|
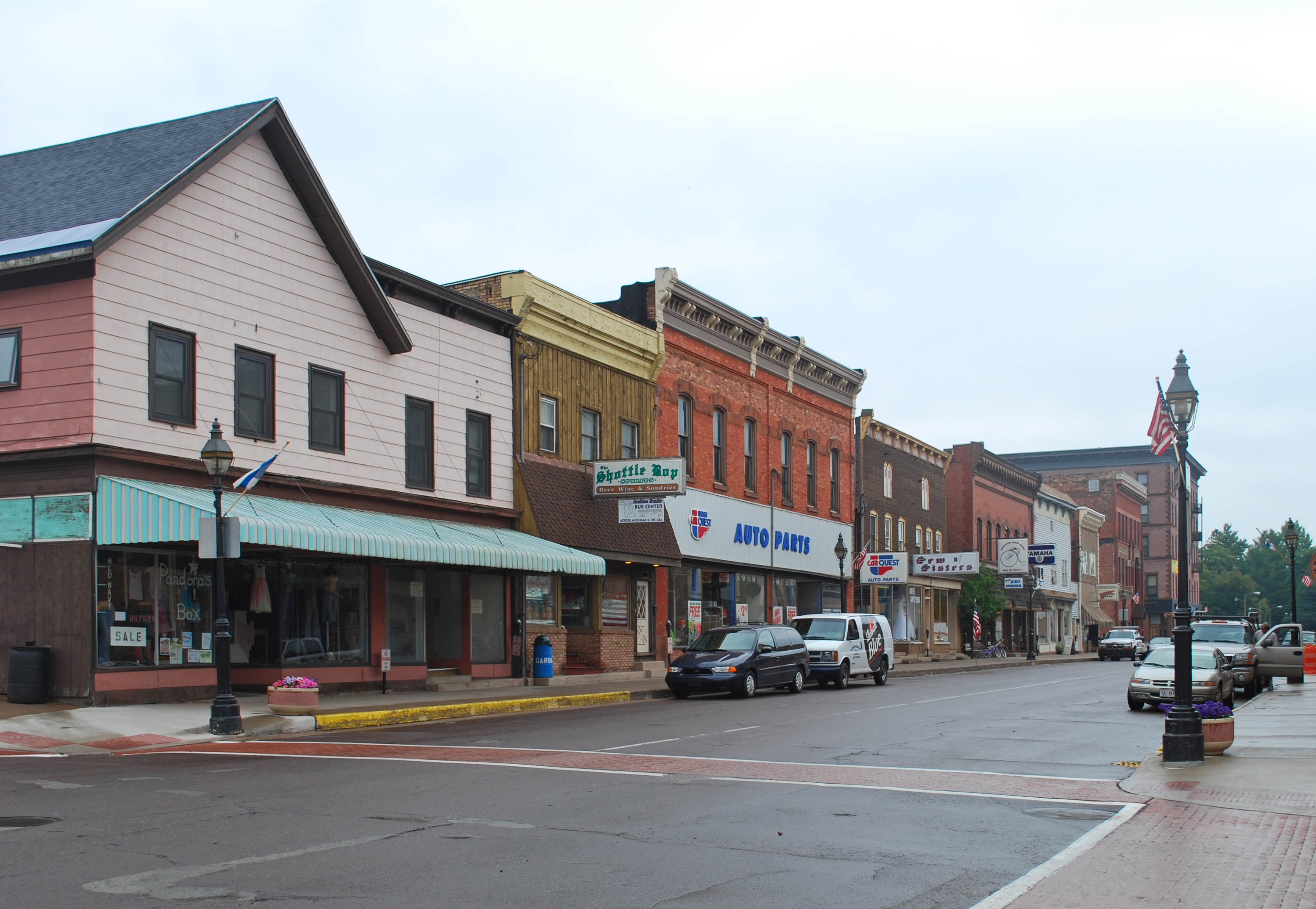
Thermopolis, Wyoming
Thermopolis is the county seat and most populous town in Hot Springs County, Wyoming, United States. As of the 2020 U.S. Census, the town population was 2,725. Thermopolis, Greek for "hot city", is home to numerous natural hot springs, in which mineral-laden waters are heated by geothermal processes. The town is named for the hot springs located there. The town claims the world's largest mineral hot spring, appropriately named "The Big Spring", as part of Hot Springs State Park. The springs are open to the public for free as part of an 1896 treaty signed with the Shoshone and Arapaho Indian tribes. Dinosaur fossils were found on the Warm Springs Ranch in 1993, and the Wyoming Dinosaur Center was founded soon after. Geography Thermopolis is located near the northern end of the Wind River Canyon and Wedding of the Waters, where the north-flowing Wind River becomes the Bighorn River. It is an unusual instance of a river changing names at a point other than a confluence of two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Town
A town is a type of a human settlement, generally larger than a village but smaller than a city. The criteria for distinguishing a town vary globally, often depending on factors such as population size, economic character, administrative status, or historical significance. In some regions, towns are formally defined by legal charters or government designations, while in others, the term is used informally. Towns typically feature centralized services, infrastructure, and governance, such as municipal authorities, and serve as hubs for commerce, education, and cultural activities within their regions. The concept of a town varies culturally and legally. For example, in the United Kingdom, a town may historically derive its status from a market town designation or City status in the United Kingdom, royal charter, while in the United States, the term is often loosely applied to incorporated municipality, municipalities. In some countries, such as Australia and Canada, distinction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between sovereign states and/or international organizations that is governed by international law. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, convention, pact, or exchange of letters, among other terms; however, only documents that are legally binding on the parties are considered treaties under international law. Treaties may be bilateral (between two countries) or multilateral (involving more than two countries). Treaties are among the earliest manifestations of international relations; the first known example is a border agreement between the Sumer, Sumerian city-states of Lagash and Umma around 3100 BC. International agreements were used in some form by most major civilizations and became increasingly common and more sophisticated during the Early modern period, early modern era. The early 19th century saw developments in diplomacy, foreign policy, and international law reflected by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Horn Basin
The Bighorn Basin is a plateau region and intermontane basin, approximately 100 miles (160 km) wide, in north-central Wyoming in the United States. It is bounded by the Absaroka Range on the west, the Pryor Mountains on the north, the Bighorn Mountains on the east, and the Owl Creek Mountains and Bridger Mountains on the south. It is drained to the north by tributaries of the Bighorn River, which enters the basin from the south, through a gap between the Owl Creek and Bridger Mountains, as the Wind River, and becomes the Bighorn as it enters the basin. The region is semi-arid, receiving only 6–10 in (15–25 cm) of rain annually. The largest cities in the basin include the Wyoming towns of Cody, Thermopolis, Worland, and Powell. Sugar beets, pinto beans, sunflowers, barley, oats, corn and alfalfa hay are grown on irrigated farms in the region. History The basin was explored by John Colter in 1807. Just west of Cody, he discovered geothermal features th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absaroka Range
The Absaroka Range is a sub- range of the Rocky Mountains in the United States. The range stretches about across the Montana–Wyoming border, and at its widest, forming the eastern boundary of Yellowstone National Park along Paradise Valley, and the western side of the Bighorn Basin. The range borders the Beartooth Mountains to the north and the Wind River Range to the south. The northern edge of the range rests along I-90 and Livingston, Montana. The highest peak in the range is Francs Peak, located in Wyoming at . There are 46 other peaks over . Geography The range is drained by the Yellowstone River and various tributaries, including the Bighorn River. Most of the range lies within protected lands including Yellowstone Park, the Absaroka-Beartooth Wilderness, North Absaroka Wilderness, Teton Wilderness, and Washakie Wilderness, spanning the Bridger-Teton National Forest, Custer National Forest, Gallatin National Forest, and Shoshone National Forest. U.S. Hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Owl Creek Mountains
The Owl Creek Mountains are a subrange of the Rocky Mountains in central Wyoming in the United States, running east to west to form a bridge between the Absaroka Range to the northwest and the Bridger Mountains to the east. The range forms the boundary between the Bighorn Basin to the north and the Shoshone Basin to the south. The Wind River passes through the gap between the range and the Bridger Mountains to the east, and becomes the Bighorn River on the north side of the mountains. The high point of the range is . The range is entirely within the Wind River Indian Reservation. Geology During the Tertiary period, the rivers in the region removed much of the basin fill exposing older bedrock. The rocks in the Owl Creek Range date from the Mississippian age through the Cretaceous period. The mountains likely emerged in the late Cretaceous, in the Laramide orogeny. In areas near the Boysen Fault, just north of Boysen Reservoir's dam at the southern mouth of Wind River Canyon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridger Mountains (Wyoming)
The Bridger Mountains are a short subrange of the Rocky Mountains, approximately long, in central Wyoming in the United States. The range forms a bridge between the Owl Creek Mountains to the west and the southern end of the Bighorn Mountains to the east. The Wind River passes through the gap between the range and the Owl Creek Mountains. Bridger Creek passes through the gap between the range and the Bighorns. The highest point in the range is Copper Mountain at . 150px, The mountains are named for Jim Bridger The range is named after Jim Bridger, who pioneered the Bridger Trail through the mountains from southern Wyoming into the Bighorn Basin in 1864. Bates Creek in the eastern part of the range is the location of Bates Battlefield, a significant battle on July 4, 1874, in which the U.S. Army soldiers from Camp Brown (Today's Fort Washakie) with 167 Shoshone scouts attacked the village of Chief Black Coal (Northern Arapaho), killing at least 34 Northern Arapahos. A tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Horn Mountains
The Bighorn Mountains ( or ) are a mountain range in northern Wyoming and southern Montana in the United States, forming a northwest-trending spur from the Rocky Mountains extending approximately northward on the Great Plains. They are separated from the Absaroka Range, which lie on the main branch of the Rockies to the west, by the Bighorn Basin. Much of the land is contained within the Bighorn National Forest. Geology The Bighorns were uplifted during the Laramide orogeny beginning approximately 70 million years ago. They consist of over of sedimentary rock strata laid down before mountain-building began: the predominantly marine and near-shore sedimentary layers range from the Cambrian through the Lower Cretaceous, and are often rich in fossils. There is an unconformity where Silurian strata were exposed to erosion and are missing. The granite bedrock below these sedimentary layers is now exposed along the crest of the Bighorns. The Precambrian formations contain some of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bighorn Basin
The Bighorn Basin is a plateau region and intermontane basin, approximately 100 miles (160 km) wide, in north-central Wyoming in the United States. It is bounded by the Absaroka Range on the west, the Pryor Mountains on the north, the Bighorn Mountains on the east, and the Owl Creek Mountains and Bridger Mountains (Wyoming), Bridger Mountains on the south. It is drained to the north by tributaries of the Bighorn River, which enters the basin from the south, through a gap between the Owl Creek and Bridger Mountains, as the Wind River (Wyoming), Wind River, and becomes the Bighorn as it enters the basin. The region is semi-arid, receiving only 6–10 in (15–25 cm) of rain annually. The largest cities in the basin include the Wyoming towns of Cody, Wyoming, Cody, Thermopolis, Wyoming, Thermopolis, Worland, Wyoming, Worland, and Powell, Wyoming, Powell. Sugar beets, pinto beans, sunflowers, barley, oats, corn and alfalfa hay are grown on irrigated farms in the region. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
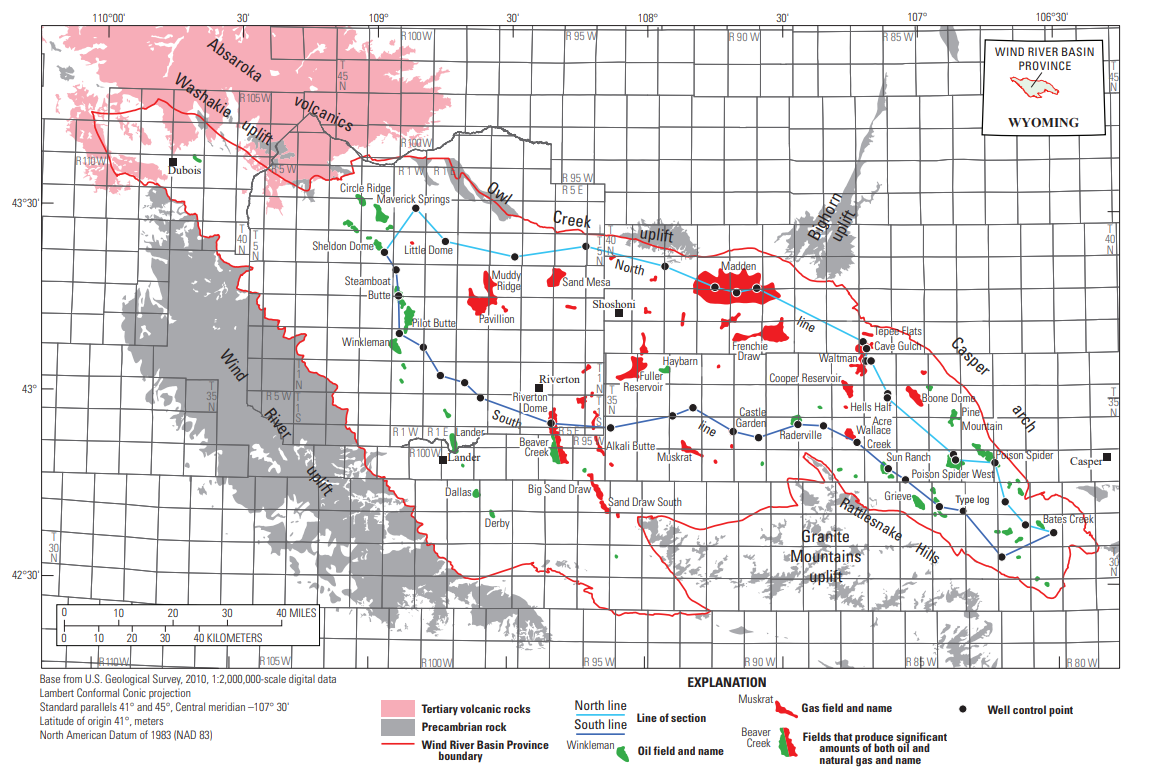
Wind River Basin
The Wind River Basin is a semi-arid intermontane foreland basin in central Wyoming, United States. It is bounded by Laramide orogeny, Laramide uplifts on all sides. On the west is the Wind River Range and on the North are the Absaroka Range and the Owl Creek Mountains. The Casper Arch separates the Wind River from the Powder River Basin to the east and the Sweetwater Uplift (Granite Mountains (Wyoming), Granite Range) lies to the south. The basin contains a sequence of of predominantly marine sediments deposited during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic Eras. During the Laramide over of Eocene lake, lacustrine and fluvial sediments were deposited within the basin. Following the Eocene an additional of sediments were deposited before, and as the basin was uplifted in the late Tertiary period, Tertiary. The geological formations within the basin are significant producers of petroleum and natural gas. The basin contains over 60 oil and gas fields mostly as structural traps within sevent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bighorn River
The Bighorn River is a tributary of the Yellowstone, approximately long, in the states of Wyoming and Montana in the western United States. The river was named in 1805 by fur trader François Larocque for the bighorn sheep he saw along its banks as he explored the Yellowstone. The upper reaches of the Bighorn, south of the Owl Creek Mountains in Wyoming, are known as the Wind River. The two rivers are sometimes referred to as the Wind/Bighorn. The Wind River officially becomes the Bighorn River at the Wedding of the Waters, on the north side of the Wind River Canyon near the town of Thermopolis. From there, the river flows through the Bighorn Basin in north central Wyoming, passing through Thermopolis and Hot Springs State Park. At the border with Montana, the river turns northeast, and flows past the north end of the Bighorn Mountains, through the Crow Indian Reservation, where the Yellowtail Dam forms the Bighorn Lake reservoir. The reservoir and the surrounding c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind River (Wyoming)
The Wind River is the name applied to the upper reaches of the Bighorn River in Wyoming in the United States. The Wind River is long. The two rivers are sometimes referred to as the Wind/Bighorn. Course Its headwaters are at Wind River Lake in the Rocky Mountains, near the summit of Togwotee Pass (pronounced TOH-guh-tee) and gathers water from several forks along the northeast side of the Wind River Range in west central Wyoming. It flows southeastward, across the Wind River Basin and the Wind River Indian Reservation and joins the Little Wind River near Riverton. Up stream from this confluence, it is known locally as the Big Wind River. It flows northward, through a gap in the Owl Creek Mountains, where the name of the river becomes the Bighorn River. In the Owl Creek Mountains, it is dammed to form Boysen Reservoir Boysen Reservoir is a reservoir formed by Boysen Dam, an earth-fill dam on the Wind River (Wyoming), Wind River in the central part of the U.S. state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
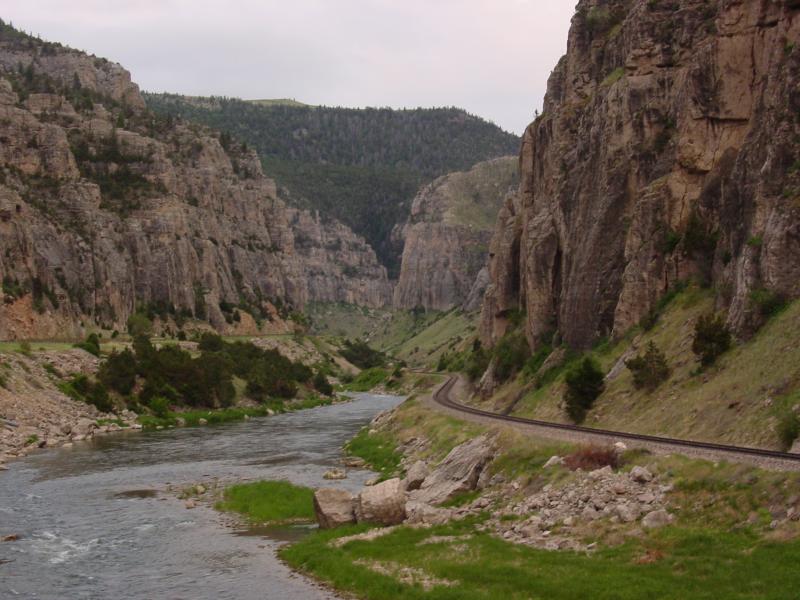
Wind River Canyon
Wind River Canyon is a scenic Wyoming canyon on the Wind River (Wyoming), Wind River. It is located between the towns of Shoshoni, Wyoming, Shoshoni and Thermopolis, Wyoming, Thermopolis and is a popular stop for visitors to Yellowstone National Park. It is accessible by U.S. Route 20, U.S. Highway 20 and Wyoming Highway 789. It was designated as a Wyoming Scenic Byway in 2005. Description Work on U.S. 20/Wyo 789 through Wind River canyon began in 1922 and was finished in 1924, replacing the Bird's Eye Pass Route over the Owl Creek Mountains. U.S. 20/Wyo 789 travels through the canyon, at times level with the canyon floor. The scenic route offers views of the canyon and landmark natural structures like the Chimney Rock. The canyon is at times as much as feet deep. The change in elevation between the Bighorn Basin and the Wind River Basin is about . The southern mouth of the canyon is near the Boysen Dam in Boysen State Park several miles north of, and about half a mile east of, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |