mythology)
Māui or Maui is the great culture hero and trickster in Polynesian mythology. Very rarely was Māui actually worshipped, being less of a deity (demigod) and more of a folk hero. His origins vary from culture to culture, but many of his main exploits remain relatively similar.Craighill Handy 1927: 118 Tales of Māui's exploits and adventures are told throughout most of Polynesia; they can be traced back as far west as islands off New Guinea. Some exploits common to most Polynesian traditions are stealing fire for humans from the underworld, fishing up islands with his magical hook, and capturing the Sun to lengthen the days. There is a great deal of variation in the representations of Māui from nation to nation, from being a handsome young man, to being a wise old wandering priest. Although Māui was said to be very rascally or "kolohe", many of his deeds were to better the lives of his fellow people. Māori mythology In Māori mythology, as in other Polynesian traditions, M� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mafuiʻe
In Samoan mythology, Mafuie is the god of earthquakes. He dwells in the volcanic regions below the Earth, and has only one arm. Mafuie was also the keeper of fire. Tiitii, a demigod, won the fire from him in a battle, thus introducing fire to the people of Samoa. Samoan mythology deeply influences cultural practices, with Mafuiʻe representing strength, balance, and ancestral wisdom. His legacy lives on in ceremonies, art, and oral storytelling, helping preserve Samoan heritage across generations. The famous story of Mafuiʻe and Tiʻitiʻi, where fire is given to the people, highlights bravery and continues to shape how Samoans understand natural forces and their cultural identity. See also *Mahuika Mahuika is a Māori fire deity and consort of the god Auahitūroa. Myths In some versions, she is the younger sister of Hine-nui-te-pō, goddess of death. It was from her that Māui (in some versions he is her grandson) obtained the secre ... References Nature gods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māui (Hawaiian Mythology)
In Hawaiian religion, Māui is a culture hero and ancient Alii, chief who appears in several different genealogies. In the Kumulipo, he is the son of Akalana and his wife Hina-a-ke-ahi (Hina (goddess), Hina). This couple has four sons, Māui-mua, Māui-waena, Māui-kiikii, and Māui-a-kalana. Māui-a-kalana's wife is named Hinakealohaila, and his son is named Nanamaoa. Māui is one of the Kupua. His name is the same as that of the Hawaiian island Maui, although native tradition holds that it is not named for him directly, but instead named after the son of Hawaiiloa, Hawaii's discoverer (who was named after Māui himself). Legendary exploits Hauling up the islands of Hawaii The great fish-hook of Māui is called ''Manaiakalani'', and it is baited with the wing of Hina's pet bird, the ''alae''. Māui is said to have created Hawaii's islands by tricking his brothers. He convinced them to take him out fishing, but caught his hook on the ocean floor. He told his brothers that he h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa and known until 1997 as Western Samoa, is an island country in Polynesia, part of Oceania, in the South Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main islands (Savai'i and Upolu), two smaller, inhabited islands (Manono Island, Manono and Apolima), and several smaller, uninhabited islands, including the Aleipata Islands (Nuʻutele, Nuʻulua, Fanuatapu and Namua). Samoa is located west of American Samoa, northeast of Tonga, northeast of Fiji, east of Wallis and Futuna, southeast of Tuvalu, south of Tokelau, southwest of Hawaii, and northwest of Niue. The capital and largest city is Apia. The Lapita culture, Lapita people discovered and settled the Samoan Islands around 3,500 years ago. They developed a Samoan language and Culture of Samoa, Samoan cultural identity. Samoa is a Unitary state, unitary Parliamentary system, parliamentary democracy with 11 Districts of Samoa, administrative divisions. It is a sovereign state and a membe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demigod
A demigod is a part-human and part-divine offspring of a deity and a human, or a human or non-human creature that is accorded divine status after death, or someone who has attained the "divine spark" (divine illumination). An immortality, immortal demigod often has tutelary status and a religious cult following, while a death, mortal demigod is one who has fallen or died, but is popular as a legendary hero in various polytheistic religions. Figuratively, it is used to describe a person whose talents or abilities are so superlative that they appear to approach being divine. Etymology The English language, English term "wiktionary:demi-, demi-god" is a calque of the Latin language, Latin word , "half-god". The Roman poet Ovid probably Derivation (linguistics), coined ''semideus'' to refer to less important gods, such as dryads. Compare the Greek language, Greek ''hemitheos''. The term demigod first appeared in English in the late sixteenth or early seventeenth century, when it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of island countries, sixth-largest island country by area and lies east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The Geography of New Zealand, country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps (), owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. Capital of New Zealand, New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and subsequently developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. In its most general sense, the word ''earthquake'' is used to describe any seismic event that generates seismic waves. Earthquakes can occur naturally or be induced by human activities, such as mining, fracking, and nuclear weapons testing. The initial point of rupture is called the hypocenter or focus, while the ground level directly above it is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilbert Islands
The Gilbert Islands (;Reilly Ridgell. ''Pacific Nations and Territories: The Islands of Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia.'' 3rd. Ed. Honolulu: Bess Press, 1995. p. 95. formerly Kingsmill or King's-Mill IslandsVery often, this name applied only to the southern islands of the archipelago, the northern half being designated as the Scarborough Islands. ''Merriam-Webster's Geographical Dictionary''. Springfield, Massachusetts: Merriam Webster, 1997. p. 594) are a chain of sixteen atolls and coral islands in the Pacific Ocean, about halfway between Papua New Guinea and Hawaii. They constitute the main part of the country of Kiribati (the name of which is a rendering of "Gilberts" in the phonology of the indigenous Gilbertese language, Gilbertese). Geography The atolls and islands of the Gilbert Islands lie in an approximate north-to-south line. The northernmost island in the group, Makin (atoll), Makin, it is approximately from southernmost, Arorae, as the crow flies. Geographi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māui (Māori Mythology)
In Māori mythology, as in other Polynesian traditions, Māui is a culture hero, demigod and a trickster, famous for his exploits and cleverness. He possessed superhuman strength, and was capable of shapeshifting into animals such as birds and worms. He was born premature and cast into the ocean by his mother, where the waves formed him into a living baby. He was discovered by his grandfather and later went to live with his siblings. One day he followed his mother to the underworld where he met his father, Makeatutara, who baptised Māui incorrectly. As a punishment from the gods for this mishap, Māui and all of humanity were doomed to die. Māui is credited with catching a giant fish using a fishhook taken from his grandmother's jaw-bone; the giant fish would become the North Island of New Zealand, known as . In some traditions, his canoe () became the South Island, known as . His last trick, which led to his death, involved the goddess Hine-nui-te-pō. While attempting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samoan Deities
Samoan may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to the Samoan Islands, an archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean ** Something of, from, or related to Samoa, a country encompassing the western part of the Samoan Islands ** Something of, from, or related to American Samoa American Samoa is an Territories of the United States, unincorporated and unorganized territory of the United States located in the Polynesia region of the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean. Centered on , it is southeast of the island count ..., a United States territory in the Samoan Islands * Samoan language, the native language of the Samoan Islands * Samoans, a Polynesian ethnic group of the Samoan Islands {{disambig Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |