|
Tibet–Ladakh–Mughal War
The Tibet–Ladakh–Mughal War of 1679–1684 was fought between the Central Tibetan Ganden Phodrang government, with the assistance of Mongol khanates, and the Namgyal dynasty of Ladakh with assistance from the Mughal Empire in Kashmir. Background In the late 17th century, Ladakh sided with Bhutan in its dispute with Tibet. The Tibetans decided to punish Ladakh for interfering in their relations with Bhutan and the oppression of Gelug monasteries in Ladakh. War In 1679 the 5th Dalai Lama appointed the lama of the Tashilhunpo Monastery, the Koshut Golden Chhewang (), as the commander of the Tibeto-Mongol expedition to Ladakh. He is said to have done so against the advice of his prime minister not to send the expedition. Galdan Chhewang first secured his flanks when he made a treaty with Raja Kehri Singh of Bashahr, granting him trade rights with Tibet. Galdan Chhewang's first campaign resulted in the defeat of the Ladakhi army led by Shakya Gyatso (, at Khan-dMar. The fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guge
Guge (; ) was an ancient dynastic kingdom in Western Tibet. The kingdom was centered in present-day Zanda County, Ngari Prefecture, Tibet Autonomous Region. At various points in history after the 10th century AD, the kingdom held sway over a vast area including south-eastern Zanskar, Upper Kinnaur district, and Spiti Valley, either by conquest or as tributaries. The ruins of the former capital of the Guge kingdom are located at Tsaparang in the Sutlej valley, not far from Mount Kailash and westwards from Lhasa. History Founding Guge was founded in the 10th century. Its capitals were located at Tholing and Tsaparang. Kyide Nyimagon, a great-grandson of Langdarma, the last monarch of the Tibetan Empire, fled from the insecure conditions in Ü-Tsang in 910 to arrive in Ngari (West Tibet). He established a kingdom around 912, annexing Purang and Guge. He established his capital in Guge. Nyimagon later divided his lands into three parts. The king's eldest son ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
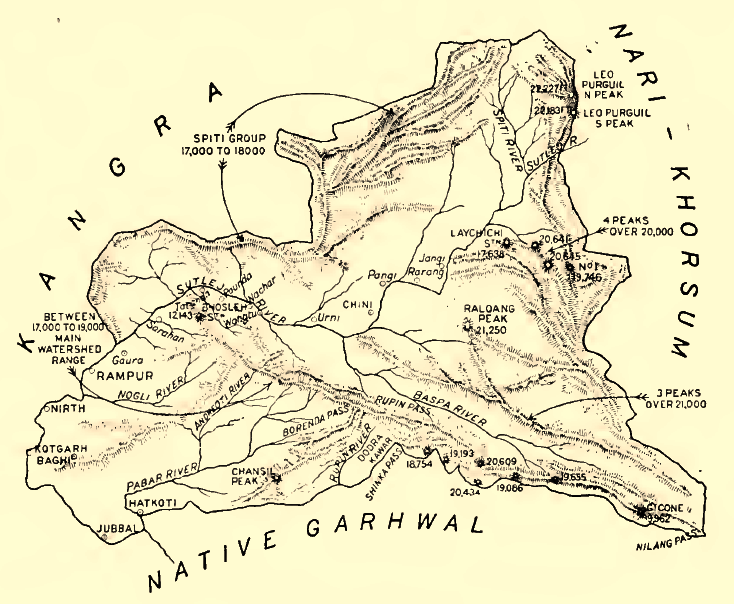
Bashahr
Bushahr, also spelt as 'Bashahr' and 'Bussahir' or 'Bushair' was a Rajput princely state in India during the British Raj. It was located in the hilly western Himalaya promontory bordering Tibet in the northern part of colonial Punjab region. The territory of this former state is now part of Kinnaur and Shimla districts of the present Himachal Pradesh state. The erstwhile Bushahr state was traversed by the Sutlej river. It was bordered on the west by the Kulu, Lahaul and Spiti states and by Tehri Garhwal on the east. It had an area of . History The erstwhile Bushahr state was occupied by a Gorkha king from central Nepal from 1803 to 1815. Ranjit Singh, the ruler of the Sikh state in the Punjab, intervened in 1809 and drove the Nepalese army east of the Satluj river. A rivalry between Nepal and the British East India Company over the annexation of minor states bordering Nepal eventually led to the Anglo-Nepalese War (1815–16) or the Gurkha War. Both parties eventually sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Ladakh
Ladakh has a long history with evidence of human settlement from as back as 9000 b.c. It has been a crossroad of high Asia for thousands of years and has seen many cultures, empires and technologies born in its neighbours. As a result of these developments Ladakh has imported many traditions and culture from its neighbours and combining them all gave rise to a unique tradition and culture of its own. Earliest history The first glimpse of political history is found in the kharosthi inscription of "Uvima Kavthisa" discovered near the ''K'a-la-rtse'' ( Khalatse) bridge on the Indus, showing that in around the 1st century, Ladakh was a part of the Kushan Empire. A few other short Brahmi and Kharosthi inscriptions have been found in Ladakh. The Chinese pilgrim monk Xuanzang, c. 634 CE, described a journey from ''Chuluduo'' (Kūluta, Kulu) to ''Luohuluo'' (Lahul) and then states that, " om here, the road, leading to the north, for over one thousand, eight hundred or nine hundred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1680s Conflicts
Year 168 ( CLXVIII) was a leap year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Apronianus and Paullus (or, less frequently, year 921 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 168 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Emperor Marcus Aurelius and his adopted brother Lucius Verus leave Rome, and establish their headquarters at Aquileia. * The Roman army crosses the Alps into Pannonia, and subdues the Marcomanni at Carnuntum, north of the Danube. Asia * Emperor Ling of Han succeeds Emperor Huan of Han as the emperor of the Chinese Han Dynasty; the first year of the ''Jianning'' era. Births * Cao Ren, Chinese general (d. 223) * Gu Yong, Chinese chancellor (d. 243) * Li Tong, Chinese general (d. 209) Deaths * Anicetus, pope of Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conflicts In 1679
Conflict may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Conflict'' (1921 film), an American silent film directed by Stuart Paton * ''Conflict'' (1936 film), an American boxing film starring John Wayne * ''Conflict'' (1937 film), a Swedish drama film directed by Per-Axel Branner * ''Conflict'' (1938 film), a French drama film directed by Léonide Moguy * ''Conflict'' (1945 film), an American suspense film starring Humphrey Bogart * ''Catholics: A Fable'' (1973 film), or ''The Conflict'', a film starring Martin Sheen * ''Judith'' (1966 film) or ''Conflict'', a film starring Sophia Loren * ''Samar'' (1999 film) or ''Conflict'', a 1999 Indian film by Shyam Benegal Games * ''Conflict'' (series), a 2002–2008 series of war games for the PS2, Xbox, and PC * ''Conflict'' (video game), a 1989 Nintendo Entertainment System war game * '' Conflict: Middle East Political Simulator'', a 1990 strategy computer game Literature and periodicals * ''Conflict'' (novel) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demchok (historical Village)
Demchok (), KNAB Place Name Databse, retrieved 27 July 2021. was described by a British boundary commission in 1847 as a village lying on the border between the Kingdom of Ladakh and the . It was a "hamlet of half a dozen huts and tents", divided into two parts by a rivulet which formed the boundary between the two states. The rivulet, a tributary of the variously called the Demchok River, Charding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lhari Stream
The Charding Nullah, traditionally known as the Lhari stream and called Demchok River by China,{{efn, name="White Paper XII" is a small river that originates near the Charding La pass that is also on the border between the two countries and flows northeast to join the Indus River near a peak called "Demchok Karpo" or "Lhari Karpo" (white holy peak of Demchok). There are villages on both sides of the mouth of the river called by the same name "Demchok", which is presumed to have been a single village originally, and has gotten split into two due to geopolitcal reasons. The river serves as the ''de facto'' border between China and India in the southern part of the Demchok sector.{{efn, name="White Paper XII" Etymology The Indian government refers to the river as "Charding Nullah" after its place of origin, the Charding La pass, with nullah meaning a mountain stream. The Chinese government uses the term "Demchok river" by the location of its mouth, near the Demchok Karpo peak and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ladakh Chronicles
The ''Ladakh Chronicles'', or ''La-dvags-rgyal-rabs'' (), is a historical work that covers the history of Ladakh from the beginnings of the first Tibetan dynasty of Ladakh until the end of the Namgyal dynasty. The chronicles were compiled by the Namgyal dynasty, mostly during the 17th century, and are considered to be the main written source for Ladakhi history. It remains one of only two surviving pre-19th century literary sources from Ladakh. Only seven original manuscripts of the chronicles are known to have existed, of which two survive to the modern day. Background Until the early 19th century, European historians believed that there were no written histories from Ladakh. After reports to the contrary, Alexander Cunningham found the first known manuscript of the chronicles (''Ms. Cunningham'') during his stay in Ladakh in 1847. The origin, intent, and time of the authorship of the ''Ladakh Chronicles'' remains unknown to modern historians. It remains one of only two surv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delek Namgyal
The Namgyal dynasty was a dynasty whose rulers were the monarchs of the former kingdom of Ladakh that lasted from 1460 to 1842 and were titled the Gyalpo of Ladakh. The Namgyal dynasty succeeded the first dynasty of Maryul and had several conflicts with the neighboring Mughal Empire and various dynasties of Tibet, including the Tibet–Ladakh–Mughal War. The dynasty eventually fell to the Sikh Empire and Dogras of Jammu and Kashmir. Most of its known history is written in the ''Ladakh Chronicles''. History Founding According to the ''Ladakh Chronicles'', the Namgyal dynasty was founded by Bhagan, the son of Bhara in the kingdom of Maryul. Bhagan was described as warlike, and established the Namgyal dynasty in 1460 after he formed an alliance with the people of Leh and dethroned the Maryul king Blo-gros-mc-og-ldan and his brothers drun-pa A-li and Slab-bstan-dar-rgyas. He took the surname Namgyal (meaning victorious) and founded a new dynasty which still survives today. Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desi Sangye Gyatso
Desi Sangye Gyatso (1653–1705) was the sixth regent (''Desi (Tibet), desi'') of the 5th Dalai Lama (1617–1682) in the Ganden Phodrang government. He founded the School of Medicine and Astrology called Men-Tsee-Khang on Chagpori (Iron Mountain) in 1694 and wrote the ''Blue Beryl'' (Blue Sapphire) treatise. His name is sometimes written as Sangye Gyamtso and Sans-rGyas rGya-mTsho By some erroneous accounts, Sangye Gyatso is believed to be the son of the "Great Fifth". He could not be the son of the Fifth Dalai Lama because he was born near Lhasa in September 1653, when the Dalai Lama had been absent on his trip to China for the preceding sixteen months. He ruled as regent, hiding the death of the Dalai Lama, while the infant 6th Dalai Lama was growing up, for 16 years. During this period, he oversaw the completion of the Potala Palace and warded off Chinese politicking. He is also known for harboring disdain for Tulku Dragpa Gyaltsen, although this lama died in 1656, when Sangye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Pangong
Pangong Tso or Pangong Lake (; ; hi, text=पैंगोंग झील) is an endorheic lake spanning eastern Ladakh and West Tibet situated at an elevation of . It is long and divided into five sublakes, called ''Pangong Tso'', ''Tso Nyak'', ''Rum Tso'' (twin lakes) and ''Nyak Tso''. Approximately 50% of the length of the overall lake lies within Tibet in China, 40% in Ladakh, India and the remaining 10% is disputed and is a de-facto buffer zone between India and China. The lake is wide at its broadest point. All together it covers almost 700 km2. During winter the lake freezes completely, despite being saline water. It has a land-locked basin separated from the Indus River basin by a small elevated ridge, but is believed to have been part of the latter in prehistoric times. Names Historically, the lake is viewed as being made up five sublakes, which are connected through narrow water channels. The name ''Pangong Tso'' only applied to the westernmost lake that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere Of Influence
In the field of international relations, a sphere of influence (SOI) is a spatial region or concept division over which a state or organization has a level of cultural, economic, military or political exclusivity. While there may be a formal alliance or other treaty obligations between the influenced and influencer, such formal arrangements are not necessary and the influence can often be more of an example of soft power. Similarly, a formal alliance does not necessarily mean that one country lies within another's sphere of influence. High levels of exclusivity have historically been associated with higher levels of conflict. In more extreme cases, a country within the "sphere of influence" of another may become a subsidiary of that state and serve in effect as a satellite state or ''de facto'' colony. This was the case with the Soviet Union and its Eastern Bloc after World War II. The system of spheres of influence by which powerful nations intervene in the affairs of others co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |