|
Timeline Of The Turkic Peoples (500–1300)
Below is the identified timeline of the History of the Turkic peoples between the 6th and 14th centuries. 6th century 7th century 8th century 9th century 10th century 11th century 12th century 13th century See also *Oghuz Turks *Nomadic empire *Göktürk family tree Notes References *''Encyclopædia Britannica'', Expo 70 ed., vol 13, pp 328–330; vol 20, pp 192–196; vol 22, pp 400–401 * Jean Paul Roux: ''Historie des Turcs''. (Translated by Prof Dr. Aykut Kazancıgil and Lale Arslan Özcan) Kabalcı Yayınevi, İstanbul, 2007 *Arthur Koestler Arthur Koestler (, ; ; ; 5 September 1905 – 1 March 1983) was an Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarian-born author and journalist. Koestler was born in Budapest, and was educated in Austria, apart from his early school years. In 1931, Koestler j ...: ''The Thirteenth Tribe'' (Translated by Belkis Çorakçı) Say Kitap Pazarlama,İstanbul, 1976 *Melek Tekin: ''Türk Tarih Ansiklopedisi'', Milliy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Turkic Peoples
Turkic history is the systematic documentation and study of events involving the Turkic peoples. Origins Turks are an important political identity of Eurasia. They first appeared at Inner Eurasian steppes and migrated to many various regions (such as Central Asia, West Asia, North Asia, and Eastern Europe.) and participated in many local civilizations there. It is not yet known when, where, and how the Turks formed as a population identity. However, it is predicted that Proto-Turkic populations have inhabited regions that they could have the lifestyle of Eurasian equestrian pastoral nomadic culture. ''Türk'' was first used as a political identity in history during the Göktürk Khaganate period. The old Turkic script was invented by Göktürks as well. The ruling Ashina clan origins are disputed. Although there are debates about its inception, the history of the Turks is an important part of world history. The history of all people that emerged in Eurasia and North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justin II
Justin II (; ; died 5 October 578) was Eastern Roman emperor from 565 until 578. He was the nephew of Justinian I and the husband of Sophia, the niece of Justinian's wife Theodora. Justin II inherited a greatly enlarged but overextended empire, with far fewer resources at his disposal compared to Justinian I. He ended the payment of tributes and adopted a hardline stance against the empire's neighbors, which resulted in rekindling of war with the Sassanid Empire, and in a Lombard invasion which cost the Romans much of their territory in Italy. Family He was a son of Vigilantia and Dulcidio (sometimes rendered as Dulcissimus), respectively the sister and brother-in-law of Justinian. His siblings included Marcellus and Praejecta. With Sophia he had a daughter Arabia and possibly a son, Justus, who died young. He also had a niece named Helena. Early life Justin's early years are largely obscure. A thirteenth-century chronicle suggests 511 as Justin's birth date, but its re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
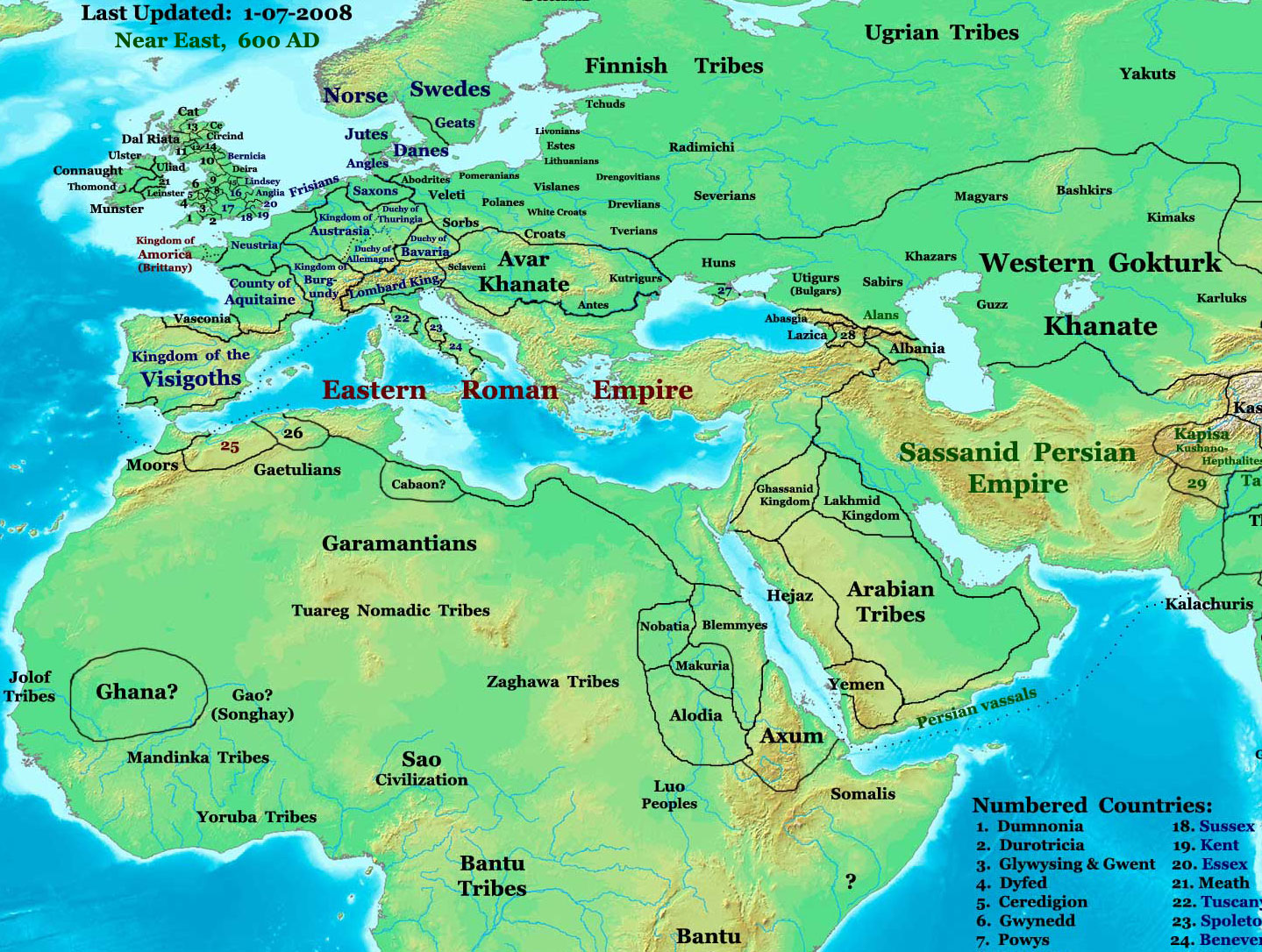
Utigurs
Utigurs were Turkic nomadic equestrians who flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe in the 6th century AD. They possibly were closely related to the Kutrigurs and Bulgars. Etymology The name ''Ut(r)igur'', recorded as , and , is generally considered as a metathesized form suggested by Gyula Németh of Turkic ''*Otur- Oğur'', thus the ''*Uturğur'' mean "Thirty Oğurs (tribes)". Lajos Ligeti proposed ''utur-'' (to resist), while Louis Bazin ''uturkar'' (the victors-conquerors), ''Quturgur'' and ''qudurmaq'' (the enrages). There has been little scholarly support for theories linking the names Kutrigur and Utigur to peoples such as the Guti/Quti and/or Udi/Uti, of Ancient Southwest Asia and the Caucasus respectively, which have been posited by scholars such as Osman Karatay, and Yury Zuev. No evidence has been presented that the Guti moved from their homeland in the Zagros Mountains (modern Iran/Iraq) to the Steppes, and they are believed to have spoken a language differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kutrigurs
The Kutrigurs were a Turkic nomadic equestrian tribe who flourished on the Pontic–Caspian steppe in the 6th century AD. To their east were the similar Utigurs and both possibly were closely related to the Bulgars. They warred with the Byzantine Empire and the Utigurs. Towards the end of the 6th century they were absorbed by the Pannonian Avars under pressure from the Türks. Etymology The name ''Kutrigur'', also recorded as ''Kwrtrgr'', ''Κουτρίγουροι'', ''Κουτούργουροι'', ''Κοτρίγουροι'', ''Κοτρίγοροι'', ''Κουτρίγοροι'', ''Κοτράγηροι'', ''Κουτράγουροι'', ''Κοτριαγήροι'', has been suggested as a metathecized form of Turkic ''*Toqur- Oğur'', with ''*quturoğur'' meaning "nine Oğur (tribes)". David Marshall Lang derived it from Turkic ''kötrügür'' (conspicuous, eminent, renowned). Few scholars support theories deriving the Kutrigurs from the Guti/Quti and the Utigurs from the Ud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgundians
The Burgundians were an early Germanic peoples, Germanic tribe or group of tribes. They appeared east in the middle Rhine region in the third century AD, and were later moved west into the Roman Empire, in Roman Gaul, Gaul. In the first and second centuries AD, they or a people with the same name were mentioned by Roman writers living west of the Vistula river, in the region of Germania, which is now part of Poland. The Burgundians were first mentioned near the Rhine regions together with the Alamanni as early as the 11th panegyric to Emperor Maximian given in Trier in 291 AD, referring to events that must have happened between 248 and 291, and these two peoples apparently remained neighbours for centuries. By 411 AD, Burgundians had established control over Roman cities on the Rhine, between Franks and Alamanni, including Worms, Germany, Worms, Speyer and Strasbourg. In 436 AD, Flavius Aetius, Aëtius defeated the Burgundians on the Rhine with the help of Huns, Hunnish forces, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Peoples
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts of the Roman Empire, but also all Germanic speaking peoples from this era, irrespective of where they lived, most notably the Goths. Another term, ancient Germans, is considered problematic by many scholars since it suggests identity with present-day Germans. Although the first Roman descriptions of ''Germani'' involved tribes west of the Rhine, their homeland of ''Germania'' was portrayed as stretching east of the Rhine, to southern Scandinavia and the Vistula in the east, and to the upper Danube in the south. Other Germanic speakers, such as the Bastarnae and Goths, lived further east in what is now Moldova and Ukraine. The term ''Germani ''is generally only used to refer to historical peoples from the 1st to 4th centuries CE. Different ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto J
Otto is a masculine German given name and a surname. It originates as an Old High German short form (variants ''Audo'', '' Odo'', '' Udo'') of Germanic names beginning in ''aud-'', an element meaning "wealth, prosperity". The name is recorded from the 7th century ( Odo, son of Uro, courtier of Sigebert III). It was the name of three 10th-century German kings, the first of whom was Otto I the Great, the first Holy Roman Emperor, founder of the Ottonian dynasty. The Gothic form of the prefix was ''auda-'' (as in e.g. '' Audaþius''), the Anglo-Saxon form was ''ead-'' (as in e.g. '' Eadmund''), and the Old Norse form was '' auð-''. Due to Otto von Bismarck, the given name ''Otto'' was strongly associated with the German Empire in the later 19th century. It was comparatively frequently given in the United States (presumably in German American families) during the 1880s to 1890s, remaining in the top 100 most popular masculine given names in the US throughout 1880–1898, but its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th centuries AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part of Scythia at the time. By 370 AD, the Huns had arrived on the Volga, causing the westwards movement of Goths and Alans. By 430, they had established a vast, but short-lived, empire on the Danubian frontier of the Roman empire in Europe. Either under Hunnic hegemony, or fleeing from it, several central and eastern European peoples established kingdoms in the region, including not only Goths and Alans, but also Vandals, Gepids, Heruli, Suebians and Rugians. The Huns, especially under their King Attila, made frequent and devastating raids into the Eastern Roman Empire. In 451, they invaded the Western Roman province of Gaul, where they fought a combined army of Romans and Visigoths at the Battle of the Catalaunian Fields, and in 452, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agathias
Agathias Scholasticus (; Martindale, Jones & Morris (1992), p. 23–25582/594) was a Greek poet and the principal historian of part of the reign of the Roman emperor Justinian I between 552 and 558. Biography Agathias was a native of Myrina (Mysia), an Aeolian city in western Asia Minor. His father was Memnonius. His mother was presumably Pericleia. A brother of Agathias is mentioned in primary sources, but his name has not survived. Their probable sister Eugenia is known by name. The ''Suda'' clarifies that Agathias was active in the reign of the Roman emperor Justinian I, mentioning him as a contemporary of Paul the Silentiary, Macedonius of Thessalonica and Tribonian. Agathias mentions being present in Alexandria as a law student at the time when an earthquake destroyed Berytus (Beirut). The law school of Berytus had been recognized as one of the three official law schools of the empire (533). Within a few years, as the result of the disastrous earthquake of 551, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimea
Crimea ( ) is a peninsula in Eastern Europe, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukraine. To the east, the Crimean Bridge, constructed in 2018, spans the Strait of Kerch, linking the peninsula with Krasnodar Krai in Russia. The Arabat Spit, located to the northeast, is a narrow strip of land that separates the Syvash lagoons from the Sea of Azov. Across the Black Sea to the west lies Romania and to the south is Turkey. The population is 2.4 million, and the largest city is Sevastopol. The region, internationally recognized as part of Ukraine, has been under Russian occupation of Crimea, Russian occupation since 2014. Called the Tauric Peninsula until the early modern period, Crimea has historically been at the boundary between the Classical antiquity, classical world and the Pontic–Caspian steppe, steppe. Greeks in pre-Rom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avars (Carpathians)
The Pannonian Avars ( ) were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in the chronicles of the Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai (), or Pseudo-Avars in Byzantine sources, and the Apar () to the Göktürks. They established the Avar Khaganate, which spanned the Pannonian Basin and considerable areas of Central and Eastern Europe from the late 6th to the early 9th century. The name Pannonian Avars (after the area in which they settled) is used to distinguish them from the Avars of the Caucasus, a separate people with whom the Pannonian Avars may or may not have had links. Although the name ''Avar'' first appeared in the mid-5th century, the Pannonian Avars entered the historical scene in the mid-6th century, on the Pontic–Caspian steppe as a people who wished to escape the rule of the Göktürks. They are probably best known for their invasions and destruction in the Avar–Byzantine wars from 568 to 626 and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taspar Qaghan
Taspar Qaghan ( Sogdian: ''t’asp’r γ’γ’n'') or Tatpar Qaghan (Sogdian: ''t’tp’r x’γ’n'', Rouran: ''Tadpar qaɣan''; Old Turkic: 𐱃𐱃𐰯𐰺𐰴𐰍𐰣 Tatpar qaγan, 佗缽可汗/佗钵可汗, Pinyin: tuóbō Kèhán, Wade-Giles: t'o-po k'o-han) was the third son of Bumin Qaghan and Wei Changle (長樂公主), and the fourth khagan of the Turkic Khaganate (572–581). Reign His reign saw further rise of Turkic power even to the point calling both Zhou and Qi emperors as his sons.'' Book of Zhou, Volume 50'' He appointed his nephews Ashina Shetu as Erzhu khagan to east and Börü khagan to west as lesser khagans. He switched his alliance from Zhou to Qi. Sent a horse as gift in 572 and granted defeated Qi prince Gao Shaoyi asylum. He transferred the former Northern Qi subjects, whether they fled to or were captured to Tujue, to be under Gao Shaoyi's command. However, he still maintained good relationship with Zhou, sending another horse as gift in 574 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |