|
Thomaston, Maine
Thomaston, formerly known as Fort St. Georges, Fort Wharf, and Lincoln, is a New England town, town in Knox County, Maine, United States. The population was 2,739 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. Noted for its antique architecture, Thomaston is an old seaport, port popular with tourists. The town was named after John Thomas (American general), Major General John Thomas. History As early as 1630, a trading post was established on the eastern bank of the Saint George River, St. George River, then considered the boundary between New England and New France. In 1704, Thomas LeFebvre from Quebec bought a large tract of land along the Weskeag River on which he built a gristmill, with a house on the shoreline at what is now South Thomaston, Maine, South Thomaston. The area became known as Thomas' Town. In 1719–1720, the old trading post was remodeled into Fort St. George (Thomaston, Maine), Fort St. George, a stockaded fort protected by two blockhouses. But Abenaki Indig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
New England Town
The town is the basic unit of Local government in the United States, local government and local division of state authority in the six New England states. Most other U.S. states lack a direct counterpart to the New England town. New England towns overlie the entire area of a state, similar to civil townships in other states where they exist, but they are fully functioning Incorporation (municipal government), municipal corporations, possessing powers similar to city, cities and county, counties in other states. Local government in New Jersey, New Jersey's system of equally powerful townships, boroughs, towns, and cities is the system which is most similar to that of New England. New England towns are often governed by a town meeting, an assembly of eligible town residents. The great majority of municipal corporations in New England are based on the town model; there, statutory forms based on the concept of a Place (United States Census Bureau), compact populated place are uncommon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
South Thomaston, Maine
South Thomaston is a town in Knox County, Maine, United States. The population was 1,511 at the 2020 census. A fishing and resort area, the town includes the village of Spruce Head. History Abenaki Indians called it Wessaweskeag, meaning "tidal creek" or "salt creek," a reference to what is now known as the Weskeag River. Thomas Lefebvre from Quebec, Canada owned a huge tract of land at the Weskeag River, where his stay began in 1704. He built a large gristmill, with a house on the shoreline. Although he would eventually return to Quebec, the area retained his name—Thomas' Town. But the adjacent St. George River was the uneasy dividing line between land controlled by New England and New France. Permanent settlement would be delayed by the French and Indian Wars, which ended with the 1763 Treaty of Paris. In 1767, Wessaweskeag was settled by Elisha Snow, who built a sawmill operated by tidal power. In 1773, Joseph Coombs arrived and built another sawmill nearby, and tog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Friendship, Maine
Friendship (formerly known as Meduncook) is a town in Knox County, Maine, United States. It is 31 miles (49.9 km) southeast of Augusta. The population was 1,142 at the 2020 census. History Abenaki Native Americans called it Meduncook, meaning "bay at the end of the sandbar". Part of the Waldo Patent, it was first settled in 1750. A garrison was built on Garrison Island, which is connected to the mainland at low tide. By 1754, 22 families lived in Meduncook, most taking shelter within the garrison when the French and Indian War broke out. Raid on Meduncook (1758) During the French and Indian War, the community was raided twice. The first attack was from the Abenaki just after sunrise on May 22, 1758. They killed and scalped Joshua and Hannah Bradford and their infant son, Winslow. An original settler from Kingston, Massachusetts, and a great-grandson of Governor William Bradford, Joshua had remained in his house, believing it close enough to the garrison that his famil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Miramichi, New Brunswick
Miramichi ( ) is the largest city in northern New Brunswick, Canada. It is situated at the mouth of the Miramichi River where it enters Miramichi Bay. The Miramichi Valley is the second longest valley in New Brunswick, after the Saint John River (Bay of Fundy), Saint John River Valley. On 1 January 2023, Miramichi annexed parts of two Local service district (New Brunswick), local service districts on its northern border; revised census information has not been released. Neighbourhoods The city of Miramichi was formed in 1995 through the forced Municipal amalgamations in New Brunswick, amalgamation of two towns, Newcastle, New Brunswick, Newcastle and Chatham, New Brunswick, Chatham, and several smaller communities, including Douglastown, New Brunswick, Douglastown, Loggieville, New Brunswick, Loggieville, and Nelson-Miramichi, New Brunswick, Nelson. Also the local service districts of Nordin, New Brunswick, Nordin, Moorefield, New Brunswick, Moorefield, Chatham Head, New Brunsw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Charles Deschamps De Boishébert Et De Raffetot
Charles Deschamps de Boishébert (also known as Courrier du Bois, Bois Hebert) was a member of the Compagnies Franches de la Marine and was a significant leader of the Acadian militia's resistance to the Expulsion of the Acadians. He settled and tried to protect Acadians refugees along the rivers of New Brunswick. At Beaubears National Park on Beaubears Island, New Brunswick he settled refugee Acadians during the Expulsion of the Acadians. King George's War Siege of Annapolis Royal From October until 3 November 1746, Boishebert took part in the unsuccessful Siege of Annapolis Royal, Nova Scotia (N.S.), the British administrative and military headquarters in Acadia. Battle at Port-la-Joye After the first Siege of Louisbourg in May–June 1745, a British force composed largely of New England irregulars proceeded to seize Île Saint-Jean (present day Prince Edward Island) and its capital Port-la-Joye, which had a French garrison consisting of about 15 soldiers and 10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
French And Indian War
The French and Indian War, 1754 to 1763, was a colonial conflict in North America between Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of France, France, along with their respective Native Americans in the United States, Native American allies. European historians generally consider it a related conflict of the wider 1756 to 1763 Seven Years' War, although in the United States it is viewed as a singular conflict unassociated with any European war. Although Britain and France were officially at peace following the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle (1748), tensions over trade continued in North America. These culminated in a dispute over the Forks of the Ohio, and the related French Fort Duquesne which controlled them. In May 1754, this led to the Battle of Jumonville Glen, when Colony of Virginia, Virginia militia led by George Washington ambushed a French patrol. In 1755, Edward Braddock, the new Commander-in-Chief, North America, planned a four-way attack on the French. None s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Norridgewock
Norridgewock (Abenaki language, Abenaki: ''Nanrantsouak'') was the name of both an Indigenous village and a Band society, band of the Abenaki ("People of the Dawn") Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans/First Nations in Canada, First Nations, an Eastern Algonquian peoples, Algonquian tribe of the United States and Canada. The French of New France called the village Kennebec. The tribe occupied an area in the interior of Maine. During colonial times, this area was territory disputed between British and French colonists, and was set along the claimed western border of Acadia, the western bank of the Kennebec River. Archaeological evidence has identified several different sites associated with the settlement known as Norridgewock. The last one, where the French Jesuit priest Sebastian Rale had a mission, is today called Old Point, and is located in Madison, Maine, Madison. Other sites are located nearby in Starks, Maine, Starks and the present-day town of Norrid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Siege
A siege () . is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or by well-prepared assault. Siege warfare (also called siegecrafts or poliorcetics) is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterized by one party holding a strong, static, defensive position. Consequently, an opportunity for negotiation between combatants is common, as proximity and fluctuating advantage can encourage diplomacy. A siege occurs when an attacker encounters a city or fortress that cannot be easily taken by a quick assault, and which refuses to surrender. Sieges involve surrounding the target to block provision of supplies and reinforcement or escape of troops (a tactic known as "investment"). This is typically coupled with attempts to reduce the fortifications by means of siege engines, artillery bombardment, mining (also known as sapping), or the use of deception or treachery to bypass defenses. Failing a military outcome, sieges can often be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dummer's War
Dummer's War (1722–1725) (also known as Father Rale's War, Lovewell's War, Greylock's War, the Three Years War, the Wabanaki-New England War, or the Fourth Anglo-Abenaki War) was a series of battles between the New England Colonies and the Wabanaki Confederacy (specifically the Mi'kmaq, Maliseet, Penobscot, and Abenaki), who were allied with New France. The eastern theater of the war was located primarily along the border between New England and Acadia in Maine, as well as in Nova Scotia; the western theater was located in northern Massachusetts and Vermont in the frontier areas between Canada (New France) and New England.The Nova Scotia theater of the Dummer War is named the "Mi'kmaq-Maliseet War". John Grenier. ''The Far Reaches of Empire: War in Nova Scotia 1710–1760''. University of Oklahoma Press. 2008. The root cause of the conflict on the Maine frontier concerned the border between Acadia and New England, which New France defined as the Kennebec River in southern Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Garrison
A garrison is any body of troops stationed in a particular location, originally to guard it. The term now often applies to certain facilities that constitute a military base or fortified military headquarters. A garrison is usually in a city, town, fort, castle, ship, or similar site. "Garrison town" is a common expression for any town that has a military base nearby. The term garrison comes from the French language, French ''garnison'', itself from the verb ''garnir'', "to equip". "Garrison towns" () were used during the Early Muslim conquests, Arab Islamic conquests of Middle Eastern lands by Arabs, Arab-Muslim armies to increase their dominance over indigenous populations. In order to occupy non-Arab, non-Islamic areas, nomadic Arab tribesmen were taken from the desert by the ruling Arab elite, conscripted into Islamic armies, and settled into garrison towns as well as given a share in the Jizya, spoils of war. The primary utility of the Arab-Islamic garrisons was to cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Indigenous Peoples Of The Americas
In the Americas, Indigenous peoples comprise the two continents' pre-Columbian inhabitants, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with them in the 15th century, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with the pre-Columbian population of the Americas as such. These populations exhibit significant diversity; some Indigenous peoples were historically hunter-gatherers, while others practiced agriculture and aquaculture. Various Indigenous societies developed complex social structures, including pre-contact monumental architecture, organized city, cities, city-states, chiefdoms, state (polity), states, monarchy, kingdoms, republics, confederation, confederacies, and empires. These societies possessed varying levels of knowledge in fields such as Pre-Columbian engineering in the Americas, engineering, Pre-Columbian architecture, architecture, mathematics, astronomy, History of writing, writing, physics, medicine, Pre-Columbian agriculture, agriculture, irrigation, geology, minin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
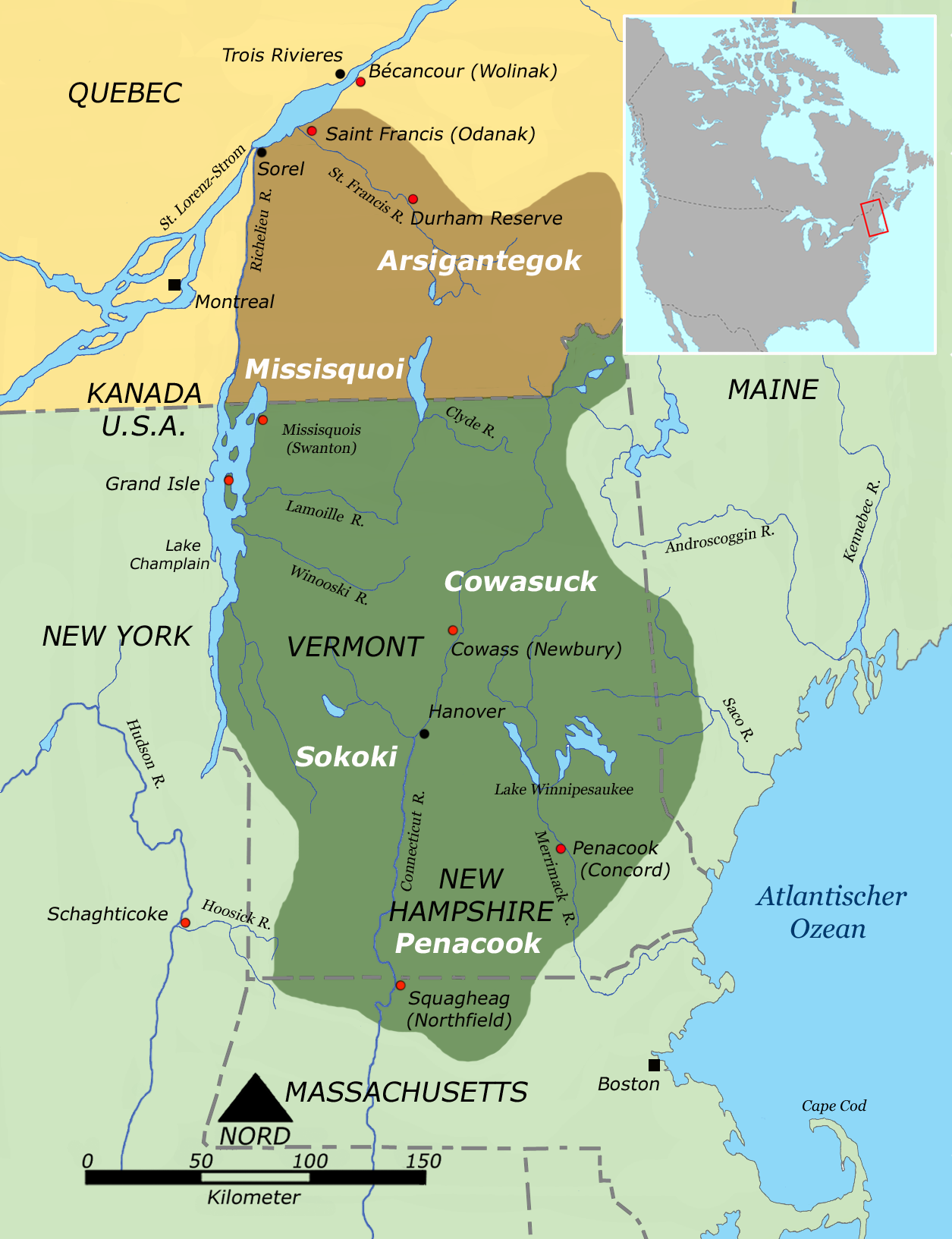
Abenaki
The Abenaki ( Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was predominantly spoken in Maine, while the Western Abenaki language was spoken in Quebec, Vermont, and New Hampshire. While Abenaki peoples have shared cultural traits, they did not historically have a centralized government. They came together as a post-contact community after their original tribes were decimated by colonization, disease, and warfare. Names The word ''Abenaki'' and its syncope, ''Abnaki,'' are both derived from ''Wabanaki'', or ''Wôbanakiak,'' meaning "People of the Dawn Land" in the Abenaki language. While the two terms are often confused, the Abenaki are one of several tribes in the Wabanaki Confederacy. Alternate spellings include: ''Abnaki'', ''Abinaki'', ''Alnôbak'', ''Abanakee'', ''Abanaki'', ''Abanaqui'', ''Abana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |