|
Thymallus
''Thymallus'', commonly known as graylings, is a genus of freshwater ray-finned fish and the only genus within the subfamily Thymallinae of the family Salmonidae. Although all ''Thymallus'' species can be generically called graylings, without specific qualification the term "grayling" typically refers to the type species '' Thymallus thymallus'', the European grayling. Name The name of the genus ''Thymallus'' first given to grayling (''T. thymallus'') described in the 1758 edition of ''Systema Naturae'' by Swedish zoologist Carl Linnaeus originates from the faint smell of the herb thyme, which emanates from the flesh. ''Thymallus'' derives from the Greek θύμαλλος, "thyme smell". Species According to FishBase, 14 species are placed in this genus. However, views differ on their taxonomic rank. * '' Thymallus arcticus'' ( Pallas, 1776) - Arctic grayling * '' Thymallus baicalensis'' Dybowski, 1874 - Baikal black grayling * '' Thymallus brevipinnis'' Svetovid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymallus Arcticus
The Arctic grayling (''Thymallus arcticus'') is a species of freshwater fish in the salmon family (biology), family Salmonidae. ''T. arcticus'' is widespread throughout the Arctic Ocean, Arctic and Pacific Ocean, Pacific drainages in Canada, Alaska, and Siberia, as well as the upper Missouri River drainage in Montana. In the U.S. state of Arizona, an introduced population is found in the Lee Valley Lake, Lee Valley and other lakes in the White Mountains (Arizona), White Mountains. They were also stocked at Toppings Lake by the Teton Range and in lakes in the high Uinta Mountains in Utah, as well as alpine lakes of the Boulder Mountains (Idaho) in central Idaho. Taxonomy The scientific name of the Arctic grayling is ''Thymallus arcticus''. It was named in 1776 by German zoologist Peter Simon Pallas from specimens collected in Russia. The name of the genus ''Thymallus'' first given to grayling (''T. thymallus'') described in the 10th edition of Systema Naturae, 1758 edition of ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymallus Thymallus
''Thymallus thymallus'', the grayling or European grayling, is a species of freshwater fish in the salmon family (biology), family Salmonidae. It is the only species of the genus ''Thymallus'' (the graylings) native to Europe, where it is widespread from the United Kingdom and France to the Ural Mountains in Russia, and Balkans on the south-east, but does not occur in the southern parts of the continent. It was introduced to Morocco in 1948, but it does not appear to have become established there. Description The grayling grows to a maximum recorded length of and a maximum recorded weight of . Of typical ''Thymallus'' appearance, the grayling proper is distinguished from the similar Arctic grayling (''T. arcticus arcticus'') by the presence of 5–8 dorsal fin, dorsal and 3–4 anal fin, anal spines, which are absent in the other species; ''T. thymallus'' also has a smaller number of soft rays in these fins. Individuals of the species have been recorded as reaching an age of 14 y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Grayling
''Thymallus thymallus'', the grayling or European grayling, is a species of freshwater fish in the salmon family Salmonidae. It is the only species of the genus ''Thymallus'' (the graylings) native to Europe, where it is widespread from the United Kingdom and France to the Ural Mountains in Russia, and Balkans on the south-east, but does not occur in the southern parts of the continent. It was introduced to Morocco in 1948, but it does not appear to have become established there. Description The grayling grows to a maximum recorded length of and a maximum recorded weight of . Of typical ''Thymallus'' appearance, the grayling proper is distinguished from the similar Arctic grayling (''T. arcticus arcticus'') by the presence of 5–8 dorsal and 3–4 anal spines, which are absent in the other species; ''T. thymallus'' also has a smaller number of soft rays in these fins. Individuals of the species have been recorded as reaching an age of 14 years. The grayling prefers cold, clean, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongolian Grayling
The Mongolian grayling (''Thymallus brevirostris'') is a freshwater species of fish of the genus ''Thymallus'' endemic to the landlocked rivers in Mongolia, Inner Mongolia Province of China and nearby parts of Russian far east. It is considered to be the largest grayling species in the world, and hence viewed as an auspicious sign by local tribes. Description Mongolian grayling grow to a recorded maximum length of 65 cm (26 inches). The dorsal side is blackish, and the abdominal side is light. Black spots are uniformly present on both sides of the body. In adults, their upper jaw extends at least below the posterior edge of the eye. The Mongolian grayling is considered by researchers to be a relic from the Tertiary period. Distribution The Mongolian grayling is native to the landlocked lake region of Mongolia and the nearby Russian and Chinese areas, such as Khovd River, Issyk-Kul Lake and other rivers and lakes of the Altai Mountains, with Arctic graylings and their hybrids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymallus Baicalensis
''Thymallus baicalensis'', also known as the Baikal black grayling, is a Siberian freshwater fish species in the salmon family Salmonidae. ''Thymallus baicalensis'' occurs in Lake Baikal, in the inflowing Selenga River and throughout the major Enisei River drainage, and also some eastern tributaries of the Ob River.Weiss, S. J., D. V. Gonçalves, G. Secci-Petretto, G. K. Englmaier, A. Gomes-Dos-Santos, G. P. J. Denys, H. Persat, A. Antonov, C. Hahn, E. B. Taylor and E. Froufe (2021) Global systematic diversity, range distributions, conservation and taxonomic assessments of graylings (Teleostei: Salmonidae; ''Thymallus'' spp.). ''Organisms Diversity & Evolution'': published online on 25 Nov. 2020. It was previously considered a subspecies of the Arctic grayling, ''Thymallus arcticus baicalensis'', but currently one of several distinct Siberian and East Asian grayling species, the closest of which are '' Thymallys nikolskyi, T. svetovidovi, T. brevicephalus '' and ''T. breviros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymallus Brevipinnis
''Thymallus brevipinnis'' is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Thymallinae, the graylings, part of the family Salmonidae. This species is endemic to Lake Baikal in Siberia where it is benthopelagic. Some workers regard this taxon as a junior synonym of ''Thymallus baicalensis ''Thymallus baicalensis'', also known as the Baikal black grayling, is a Siberian freshwater fish species in the salmon family Salmonidae. ''Thymallus baicalensis'' occurs in Lake Baikal, in the inflowing Selenga River and throughout the majo ...''. References {{taxonbar, from=Q5742968 Fish of Lake Baikal brevipinnis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amur Grayling
The Amur grayling (''Thymallus grubii'') is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish from the genus ''Thymallus'' (graylings) of the family Salmonidae, endemic to the Amur basin in Russian Far East and Northeast China and also the Onon and Kherlen basins in Mongolia. It is sometimes difficult to differentiate the species with the Lower Amur grayling (''Thymallus tugarinae''). It is seen as a game fish and food fish in Russian Far East and the Chinese Heilongjiang province. Description The body of Amur grayling is usually dark, with its back being slightly purple. There are some small dark spots on the sides of the body. The edge of the dorsal fin is purplish red mixed with some spots. It can reach a maximum length of 31.3 cm. Life cycle In winter, adult Amur grayling are found in deep parts of mountain streams. While in summer, they are usually found in clear streams flowing slowly with thick aquatic weeds. Most Amur grayling is feed on benthic organisms and insects. They f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
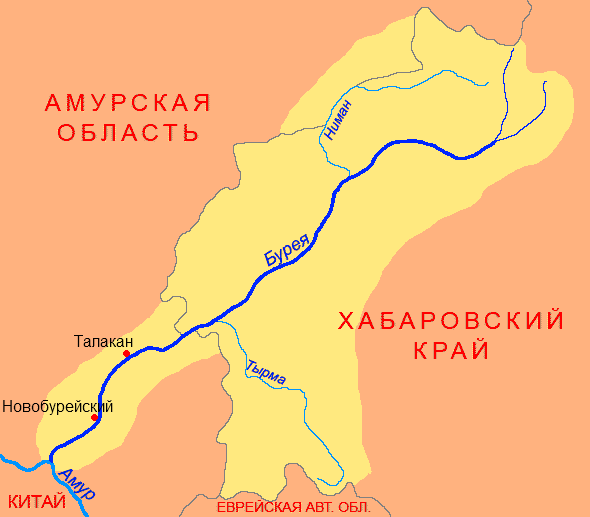
Thymallus Burejensis
The Bureya grayling (''Thymallus burejensis'') is a grayling in the salmon family Salmonidae. It is found in the basin of the Bureya, a tributary of the Amur, Russian Far East. In its natural freshwater habitat it is sympatric with other grayling species. See also *List of freshwater fish of Russia List of freshwater fish of Russia includes species of freshwater fish found in Russian Federation, and includes those introduced. Acipenseriformes Acipenseridae (Sturgeons) * Acipenser ** '' Acipenser baerii'' — Siberian sturgeon ** '' A ... References External linksYury Valentinovich Dyldin. ''A review of the genus Thymallus'' {{Taxonbar, from=Q5582219 Thymallus Fish described in 1848 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymallus Flavomaculatus
''Thymallus flavomaculatus'', also known as yellow-spotted grayling, is a species of brackish-water fish in the salmon family. It is found in Khabarovsk and Primorsky Krai of the Russian Far East, as well as the Sea of Japan and the Sea of Okhotsk. They usually live near or on the bottom of the water body. Description It is unclear about the range of their sizes. There is a yellow-orange spot on the last two-five interray membranes on the upper posterior of the dorsal fin A dorsal fin is a fin on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates. Dorsal fins have evolved independently several times through convergent evolution adapting to marine environments, so the fins are not all homologous. They are found .... From the fin base upwards there are 4-5 rows of small round spots with dull fringing. The upper jaw reaches beyond anterior eye edge and reaches the pupil. There are no teeth on the vomer and tongue. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q28802238 flavomaculatus Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmonidae
Salmonidae (, ) is a family (biology), family of ray-finned fish, the only extant member of the suborder Salmonoidei, consisting of 11 extant genera and over 200 species collectively known as "salmonids" or "salmonoids". The family includes salmon (both Atlantic and Pacific species), trout (both ocean-going and landlocked), Salvelinus, char, Thymallus, graylings, freshwater whitefishes, taimens and lenoks, all coldwater fish, coldwater mid-trophic level, level predatory fish that inhabit the subarctic and cool temperate waters of the Northern Hemisphere. The Atlantic salmon (''Salmo salar''), whose Latin name became that of its genus ''Salmo'', is also the eponym of the family and order names. Salmonids have a relatively primitive appearance among teleost fish, with the pelvic fins being placed far back, and an adipose fin towards the rear of the back. They have slender bodies with rounded fish scale, scales and forked caudal fin, tail fins, and their fish jaw, mouths contain a si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyme
Thyme () is a culinary herb consisting of the dried aerial parts of some members of the genus ''Thymus (plant), Thymus'' of flowering plants in the mint family Lamiaceae. Thymes are native to Eurasia and north Africa. Thymes have culinary, medicinal, and ornamental uses. The species most commonly cultivated and used for culinary purposes is ''Thymus vulgaris'', native to Southeast Europe. History Thymus serpyllum, Wild thyme grows in the Levant, where it might have been first cultivated. Ancient Egyptians used common thyme (''Thymus vulgaris'') for embalming. The Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks used it in their baths and burnt it as incense in their temples, believing it was a source of courage. The spread of thyme throughout Europe was thought to be due to the Ancient Rome, Romans, as they used it to purify their rooms and to "give an aromatic flavour to cheese and liqueurs". In the European Middle Ages, the herb was placed beneath pillows to aid sleep and ward off nightmares ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Simon Pallas
Peter Simon Pallas Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS FRSE (22 September 1741 – 8 September 1811) was a Prussia, Prussian zoologist, botanist, Ethnography, ethnographer, Exploration, explorer, Geography, geographer, Geology, geologist, Natural history, natural historian, and Taxonomy, taxonomist. He studied natural sciences at various universities in Germany in the early modern period, early modern Germany and worked primarily in the Russian Empire between 1767 and 1810. Life and work Peter Simon Pallas was born in Berlin, Kingdom of Prussia, the son of Professor of Surgery Simon Pallas. He studied with private tutors and took an interest in natural history, later attending the University of Halle and the University of Göttingen. In 1760, he moved to the University of Leiden and passed his doctor's degree at the age of 19. Pallas travelled throughout the Dutch Republic and to London, improving his medical and surgical knowledge. He then settled at The Hague, and his new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |