|
Thomas Dillon, 4th Viscount Dillon
Thomas Dillon, 4th Viscount Dillon PC (Ire) (March 1615 – 1673) held his title for 42 years that saw Strafford's administration, the Irish Rebellion of 1641, the Irish Confederate Wars and the Cromwellian Conquest of Ireland. He was a royalist and supported Strafford and Ormond. He sided with the Confederates for a while but was a moderate who opposed Rinuccini, the papal nuncio. Lord Dillon fled the field at the Battle of Dungan's Hill (1647) and did not rescue Ormond at the Battle of Rathmines (1649). However, he defended Athlone successfully against Ireton in 1650. Birth and origins Thomas was born in March 1615 in Ireland. He was the second son of Christopher Dillon and his wife Jane Dillon. His father was the eldest son and heir apparent of Theobald Dillon, 1st Viscount Dillon. Christopher predeceased his father and therefore never succeeded as viscount. He was a member of the landed gentry and known as Christopher Dillon of Ballylaghan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscount Dillon
Viscount Dillon, of Barony of Costello, Costello-Gallen (barony), Gallen in the County Mayo, County of Mayo, is a title in the Peerage of Ireland. It was created in 1622 for Theobald Dillon, 1st Viscount Dillon, Theobald Dillon, Lord President of Connaught. The Dillons were a Hiberno-Normans, Hiberno-Norman landlord family from the 13th century in a part of County Westmeath called 'Dillon's Country'. His great-grandson, the seventh Viscount, was a supporter of the Catholic James II of England, King James II of England and was outlawed after the Glorious Revolution. He founded 'Dillon Regiment, Dillon's Regiment' of the Irish Brigade (French)#Formation, Irish Brigade in the French Army, which was supported by the Flight of the Wild Geese, Wild Geese and achieved success at Battle of Fontenoy, Fontenoy in 1745. However, his son Henry, the eighth Viscount, managed to obtain a reversal of the outlawry in 1694 and later served as Lord Lieutenant of Roscommon, Lord Lieutenant of Count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theobald Dillon, 7th Viscount Dillon
Theobald Dillon, 7th Viscount Dillon of Costello-Gallin (died 1691) supported James II of England, King James II, was Attainder, attainted on 11 May 1691, and fell in the Battle of Aughrim during the Williamite War. His attainder was reversed in favour of the Henry Dillon, 8th Viscount Dillon, 8th Viscount on 20 June 1694. Birth and origins Theobald was probably born at Loughglynn, his parents' habitual residence. He was a son of Robert Dillon and his wife Rose Dillon. His father, Captain Robert Dillon of Loughglynn, was a member of the landed gentry. He was son and heir of Lucas Dillon of Loughglynn, who had been the second son of Theobald Dillon, 1st Viscount Dillon. At the time of Theobald's birth, the Dillons of Loughglynn were a cadet branch of the Viscount Dillon, Viscounts Dillon. Theobald's mother was a daughter of John Dillon of Streamstown, County Westmeath, Streamstown. Theobald appears as the elder of two brothers: #Theobald (died 1691) #Lucas, died unma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John, King Of England
John (24 December 1166 – 19 October 1216) was King of England from 1199 until his death in 1216. He lost the Duchy of Normandy and most of his other French lands to King Philip II of France, resulting in the collapse of the Angevin Empire and contributing to the subsequent growth in power of the French Capetian dynasty during the 13th century. The First Barons' War, baronial revolt at the end of John's reign led to the sealing of Magna Carta, a document considered a foundational milestone in English and later British constitution of the United Kingdom, constitutional history. John was the youngest son of King Henry II of England and Duchess Eleanor of Aquitaine. He was nicknamed John Lackland () because, as a younger son, he was not expected to inherit significant lands. He became Henry's favourite child following the failed revolt of 1173–1174 by his brothers Henry the Young King, Richard I of England, Richard, and Geoffrey II, Duke of Brittany, Geoffrey against their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
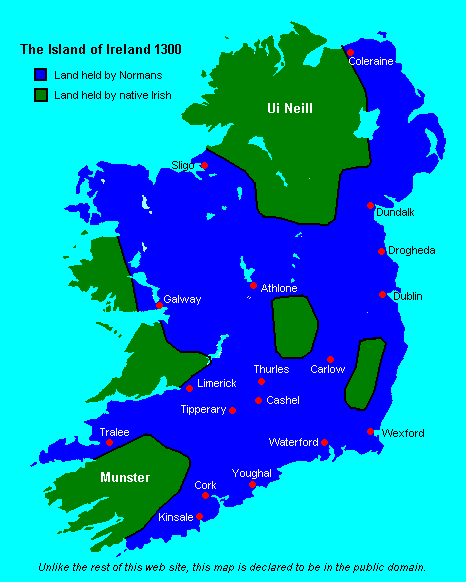
Normans In Ireland
Norman Irish or Hiberno-Normans (; ) is a modern term for the descendants of Norman settlers who arrived during the Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland in the 12th century. Most came from England and Wales. They are distinguished from the native Gaelic Irish; although some Normans eventually became Gaelicised. The Hiberno-Normans were a feudal aristocracy and merchant oligarchy who controlled the Lordship of Ireland. The Hiberno-Normans were associated with the Gregorian Reform of the Catholic Church in Ireland and contributed to the emergence of a Hiberno-English dialect. Some of the most prominent Hiberno-Norman families were the Burkes (de Burghs), Butlers, and FitzGeralds. One of the most common Irish surnames, Walsh, derives from Welsh Normans who arrived in Ireland as part of this group. Some Norman families were said to have become " more Irish than the Irish themselves" by merging culturally and intermarrying with the Gaels. The dominance of the Catholic Hiberno-N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Dillon, 1st Earl Of Roscommon
James Dillon, 1st Earl of Roscommon (died March 1641) fought for the crown in the Nine Years' War. He was ennobled despite being a Catholic after his son Robert turned Protestant. Birth and origins James was born in Ireland, the eldest son of Lucas Dillon ( – 1593) and his first wife Jane Bathe. At the time of his birth, his father was a lawyer but would later become a judge and finish his career as Chief Baron of the Irish Exchequer. His father's family was Old English and descended from Sir Henry Dillon who came to Ireland with Prince John in 1185 during the Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland. His family held substantial lands in Meath, Westmeath, Longford, and Roscommon. James's mother was a daughter of James Bathe (c. 1500 – 1570), who preceded James's father as chief baron of the Irish Exchequer. She was James's father's first wife. His father's second marriage was childless. James was one of 12 siblings, who are listed in his father's articl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Mayo
County Mayo (; ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. In the West Region, Ireland, West of Ireland, in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Connacht, it is named after the village of Mayo, County Mayo, Mayo, now generally known as Mayo Abbey. Mayo County Council is the Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local authority. The population was 137,231 at the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census. The boundaries of the county, which was formed in 1585, reflect the Mac William Íochtar lordship at that time. Geography It is bounded on the north and west by the Atlantic Ocean; on the south by County Galway; on the east by County Roscommon; and on the northeast by County Sligo. Mayo is the third-largest of Ireland's 32 counties in area and 18th largest in terms of population. It is the second-largest of Connacht's five counties in both size and population. Mayo has of coastline, or approximately 21% of the total coastline of the State. It is one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heir Apparent
An heir apparent is a person who is first in the order of succession and cannot be displaced from inheriting by the birth of another person. A person who is first in the current order of succession but could be displaced by the birth of a more eligible heir is known as an heir presumptive. Today these terms most commonly describe heirs to hereditary titles (e.g. titles of nobility) or offices, especially when only inheritable by a single person. Most monarchies refer to the heir apparent of their thrones with the descriptive term of ''crown prince'' or ''crown princess'', but they may also be accorded with a more specific substantive title: such as Prince of Orange in the Netherlands, Duke of Brabant in Belgium, Prince of Asturias in Spain (also granted to heirs presumptive), or the Prince of Wales in England and Wales; former titles include Dauphin in the Kingdom of France, and Tsesarevich in Imperial Russia. The term is also applied metaphorically to an expected succe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cokayne
George Edward Cokayne (29 April 1825 – 6 August 1911) was an English genealogist and long-serving herald at the College of Arms in London, who eventually rose to the rank of Clarenceux King of Arms. He wrote such authoritative and standard reference works as ''The Complete Peerage'' and '' The Complete Baronetage''. Origins Cokayne was born on 29 April 1825, with the surname Adams, being the son of William Adams by his wife the Hon. Mary Anne Cokayne, a daughter of Viscount Cullen. He was baptised George Edward Adams. On 15 August 1873, he changed his surname by Royal Licence to Cokayne (such changes were frequently made to meet the terms of bequests from childless relatives, often in the maternal line, who wished to see their name and arms continue). Career Education He matriculated from Exeter College, Oxford on 6 June 1844, and graduated BA in 1848 and MA in 1852. He was admitted a student of Lincoln's Inn on 16 January 1850, and was called to the bar on 30 April 1853 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Style And New Style Dates
Old Style (O.S.) and New Style (N.S.) indicate dating systems before and after a calendar change, respectively. Usually, they refer to the change from the Julian calendar to the Gregorian calendar as enacted in various Europe, European countries between 1582 and 1923. In England, Wales, Ireland and British America, Britain's American colonies, there were two calendar changes, both in 1752. The first adjusted the start of a new year from 25 March (Lady Day, the Feast of the Annunciation) to 1 January, a change which Scotland had made in 1600. The second discarded the Julian calendar in favour of the Gregorian calendar, skipping 11 days in the month of September to do so.. "Before 1752, parish registers, in addition to a new year heading after 24th March showing, for example '1733', had another heading at the end of the following December indicating '1733/4'. This showed where the Historical Year 1734 started even though the Civil Year 1733 continued until 24th March. ... We as h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julian Calendar
The Julian calendar is a solar calendar of 365 days in every year with an additional leap day every fourth year (without exception). The Julian calendar is still used as a religious calendar in parts of the Eastern Orthodox Church and in parts of Oriental Orthodox Churches, Oriental Orthodoxy as well as by the Amazigh, Amazigh people (also known as the Berbers). The Julian calendar was proposed in 46 BC by (and takes its name from) Julius Caesar, as a reform of the earlier Roman calendar, which was largely a lunisolar calendar, lunisolar one. It took effect on , by his edict. Caesar's calendar became the predominant calendar in the Roman Empire and subsequently most of the Western world for more than 1,600 years, until 1582 when Pope Gregory XIII promulgated a revised calendar. Ancient Romans typically designated years by the names of ruling consuls; the ''Anno Domini'' system of numbering years was not devised until 525, and became widespread in Europe in the eighth cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Latin Phrases (D)
References Further reading * * {{Latin phrases D ca:Locució llatina#D fr:Liste de locutions latines#D id:Daftar frasa Latin#D it:Locuzioni latine#D nl:Lijst van Latijnse spreekwoorden en uitdrukkingen#D pt:Lista de provérbios e sentenças em latim#D ro:Listă de locuțiuni în limba latină#D sl:Seznam latinskih izrekov#D sv:Lista över latinska ordspråk och talesätt#D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Dillon, 11th Viscount Dillon
Henry Dillon, 11th Viscount Dillon (1705–1787) was an Irish peer and a soldier in French service. He was the colonel proprietor of Dillon's Regiment, an Irish regiment of foot in French service, in 1741–1744 and again in 1747–1767. In the War of the Polish Succession (1733–1735), he fought at the sieges of Kehl and Philippsburg. In the War of the Austrian Succession (1740–1748), he was present at the Battle of Dettingen in 1743, on the French side, while King George II was present on the English side. He then resigned from the colonelcy, left France and married the rich English heiress Charlotte Lee, daughter of George Lee, 2nd Earl of Lichfield, acquiring lands in Oxfordshire, England, in addition to his Irish lands. During his second term as colonel he was absent and the regiment was led by hired soldiers. Birth and origins Henry was born in 1705, most likely at the Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France, where the Jacobite court ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |