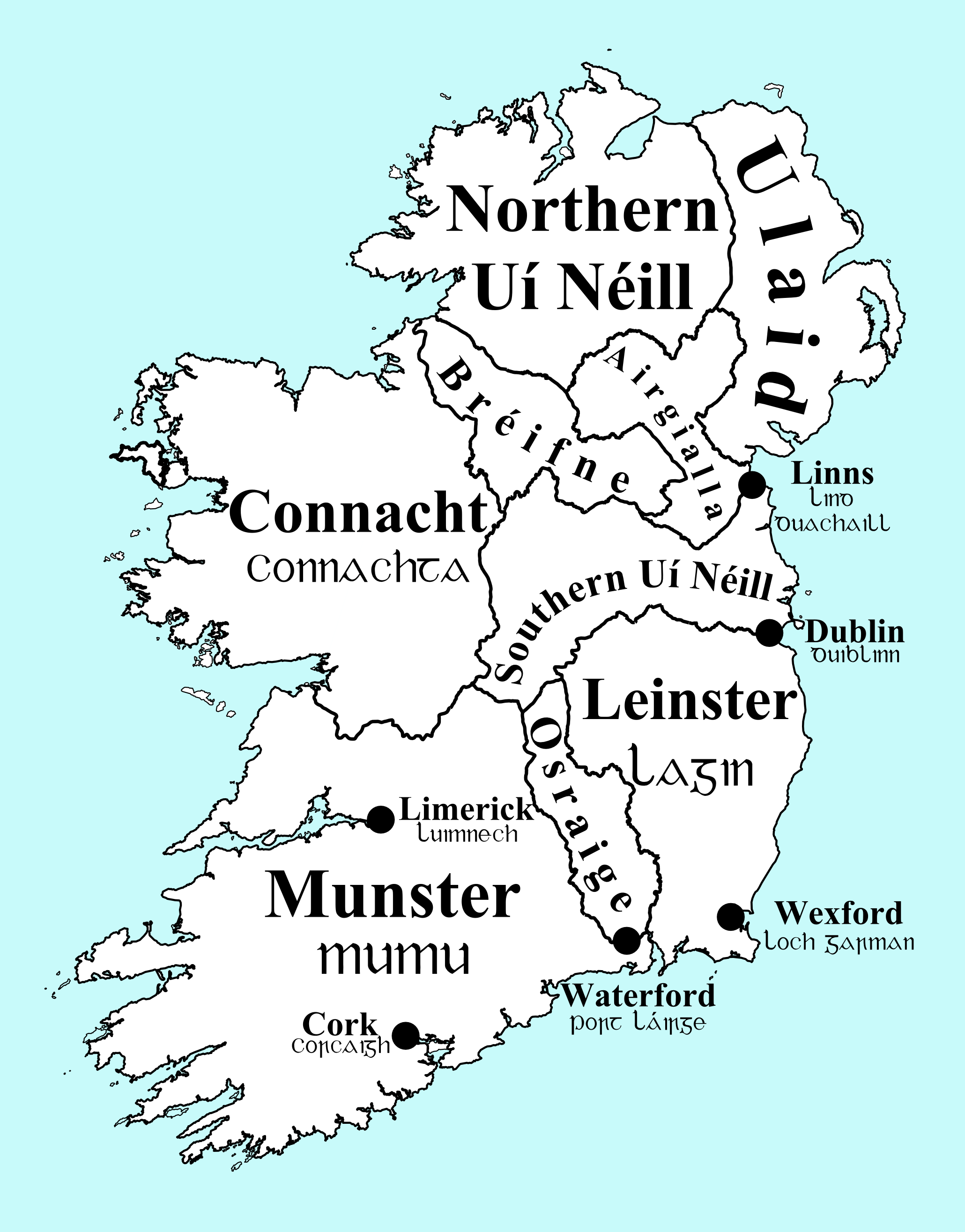
|
Tigernán Ua Ruairc
Tighearnán Mór Ua Ruairc (older spelling: Tigernán Mór Ua Ruairc), anglicised as Tiernan O'Rourke (fl. 1124– 1172) ruled the kingdom of Breifne as the 19th king in its Ua Ruairc (later O'Rourke) dynasty (964–1605 CE), a branch of the Uí Briúin. As one of the provincial kings in Ireland in the twelfth century, he constantly expanded his kingdom through shifting alliances, of which the most long-standing was with Toirdelbach Ua Conchobair King of Connacht and High King of Ireland, and subsequently his son and successor Ruaidhrí Ua Conchobair. He is known for his role in the expulsion of Diarmait Mac Murchada, King of Leinster, from Ireland in 1166. Mac Murchada's subsequent recruitment of Marcher Lords to assist him in the recovery of his Kingdom of Leinster ultimately led to the Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland. Early career Ua Ruairc may have ruled Bréifne as early as 1124, as indicated in Mac Carthaigh's Book and the Annals of the Four Masters, the former ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals Of Ulster
The ''Annals of Ulster'' () are annals of History of Ireland, medieval Ireland. The entries span the years from 431 AD to 1540 AD. The entries up to 1489 AD were compiled in the late 15th century by the scribe Ruaidhrí Ó Luinín, under his patron Cathal Óg Mac Maghnusa, on the island of ''Senadh-Mic-Maghnusa'', also known as ''Senad'' or Ballymacmanus Island (now known as Belle Isle, where Belle Isle Castle is located), near Lisbellaw, on Lough Erne in the kingdom of ''Fir Manach'' (Fermanagh). Later entries (up to AD 1540) were added by others. Entries up to the mid-6th century are retrospective, drawing on earlier annalistic and historical texts, while later entries were contemporary, based on recollection and oral history. Thomas Charles-Edwards, T. M. Charles-Edwards has claimed that the main source for its records of the first millennium A.D. is a now-lost Armagh continuation of the ''Chronicle of Ireland''. The Annals used the Irish language, with some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hervey De Montmorency
Herve de Montmorency () was an Anglo-Norman adventurer and invader of Ireland. Biography Herve was the son of Bouchard IV of Montmorency and Agnes of Pontoise, daughter of Raoul de Pontoise. He served Louis VI and Louis VII of France. He married Elizabeth, daughter of Robert de Beaumont (d. 1118), Count of Meulan, and widow of Gilbert de Clare. Hervey was a gallant warrior. He was sent by his nephew, Earl Richard, to Ireland with Robert FitzStephen in 1169 to report on affairs there. After the victory of these first invaders at Wexford their ally Derruot, king of Leinster, rewarded him with two cantreds of land on the coast between Wexford and Waterford, and he appears to have shared in Dermot's raids on Ossory and Offaly. On the landing of Raymond FitzGerald at Dundunnolf, near Waterford, Hervey joined him, and shared in his victory over the people of Waterford and the chief, Donnell O'Phelan. Giraldus puts into his mouth a speech recommending the slaughter of seventy Wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Fitz Stephen
Robert FitzStephen (died 1183) was a Cambro-Norman soldier, one of the leaders of the Norman invasion of Ireland, for which he was granted extensive lands in Ireland. He was a son of the famous Nest, daughter of Rhys ap Tewdwr, the last king of Deheubarth (South Wales). His father was Nest's second husband, Stephen, Constable of Cardigan (). Following the death of her first husband, Gerald de Windsor, her sons had married her to Stephen, her husband's constable for Cardigan. By Stephen, she had another son, possibly two; the eldest was Robert, and the younger may have been Hywel. Career In Wales Robert succeeded his father in his office (''Custos Campe Abertivi''). He first appears in history in 1157, when King Henry II of England invaded Gwynedd. While the main royal army faced the forces of Owain Gwynedd east of the River Conwy, a force including Robert and his half-brother Henry Fitzroy (the illegitimate son of Nest and King Henry I) attacked Anglesey by sea. However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard De Clare, 2nd Earl Of Pembroke
Richard de Clare (c. 1130 – 20 April 1176), the second Earl of Pembroke, also Lord of Leinster and Lord Chief Justice of Ireland, Justiciar of Ireland (sometimes known as Richard FitzGilbert), was an Anglo-Norman nobleman notable for his leading role in the Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland. Like Gilbert de Clare, 1st Earl of Pembroke, his father, Richard is commonly known by his nickname, Strongbow (). After his son and heir, Gilbert, died childless before 1189, the earldom passed through Richard's daughter Isabel de Clare, 4th Countess of Pembroke, Isabel de Clare and to her husband, William Marshal, 1st Earl of Pembroke, William Marshal. Nickname During the Middle Ages, official documents, with few exceptions, were written in Latin; in the Domesday Exchequer annals, written between 1300 and 1304 (that means, over 120 years after Richard's death), he was referred to as "''Ricardus cognomento Stranghose Comes Strugulliae"'', which translates to "Richard, known as Stranghose, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry II Of England
Henry II () was King of England The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the form of government used by the United Kingdom by which a hereditary monarch reigns as the head of state, with their powers Constitutional monarchy, regula ... from 1154 until his death in 1189. During his reign he controlled Kingdom of England, England, substantial parts of Wales in the High Middle Ages, Wales and Lordship of Ireland, Ireland, and much of Kingdom of France, France (including Duchy of Normandy, Normandy, County of Anjou, Anjou, and Duchy of Aquitaine, Aquitaine), an area that altogether was later called the Angevin Empire, and also held power over Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland and the Duchy of Brittany. Henry was the eldest son of Geoffrey Plantagenet, Count of Anjou, and Empress Matilda, Matilda, daughter of Henry I of England. By the age of fourteen, he became politically and militarily involved in The Anarchy, his mother's efforts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giraldus Cambrensis
Gerald of Wales (; ; ; ) was a Cambro-Norman priest and historian. As a royal clerk to the king and two archbishops, he travelled widely and wrote extensively. He studied and taught in France and visited Rome several times, meeting the Pope. He was nominated for several bishoprics but turned them down in the hope of becoming Bishop of St Davids, but was unsuccessful despite considerable support. His final post was as Archdeacon of Brecon, from which he retired to academic study for the remainder of his life. Much of his writing survives. Life Early life Born at Manorbier Castle in Pembrokeshire, Wales, Gerald was of mixed Norman and Welsh descent. Gerald was the youngest son of William Fitz Odo de Barry (or Barri), the common ancestor of the De Barry family of Barry, Glamorganshire, who subsequently invaded Ireland, a retainer of Arnulf de Montgomery and Gerald de Windsor, and one of the most powerful Anglo-Norman barons in Wales. His mother was Angharad FitzGerald, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Song Of Dermot And The Earl
''The Song of Dermot and the Earl'' () is an anonymous Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman verse chronicle written in the early 13th century in England. It tells of the arrival of Richard de Clare, 2nd Earl of Pembroke, Richard de Clare (Strongbow) in Ireland in 1170 (the "earl" in the title), and of the subsequent arrival of Henry II of England. The poem mentions one Morice Regan, secretary to Diarmaid mac Murchadha, king of Leinster, who was eyewitness to the events and may have provided an account to the author. The chronicle survives only in a single manuscript which was re-discovered in the 17th century in London. The work bears no title in the manuscript, but has been commonly referred to as ''The Song of Dermot and the Earl'' since Goddard Henry Orpen in 1892 published a diplomatic edition under this title. It has also been known as The Conquest of Ireland and The Conquest of Ireland by Henry II; in the most recent edition it was called La Geste des Engleis en Yrlande ("The Deeds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diarmait Ua Mealseachlainn
Diarmuid Ua Duibhne (, ), also known as Diarmuid of the Love Spot, is a hero and demigod in the Fenian Cycle of Irish mythology, traditionally thought to be set in the 2nd to 4th century. He is the son of Donn, son of Duibhne of the Fianna, and Cochrann, daughter of Cathaír Mór. Diarmuid becomes the foster son and protégé of Aengus Óg, one of the Tuatha Dé Danann and the god of love, to the extent that a god of love can be said to exist in the corpus. He grows up to be a skilled warrior and a well-liked, valued member of the Fianna who on one occasion saves Fionn and his band by single-handedly slaying over three thousand enemies in battle. Diarmuid is best known as the lover of Gráinne, the intended wife of Fianna leader Fionn mac Cumhaill in the legend ''The Pursuit of Diarmuid and Gráinne''. Among his sons were Donnchadh, Iollann, Ruchladh and Ioruad. Diarmuid Ua Duibhne is said to be the founder of the Scottish Clan Campbell. On the Campbell crest is a boar's hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derbforgaill
Dearbhfhorghaill (older spelling: Derbforgaill) (1108–1193), anglicised as Derval, was a daughter of Murchad Ua Maeleachlainn, king of Meath, and of his wife Mor (died 1137), daughter of Muirchertach Ua Briain. She is famously known as the " Helen of Ireland" as her abduction from her husband Tigernán Ua Ruairc by Diarmait Mac Murchada, king of Leinster, in 1152 played some part in bringing the Anglo-Normans to Irish shores, although this is a role that has often been greatly exaggerated and often misinterpreted. Unusually for a woman of her time, she is mentioned no fewer than five times in contemporary annals: her abduction by Diarmait in 1152 (Annals of Clonmacnoise), (although by the end of the next year she had left Leinster and returned to her family's lands in Meath, possibly after negotiations with her father's family); her donation to the Cistercian abbey of Mellifont of altar cloths, a gold chalice, and 60 ounces of gold during the consecration ceremony in 1157 (Anna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh De Lacy
Hugh de Lacy or Hugh Lacy may refer to: *Hugh de Lacy, Lord of Lassy (c. 1020–1085), first recorded member of the Norman noble family de Lacy *Hugh de Lacy, Lord of Meath (died 1186), 4th Baron Lacy *Hugh de Lacy, Abbot of Shrewsbury (died c. 1215/18) *Hugh de Lacy, 1st Earl of Ulster (c. 1176–1242), younger son of Hugh de Lacy, Lord of Meath *Hugh De Lacy (politician) Emerson Hugh De Lacy (May 9, 1910 – August 19, 1986) was an American politician and socialist. He served on the Seattle City Council from 1937 to 1940 and as a member of the United States House of Representatives from 1945 to 1947. He repre ... (1910–1986), American politician * Hugh Lacy (bishop) (died 1580), Anglican bishop in Ireland *Hugh Lacy (1943–1998), 3rd baronet of the Lacy baronets {{human name disambiguation, Lacy, Hugh de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diarmaid Mac Murrough Expugnatio Hibernica
Diarmaid () is a masculine given name in the Irish language, which has historically been anglicized as Jeremiah or Jeremy, names with which it is etymologically unrelated. The name Dimity might have been used as a feminine English equivalent of the name in Ireland. Earlier forms of the name include Diarmit and Diarmuit. Variations of the name include Diarmait and Diarmuid. Anglicised forms of the name include Dermody, Dermot (, ) and Dermod. Mac Diarmata, anglicised ''McDermott'' and similar, is the patronymic and surname derived from the personal name. The exact etymology of the name is debated. There is a possibility that the name is derived in part from ''dí'', which means "without"; and either from , which means "injunction", or , which means "envy".. The Irish name later spread to Scotland where in Scottish Gaelic the form of the name is ''Diarmad''; Anglicised forms of this name include ''Diarmid'' and ''Dermid''.. Diarmaid * Diarmaid Mac an Bhaird (fl. 1670) Irish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |