|
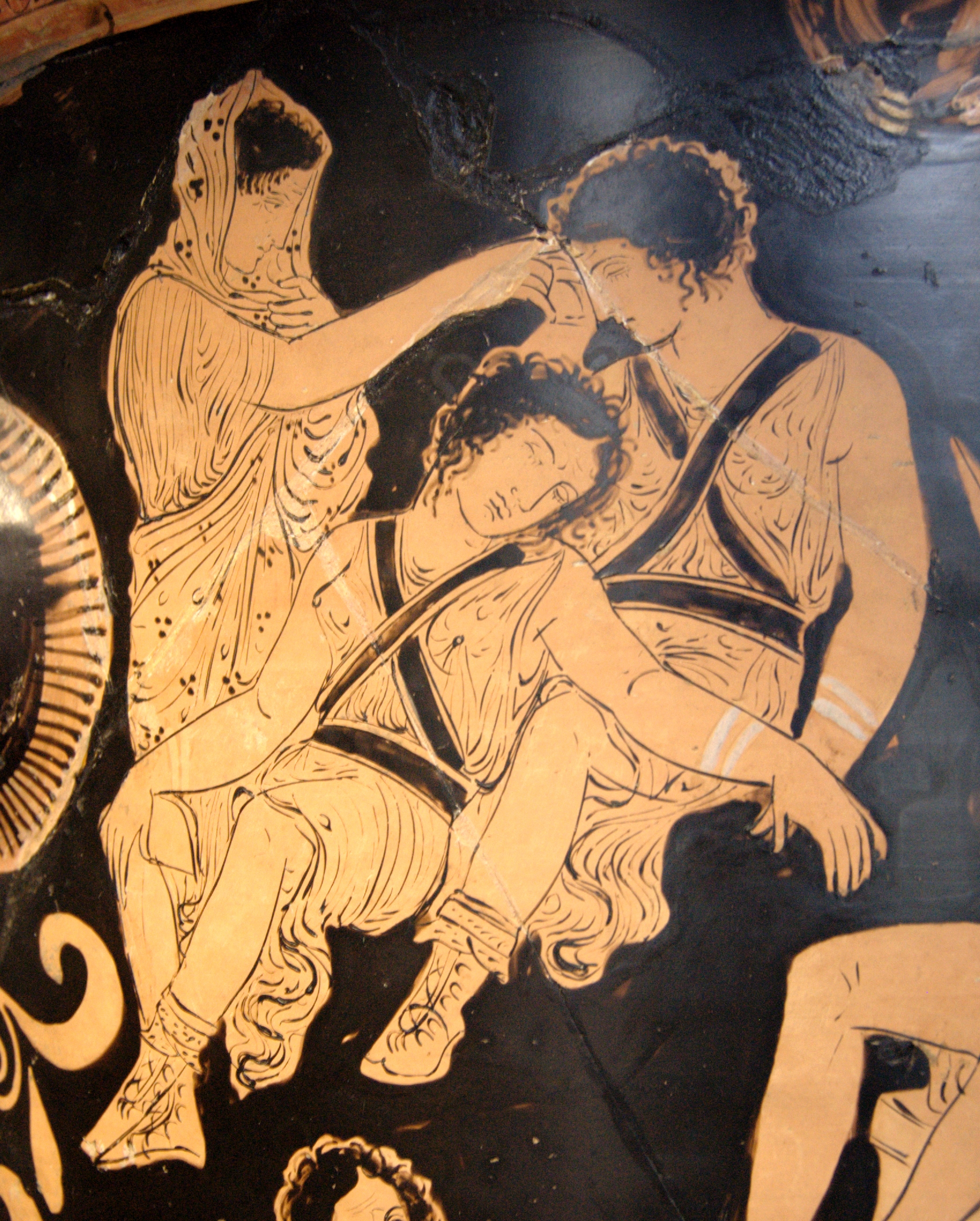
Tisiphone
Tisiphone (, "Avenger of murder"),Tisiphone Encyclopedia Britannica, Retrieved 4 February 2025; from ''tísis'' "payment, punishment" and ''phónos'' "murder" or Tilphousia, was one of the three or Furies in . Her sisters were Alecto and Megaera. They resided in the and asce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erinyes
The Erinyes ( ; , ), also known as the Eumenides (, the "Gracious ones"), are chthonic goddesses of vengeance in ancient Greek religion and mythology. A formulaic oath in the ''Iliad'' invokes them as "the Erinyes, that under earth take vengeance on men, whosoever hath sworn a false oath". Walter Burkert suggests that they are "an embodiment of the act of self-cursing contained in the oath". Their Roman counterparts are the Furies, also known as the Dirae. The Roman writer Maurus Servius Honoratus ( AD) wrote that they are called "Eumenides" in hell, "Furiae" on Earth, and "Dirae" in heaven. Erinyes are akin to some other Greek deities, called Poenai. According to Hesiod's '' Theogony'', when the Titan Cronus castrated his father, Uranus, and threw his genitalia into the sea, the Erinyes (along with the Giants and the Meliae) emerged from the drops of blood which fell on the Earth ( Gaia), while Aphrodite was born from the crests of sea foam. Apollodorus also re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thebaid (Latin Poem)
The ''Thebaid'' (; ) is a Latin epic poem written by the Roman poet Statius. Published in the early 90s AD, it contains 9748 lines arranged in 12 books, and recounts the clash of two brothers, Eteocles and Polynices, over the throne of the Greek city of Thebes, Greece, Thebes. After Polynices is sent into exile, he forges an alliance of Seven against Thebes, seven Greek princes and embarks on a military campaign against his brother. Although its source material derives predominantly from the Ancient Greek literature, Greek literary tradition, the ''Thebaid'' has close ties with other Latin texts such as Virgil's ''Aeneid'' and Senecan tragedy, the tragedies of Seneca the Younger. The poem's central themes include the relationship between politics and the family, civil war, and the amoral acts to which it gives rise. Critics have also noted the poem's innovative depiction of Roman mythology. Following in the footsteps of Ovid, Ovid's ''Metamorphoses'', Statius used an episodic w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megaera
Megaera ( ; ) is one of the Erinyes, Eumenides or "Furies" in Greek mythology. '' Bibliotheca Classica'' states "According to the most received opinions, they were three in number, Tisiphone, "Megaera ... daughter of Nyx and Acheron", and Alecto". In other versions, she and her sisters, as well as the Meliae, were born of the blood of Uranus when Cronus castrated him. In modern French (), Portuguese (), Modern Greek (), Italian (), Polish (), Russian (), Ukrainian () and Czech (), this name denotes a jealous or spiteful woman. She is not to be confused with Megara, the wife of Heracles. Cultural depictions Minor planet 464 Megaira is named in her honour. The 1964 Hammer horror film '' The Gorgon'' revolves around the re-emergence of Megaera in a Central European village circa 1910. Magaera is one of the main characters in the '' Twilight Zone'' episode " Ye Gods", which depicts her as the true love of Cupid. Megaera is a major character in the video game ''Hade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athamas
In Greek mythology, Athamas (; ) was a Boeotian king. Apollodorus1.9.1/ref> Family Athamas was formerly a Thessalian prince and the son of King Aeolus of Aeolia and Enarete, daughter of Deimachus. He was the brother of Salmoneus, Sisyphus, Cretheus, Perieres, Deioneus, Magnes, Calyce, Canace, Alcyone, Pisidice and Perimede. Athamas sired several children by his first wife, the goddess Nephele, and his other wives Ino and Themisto. Nephele first bore to him twins, a son Phrixus and a daughter Helle;Apollodorus1.9.1 Hyginus, ''Fabulae'1/ref> and also a second son, Makistos. He subsequently married Ino, daughter of Cadmus, with whom he had two children: Learches and Melicertes. By the daughter of Hypseus, Themisto, he was the father of Sphincius and Orchomenus Hyginus, ''Fabulae'1/ref> or Schoeneus and Leucon and also, Erythrius and Ptous.Apollodorus, 1.9.2; Tzetzes on Lycophron, 22 Mythology Phrixus and Helle were hated by their stepmother, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ino (Greek Mythology)
In Greek mythology, Ino ( ; ) was a Theban princess who later became a queen of Boeotia. After her death and transfiguration, she was worshiped as a goddess under her epithet Leucothea, the "white goddess." Alcman called her "Queen of the Sea" ( ''thalassomédousa''), which, if not hyperbole, would make her a goddess parallel to Amphitrite. Family Ino was the second daughter of the King Cadmus and Queen Harmonia of Thebes and one of the three sisters of Semele, the mortal woman of the house of Cadmus who gave birth to Dionysus. Her only brother was Polydorus, another ruler of Thebes. Together with her two sisters, Agave and Autonoë, they were the surrogates and divine nurses of Dionysus: : Ino was a primordial Dionysian woman, nurse to the god and a divine maenad. () Ino was the second wife of the Minyan king Athamas, mother of Learchus and Melicertes and stepmother of Phrixus and Helle. Mythology In the back-story to the heroic tale of Jason and the Golde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
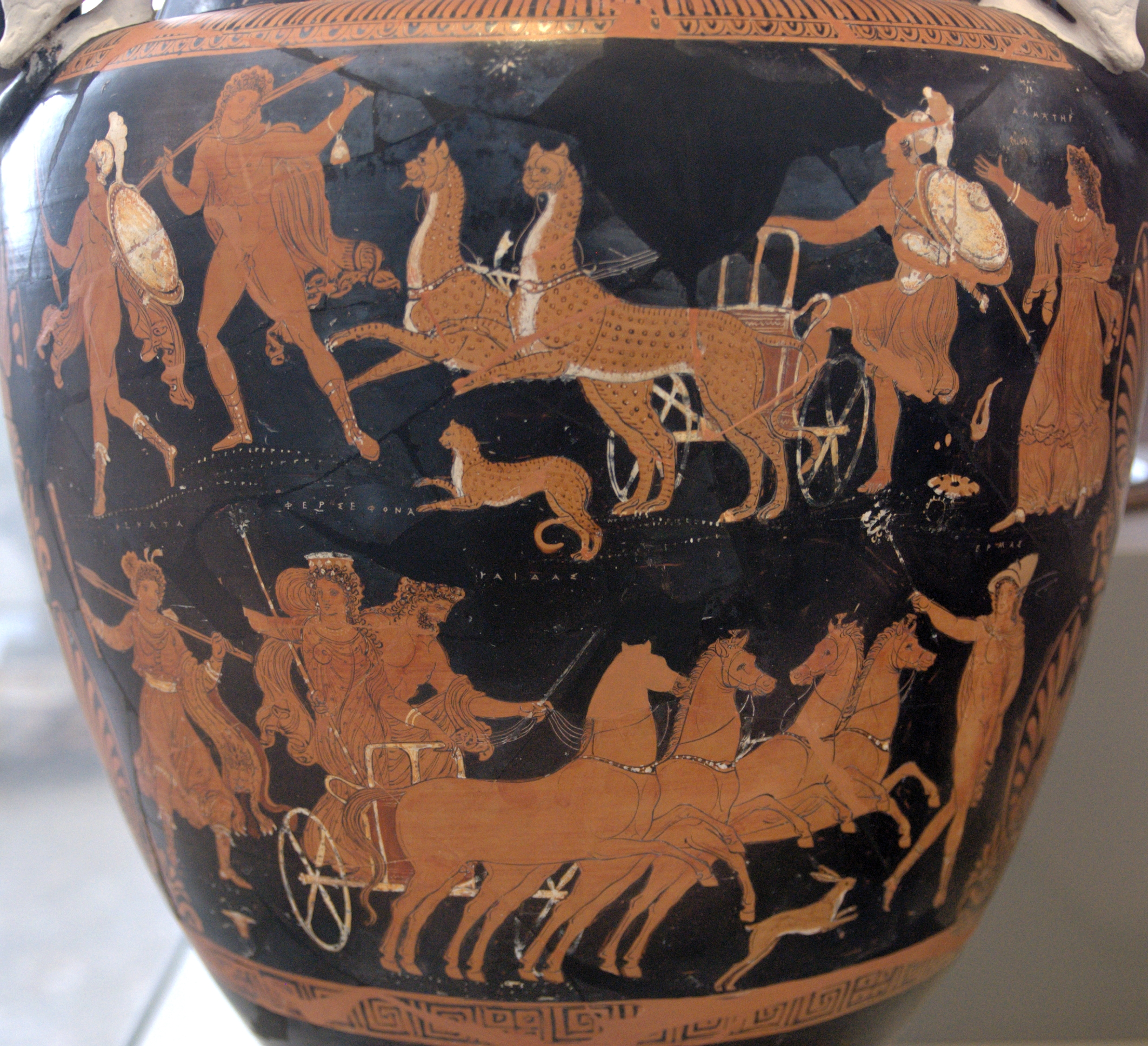
Tartarus
In Greek mythology, Tartarus (; ) is the deep abyss that is used as a dungeon of torment and suffering for the wicked and as the prison for the Titans. Tartarus is the place where, according to Plato's '' Gorgias'' (), souls are judged after death and where the wicked received divine punishment. Tartarus appears in early Greek cosmology, such as in Hesiod's ''Theogony'', where the personified Tartarus is described as one of the earliest beings to exist, alongside Chaos and Gaia (Earth). Greek mythology In Greek mythology, Tartarus is both a deity and a place in the underworld. As a deity In the Greek poet Hesiod's ''Theogony'' ( late 8th century BC), Tartarus was the third of the primordial deities, following after Chaos and Gaia (Earth), and preceding Eros, and was the father, by Gaia, of the monster Typhon. According to Hyginus, Tartarus was the offspring of Aether and Gaia. As a location Hesiod asserts that a bronze anvil falling from heaven woul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Underworld
In Greek mythology, the underworld or Hades () is a distinct realm (one of the three realms that make up the cosmos) where an individual goes after death. The earliest idea of afterlife in Greek myth is that, at the moment of death, an individual's essence (''psyche'') is separated from the corpse and transported to the underworld. In early mythology (e.g., Homer's ''Iliad'' and ''Odyssey'') the dead were indiscriminately grouped together and led a shadowy post-existence; however, in later mythology (e.g., Platonism, Platonic philosophy) elements of post-mortem judgment began to emerge with good and bad people being separated (both spatially and with regards to treatment). The underworld itself—commonly referred to as Hades, after its Hades, patron god, but also known by various metonyms—is described as being located at the periphery of the earth, either associated with the outer limits of the ocean (i.e., ''Oceanus'', again also a god) or beneath the earth. Darkness and a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alecto
Alecto () is one of the Erinyes or Furies in Greek mythology. Family and description According to Hesiod, Alecto was the daughter of Gaea fertilized by the blood spilled from Uranus when Cronus castrated him. She is the sister of Tisiphone and Megaera. These three Furies had snakes for hair and blood dripped from their eyes; plus, they had wings. Alecto's job as a Fury is castigating the moral crimes (such as anger) of humans, especially if they are against others. Alecto's function is similar to Nemesis, with the difference that Nemesis's function is to castigate crimes against the gods, not mortals. Her punishment for mortals was Madness. In mythology In Virgil's ''Aeneid'' (Book VII), Juno commanded the Fury Allecto (spelled with two l's) to prevent the Trojans from having their way with King Latinus by marriage or besieging Italian borders. Allecto's mission is to wreak havoc on the Trojans and cause their downfall through war. To do this, Allecto takes over the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoffrey Chaucer
Geoffrey Chaucer ( ; – 25 October 1400) was an English poet, author, and civil servant best known for ''The Canterbury Tales''. He has been called the "father of English literature", or, alternatively, the "father of English poetry". He was the first writer to be buried in what has since come to be called Poets' Corner, in Westminster Abbey. Chaucer also gained fame as a philosopher and astronomer, composing the scientific ''A Treatise on the Astrolabe'' for his 10-year-old son, Lewis. He maintained a career in public service as a bureaucrat, courtier, diplomat, and member of parliament, having been elected as Knight of the shire, shire knight for Kent. Among Chaucer's many other works are ''The Book of the Duchess'', ''The House of Fame'', ''The Legend of Good Women'', ''Troilus and Criseyde'', and ''Parlement of Foules''. He is seen as crucial in legitimising the literary use of Middle English when the dominant literary languages in England were still Anglo-Norman Fren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocytus
Cocytus or Kokytos (, literally "lamentation") is the river of wailing in the underworld in Greek mythology. Cocytus flows into the river Acheron, on the other side of which lies Hades, the underworld, the mythological abode of the dead. There are five rivers encircling Hades: the Styx, Phlegethon, Lethe, Acheron and Cocytus. In literature The Cocytus river was one of the rivers that surrounded Hades. Cocytus, along with the other rivers related to the underworld, was a common topic for ancient authors. Of the ancient authors, Cocytus was mentioned by Virgil, Homer, Cicero, Aeschylus, Apuleius and Plato, among others. Cocytus also makes an appearance in John Milton's epic poem ''Paradise Lost''. In Book Two, Milton speaks of "Cocytus, named of lamentation loud / Heard on the rueful stream". It is also mentioned in William Shakespeare's ''Titus Andronicus'' and in Rick Riordan's '' The House of Hades''. Cocytus also appears in Friedrich Schiller's poem "''Gruppe aus de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tydeus
Tydeus (; Ancient Greek: Τυδεύς ''Tūdeus'') was an Aetolian hero in Greek mythology, belonging to the generation before the Trojan War. He was one of the Seven against Thebes, and the father of Diomedes, who is frequently known by the patronymic ''Tydides''. Life Tydeus was a son of Oeneus and either Periboea, Oeneus's second wife, or Gorge, Oeneus's daughter. He was the husband of Deipyle, the mother of Diomedes. Tydeus was banished from Calydon by his uncle Agrius because he had killed either his brother or a different uncle or six of his cousins. He travelled to Argos, where he married Deipyle, daughter of king Adrastus. Seven against Thebes Gathering of the Seven While housing Tydeus, King Adrastus of Argos also lodged Polynices, the exiled son of Oedipus who had shared the rule of Thebes with his brother Eteocles before he was expelled by the latter. Late one night, the two young exiles got into a fierce dispute over the guest room in Adrastus's palace. Awake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oedipus
Oedipus (, ; "swollen foot") was a mythical Greek king of Thebes. A tragic hero in Greek mythology, Oedipus fulfilled a prophecy that he would end up killing his father and marrying his mother, thereby bringing disaster to his city and family. The story of Oedipus is the subject of Sophocles' tragedy ''Oedipus Rex'', which is followed in the narrative sequence by '' Oedipus at Colonus'' and then '' Antigone''. Together, these plays make up Sophocles' three Theban plays. Oedipus represents two enduring themes of Greek myth and drama: the flawed nature of humanity and an individual's role in the course of destiny in a harsh universe. In the best-known version of the myth, Oedipus was born to King Laius and Queen Jocasta of Thebes. Laius wished to thwart the prophecy, so he sent a shepherd-servant to leave Oedipus to die on a mountainside. However, the shepherd took pity on the baby and passed him to another shepherd who gave Oedipus to King Polybus and Queen Merope to raise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |