|
Thimphu
Thimphu (; ) is the capital and largest city of Bhutan. It is situated in the western central part of Bhutan, and the surrounding valley is one of Bhutan's '' dzongkhags'', the Thimphu District. The ancient capital city of Punakha was replaced by Thimphu as the capital in 1955, and in 1961 Thimphu was officially declared the capital of the Kingdom of Bhutan by the 3rd Druk Gyalpo Jigme Dorji Wangchuck. The city extends in a north–south direction on the west bank of the valley formed by the Wang Chhu, which flows out into India as the Raidāk River. Thimphu is the sixth highest capital in the world by altitude, ranging from to . Unlike many capitals, Thimphu does not have its own airport, instead relying on the Paro Airport, accessible by road away. Thimphu, as the political and economic center of Bhutan, has a dominant agriculture and livestock base, contributing to about 45% of the country's GNP. Tourism, though a contributor to the economy, is strictly regulated, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhutan
Bhutan, officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked country in South Asia, in the Eastern Himalayas between China to the north and northwest and India to the south and southeast. With a population of over 727,145 and a territory of , Bhutan ranks List of countries and dependencies by area, 133rd in land area and List of countries and dependencies by population, 160th in population. Bhutan is a Democracy, democratic constitutional monarchy with a King of Bhutan, King as the head of state and a Prime Minister of Bhutan, prime minister as the head of government. The Je Khenpo is the head of the state religion, Vajrayana Buddhism. The Himalayas, Himalayan mountains in the north rise from the country's lush subtropical plains in the south. In the Mountains of Bhutan, Bhutanese Himalayas, there are peaks higher than above sea level. Gangkhar Puensum is Bhutan's highest peak and is the highest unclimbed mountain in the world. The wildlife of Bhutan is notable for its diversi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
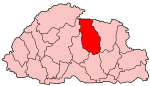
Thimphu District
Thimphu District (Dzongkha: ཐིམ་ཕུ་རྫོང་ཁག་; Wylie transliteration, Wylie: ''Thim-phu rdzong-khag'') is a dzongkhag (district) of Bhutan. Thimphu is also the capital of Bhutan and the largest city in the whole kingdom. Languages The dominant language throughout the district is Dzongkha; however, within the capital nearly every language of Bhutan may be encountered. Cultural sites Important cultural sites of Thimphu include: * Druk Wangditse Lhakhang * Dechen Phodrang Monastery, Dechen Phodrang Central Monastic School Tshelung Neyis the second Draphu Maratika where Guru Rinpoche received life empowerment (''Tse Ngedrup'') from Tsepakme. * Chagri Monastery, Chari Meditation Centre * Dochula Pass, Druk Wangyel Complex, Dochula * Memorial Chorten, Thimphu, National Memorial Chorten * Tango Monastery, Tango Choeying Dzong is the most important site of Phajo Drugom Zhigpo where ''Yidam Tandin'' appeared before him in person and delivered precepts t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jigme Dorji Wangchuck
Jigme Dorji Wangchuck (, ; 2 May 1928 – 21 July 1972) was the 3rd Druk Gyalpo of Bhutan. He began to open Bhutan to the outside world, began modernization, and took the first step towards democratization. Early life Jigme Dorji Wangchuck was born in 1928 in Thruepang Palace in Trongsa. At a young age, he was apprenticed in etiquette and leadership at the royal court of his father the King. Wangchuck was educated in a British manner in Kalimpong and Bishop Cotton School, Simla and he went on study tours to many foreign countries such as Scotland and Switzerland from where he drew inspiration to develop Bhutan with suitable adaptations. In 1943, he was appointed Trongsa '' Dronyer'' and then elevated as the 25th Paro '' Penlop'' in 1950, upon the death of the 24th Paro ''Penlop'', Tshering Penjor (1902–1949). Wangchuck married ''Ashi'' Kesang Choden Wangchuck (born 1930), the daughter of '' Gongzim'' (Lord Chamberlain) Sonam Topgay Dorji (1896–1953), at the Ugyen Pelr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dechencholing Palace
Dechencholing Palace (, ') is located in Thimphu, the capital of Bhutan, to the north of the Tashichho Dzong and north of the city centre. It was built in 1953 by the third List of rulers of Bhutan, king of Bhutan ''Druk Gyalpo'' Jigme Dorji Wangchuck. Geography The palace lies at the northern end of the Thimphu Valley, on the west bank of the Thimphu River. The palace is accessed via the Dechhen Lam (road) which runs along the eastern bank of the Thimphu river from the district of Yangchenphug, through Langjupakha for several kilometres before approaching the palace. On the way to the palace the road passes the Royal Banquet Hall, the Centre for Bhutan Studies, the Woodcraft Centre and then passes the Indian Estate on the other side of the river. Just south of the palace on the other side of the river is the suburb of Taba. The palace is surrounded by forest to the east and west; the eastern forest is denser and is said to be the only leafy forest in the city. Opposite on a slop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tashichho Dzong
Tashichho Dzong () is a Buddhist monastery and fortress on the northern edge of the city of Thimphu in Bhutan Bhutan, officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked country in South Asia, in the Eastern Himalayas between China to the north and northwest and India to the south and southeast. With a population of over 727,145 and a territory of , ..., on the western bank of the Wang Chu. It has traditionally been the seat of the Druk Desi (or "Deb Raja"), the head of Bhutan's civil government, an office which has been combined with the kingship since the creation of the monarchy in 1907, and summer capital of the country. In old British documents, it is known as Tassisudon. According to a 1922 traveller: The main structure of the whitewashed building is two-storied with three-storied towers at each of the four corners topped by triple-tiered golden roofs. There is also a large central tower or ''utse''. History The original Thimphu dzong (the Do-Ngön Dzong, or Bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts Of Bhutan
The Bhutan, Kingdom of Bhutan is divided into 20 districts (Dzongkha: ). Bhutan is located between the Tibet Autonomous Region of China and India on the eastern slopes of the Himalayas in South Asia. are the primary subdivisions of Bhutan. They possess a number of powers and rights under the Constitution of Bhutan, such as regulating commerce, running elections, and creating local governments. Local Government Act of Bhutan 2009, The Local Government Act of 2009 established local governments in each of the 20 overseen by the Ministry of Home and Cultural Affairs. Each has its own elected government with non-legislative executive powers, called a (district council). The is assisted by the administration headed by a (royal appointees who are the chief executive officer of each ). Each also has a Dzongkhag Court, court presided over by a (judge), who is appointed by the Chief Justice of Bhutan on the advice of Royal Judicial Service Council. The , and their residents, ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dzongkhag
The Kingdom of Bhutan is divided into 20 districts (Dzongkha: ). Bhutan is located between the Tibet Autonomous Region of China and India on the eastern slopes of the Himalayas in South Asia. are the primary subdivisions of Bhutan. They possess a number of powers and rights under the Constitution of Bhutan, such as regulating commerce, running elections, and creating local governments. The Local Government Act of 2009 established local governments in each of the 20 overseen by the Ministry of Home and Cultural Affairs. Each has its own elected government with non-legislative executive powers, called a (district council). The is assisted by the administration headed by a (royal appointees who are the chief executive officer of each ). Each also has a court presided over by a (judge), who is appointed by the Chief Justice of Bhutan on the advice of Royal Judicial Service Council. The , and their residents, are represented in the Parliament of Bhutan, a bicameral le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thromde
A Thromde (Dzongkha: ཁྲོམ་སྡེ་; Wylie: ''khrom-sde'') is a second-level administrative division in Bhutan. The legal administrative status of thromdes was most recently codified under the Local Government Act of 2009, and the role of thromdes in elections in Bhutan was defined in the Election Act of 2008. Governance Thromde administration is a product of the Bhutanese program of decentralization and devolution of power and authority. Thromdes are administered independently by a Thromde Tshogde if sufficiently developed and populated (Class A Thromdes); or directly by Dzongkhag Administration or the Gewog Administration as decided by the Government (Class B Thromdes and Yenlag Thromdes). From time to time, Parliament decides the boundaries of Thromde in consultation with the National Land Commission Secretariat and local authorities. Each Thromde Tshogde is composed of seven to ten elected members and headed by a Thrompon. Thromde Tshogdes are empowered to r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tshechu
A tshechu (, literally "tenth day") is any of the annual religious Bhutanese festivals held in each district or dzongkhag of Bhutan on the tenth day of a month of the lunar Tibetan calendar. The month depends on the place. Tshechus are religious festivals of the Drukpa Lineage of the Kagyu school of Tibetan Buddhism. Tshechus are large social gatherings, which perform the function of social bonding among people of remote and spread-out villages. Large markets also congregate at the fair locations, leading to brisk commerce.Dancing on the demon's back: the dramnyen dance and song of Bhutan by Elaine Dobson, John Blacking Symposium: Music Culture and Society, Callaway Centre, University of Western Australia, July 2003 The |
Gewogs Of Bhutan
A gewog ( ''geok'', block), in the past also spelled as geog, is a group of villages in Bhutan. The head of a ''gewog'' is called a ''gup'' ( ''gepo''). Gewogs form a geographic administrative unit below dzongkhag districts (and dungkhag subdistricts, where they exist), and above Dzongkhag Thromde class B and Yenlag Thromde municipalities. Dzongkhag Thromde class A municipalities have their own independent local government body. Bhutan comprises 205 gewogs, which average in area. The gewogs in turn are divided into chewogs for elections and thromdes "municipalities" for administration. The Parliament of Bhutan passed legislation in 2002 and 2007 on the status, structure, and leadership of local governments, including gewogs. The most recent legislation by parliament regarding gewogs is the Local Government Act of Bhutan 2009. In July 2011, the government slated 11 gewogs across Bhutan for reorganization, including both mergers and bifurcations, to be debated in dzongkhag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang Gewog
Chang Gewog (Dzongkha: ལྕང་) is a gewog (village block) of Thimphu District, Bhutan Bhutan, officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked country in South Asia, in the Eastern Himalayas between China to the north and northwest and India to the south and southeast. With a population of over 727,145 and a territory of , .... References Gewogs of Bhutan Thimphu District {{coord missing, Bhutan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Library Of Bhutan
The National Library of Bhutan (NLB; ), located in Thimphu, Bhutan, was established in 1967 for the purpose of "preservation and promotion of the rich cultural and religious heritage" of Bhutan. It is located in the Kawajangtsa area of Thimphu, above the Royal Thimphu Golf Course, near the Folk Heritage Museum and the National Institute for Zorig Chusum (Traditional Arts and Crafts). History The National Library of Bhutan was first established in 1967 under the patronage of HM Queen Ashi Phuntso Choden (1911–2003), with a small collection of precious texts. The library was initially housed within the central tower (utse) of Tashichodzong. Later, due to its growing collection, it had to move to a building in the Changgangkha area of Thimphu. To provide a permanent home for the sacred religious books and manuscripts in the growing collection, construction of the present four-storeyed eight-cornered traditional building, which looks like the central tower temple of a Bhutanese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |