|
Thutmose II
Thutmose II was the fourth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, and his reign is thought to have lasted for 13 years, from 1493 to 1479 BC (Low Chronology), or just 3 years from around 1482 to 1479 BC. Little is known about him, and he is overshadowed by his father Thutmose I, half-sister and wife Hatshepsut, and son Thutmose III. There are relatively few monuments that refer to Thutmose II. He died before the age of 30 and a body claimed to be his was found in the Deir el-Bahari Cache above the Mortuary Temple of Hatshepsut. His tomb, in the Western Wadis near the Valley of the Queens, was found in 2022 and confirmed to be his in 2025. The tomb was built under waterfalls, leading to periodic flooding which damaged the tomb throughout the ages. His mummified body was moved in ancient times and its final location is disputed. Family The name Thutmose II is read as Thutmosis or Tuthmosis II, Thothmes in older history works in Latinized Greek, and derives from Anci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thutmose III
Thutmose III (variously also spelt Tuthmosis or Thothmes), sometimes called Thutmose the Great, (1479–1425 BC) was the fifth pharaoh of the 18th Dynasty of Egypt. He is regarded as one of the greatest warriors, military commanders, and military strategists of all time; as Egypt's preeminent warrior pharaoh and conqueror; and as a dominant figure in the New Kingdom period. Officially, Thutmose III ruled Egypt from his coronation on 28 April 1479 BC at the age of two until his death on 11 March 1425 BC. But for the first 22 years of his reign, he was coregent with his stepmother and aunt, Hatshepsut, who was named the pharaoh.Partridge, R., 2002. Fighting Pharaohs: Weapons and warfare in ancient Egypt. Manchester: Peartree. pp. 202–203 He became sole ruler after Hatshepsut's death in 1458. Thutmose III conducted between 17 and 20 military campaigns, all victorious, which brought ancient Egypt's empire to its zenith. They are detailed in the inscriptions known as the Ann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thutmose III Of Egypt
Thutmose III (variously also spelt Tuthmosis or Thothmes), sometimes called Thutmose the Great, (1479–1425 BC) was the fifth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, 18th Dynasty of Egypt. He is regarded as one of the greatest warriors, military commanders, and military strategists of all time; as Egypt's preeminent warrior pharaoh and conqueror; and as a dominant figure in the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom period. Officially, Thutmose III ruled Ancient Egypt, Egypt from his coronation on 28 April 1479 BC at the age of two until his death on 11 March 1425 BC. But for the first 22 years of his reign, he was coregency, coregent with his stepmother and aunt, Hatshepsut, who was named the pharaoh.Partridge, R., 2002. Fighting Pharaohs: Weapons and warfare in ancient Egypt. Manchester: Peartree. pp. 202–203 He became sole ruler after Hatshepsut's death in 1458. Thutmose III conducted between 17 and 20 military campaigns, all victorious, which brought ancient Egypt's empi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
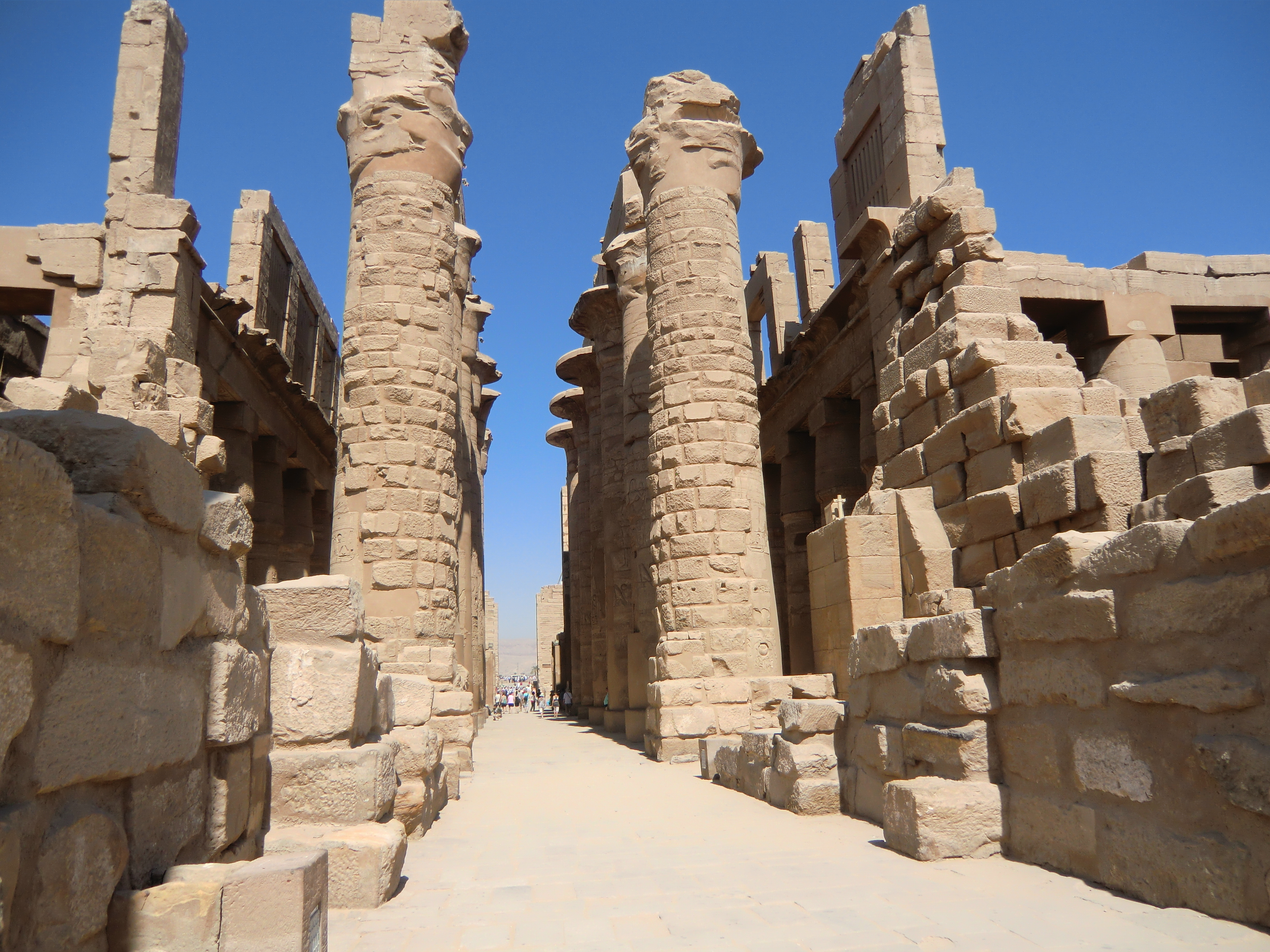
Karnak
The Karnak Temple Complex, commonly known as Karnak (), comprises a vast mix of temples, pylons, chapels, and other buildings near Luxor, Egypt. Construction at the complex began during the reign of Senusret I (reigned 1971–1926 BC) in the Middle Kingdom () and continued into the Ptolemaic Kingdom (305–30 BC), although most of the extant buildings date from the New Kingdom. The area around Karnak was the ancient Egyptian ''Ipet-isut'' ("The Most Selected of Places") and the main place of worship of the 18th Dynastic Theban Triad, with the god Amun as its head. It is part of the monumental city of Thebes, and in 1979 it was added to the UNESCO World Heritage List along with the rest of the city. Karnak gets its name from the nearby, and partly surrounded, modern village of El-Karnak, north of Luxor. Name The original name of the temple was ''Ipet-isut'', meaning "The Most Select of Places". The complex's modern name "Karnak" comes from the nearby village of el-Karnak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sirius
Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky. Its name is derived from the Greek word (Latin script: ), meaning 'glowing' or 'scorching'. The star is designated Canis Majoris, Latinized to Alpha Canis Majoris, and abbreviated CMa or Alpha CMa. With a visual apparent magnitude of −1.46, Sirius is almost twice as bright as Canopus, the next brightest star. Sirius is a binary star consisting of a main-sequence star of spectral type A0 or A1, termed Sirius A, and a faint white dwarf companion of spectral type DA2, termed Sirius B. The distance between the two varies between 8.2 and 31.5 astronomical units as they orbit every 50 years. Sirius appears bright because of its intrinsic luminosity and its proximity to the Solar System. At a distance of , the Sirius system is one of Earth's nearest neighbours. Sirius is gradually moving closer to the Solar System and it is expected to increase in brightness slightly over t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heliacal Rising
The heliacal rising ( ) of a star or a planet occurs annually when it becomes visible above the eastern horizon at dawn just before sunrise (thus becoming "the Morning Star (other)#Astronomy, morning star"). A heliacal rising marks the time when a star or planet becomes visible for the first time again in the night sky after having set with the Sun at the western horizon in a previous sunset (its heliacal setting), having since been in the sky only during daytime, obscured by sunlight. Historically, the most important such rising is that of Sirius, which was an important feature of the Egyptian calendar and Egyptian astronomy, astronomical development. The rising of the Pleiades heralded the start of the Ancient Greek sailing season, using celestial navigation, as well as the farming season (attested by Hesiod in his Works and Days). Heliacal rising is one of several types of risings and settings, mostly they are grouped into morning and evening risings and settings of obj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptologists
This is a partial list of Egyptologists. An Egyptologist is any archaeologist, historian, linguist, or art historian who specializes in Egyptology, the scientific study of Ancient Egypt and its antiquities. Demotists are Egyptologists who specialize in the study of the Demotic language and field of Demotic Studies. Although a practitioner of the disciplined study of Ancient Egypt and Egyptian antiquities is an "Egyptologist", the field of Egyptology is not exclusive to such practitioners. A * Barbara G. Adams (British, 1945–2002) * Johan David Åkerblad (Swedish, 1763–1819) * Cyril Aldred (British, 1914–1991) * James Peter Allen (American, born 1945) * Maurice Alliot (French, 1903–1960) *Hartwig Altenmüller (German, born 1938) *Émile Amélineau (French, 1850–1915) * Alessia Amenta (Italian) * Guillemette Andreu (French, born 1948) * Tadeusz Andrzejewski (Polish, 1923–1961) *Jan Assmann (German, 1938–2024) *Éric Aubourg (French) * Sydney Hervé Aufrère (French, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manetho
Manetho (; ''Manéthōn'', ''gen''.: Μανέθωνος, ''fl''. 290–260 BCE) was an Egyptian priest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom who lived in the early third century BCE, at the very beginning of the Hellenistic period. Little is certain about his life. He is known today as the author of a history of Egypt in Greek called the '' Aegyptiaca'' (''History of Egypt''), written during the reign of Ptolemy I Soter or Ptolemy II Philadelphus (285–246 BCE). None of Manetho’s original texts have survived; they are lost literary works, known only from fragments transmitted by later authors of classical and late antiquity. The remaining fragments of the ''Aegyptiaca'' continue to be a singular resource for delineating Egyptian chronology, more than two millennia since its composition. Until the decipherment of Ancient Egyptian scripts in the early 19th century CE, Manetho's fragments were an essential source for understanding Egyptian history. His work remains of unique importan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bedouins
The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu ( ; , singular ) are pastorally nomadic Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia (Iraq). The Bedouin originated in the Syrian Desert and Arabian Desert but spread across the rest of the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa after the spread of Islam. The English word ''bedouin'' comes from the Arabic ''badawī'', which means "desert-dweller", and is traditionally contrasted with ''ḥāḍir'', the term for sedentary people. Bedouin territory stretches from the vast deserts of North Africa to the rocky ones of the Middle East. They are sometimes traditionally divided into tribes, or clans (known in Arabic as ''ʿašāʾir''; or ''qabāʾil'' ), and historically share a common culture of herding camels, sheep and goats. The vast majority of Bedouins adhere to Islam, although there are some fewer numbers of Christian Bedouins present in the Fertile Cres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomads
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, Nomadic pastoralism, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and Merchant, trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pastoral tribes slowly decreased, reaching an estimated 30–40 million nomads in the world . Nomadic hunting and gathering—following seasonally available wild plants and game—is by far the oldest human subsistence method known. Pastoralists raise herds of domesticated livestock, driving or accompanying them in patterns that normally avoid depleting pastures beyond their ability to recover. Nomadism is also a Lifestyle (sociology), lifestyle adapted to infertile regions such as steppe, tundra, or desert, ice and sand, where mobility is the most efficient strategy for exploiting scarce resources. For example, many groups living in the tundra are reindeer herders and are semi-nomadic, following forage for their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is equivalent to Cyprus and a stretch of land bordering the Mediterranean Sea in Western AsiaGasiorowski, Mark (2016). ''The Government and Politics of the Middle East and North Africa''. p. 5: "... today the term ''Levantine'' can describe shared cultural products, such as Levantine cuisine or Levantine archaeology". .Steiner & Killebrew, p9: "The general limits ..., as defined here, begin at the Plain of 'Amuq in the north and extend south until the Wâdī al-Arish, along the northern coast of Sinai. ... The western coastline and the eastern deserts set the boundaries for the Levant ... The Euphrates and the area around Jebel el-Bishrī mark the eastern boundary of the northern Levant, as d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nubia
Nubia (, Nobiin language, Nobiin: , ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the confluence of the Blue Nile, Blue and White Nile, White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), and the Cataracts of the Nile, first cataract of the Nile (south of Aswan in southern Egypt) or more strictly, Al Dabbah, Sudan, Al Dabbah. It was the seat of one of the earliest civilizations of ancient Africa, the Kerma culture, which lasted from around 2500 BC until its conquest by the New Kingdom of Egypt under Pharaoh Thutmose I around 1500 BC, whose heirs ruled most of Nubia for the next 400 years. Nubia was home to several African empires, empires, most prominently the Kingdom of Kush, which conquered Egypt in the eighth century BC during the reign of Piye and ruled the country as its Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt, 25th Dynasty. From the 3rd century BC to 3rd century AD, northern Nubia was invaded and annexed to Egypt, ruled by the Ptolemaic Kingdom, Greeks and Roman Empire, R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |