|
Theodoric III Of Montbéliard
Theodoric is a Germanic given name. First attested as a Gothic name in the 5th century, it became widespread in the Germanic-speaking world, not least due to its most famous bearer, Theodoric the Great, king of the Ostrogoths. Overview The name was Latinisation of names, Latinized as ''Theodoricus'' or ''Theodericus'', originally from a Proto-Germanic language, Common Germanic form ''*wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Germanic/Þeudarīks, Þeudarīks'' ("people-ruler") from *''wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Germanic/þeudō, þeudō'' ("people") and *''wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Germanic/rīks, rīks'', which would have resulted in a Gothic language, Gothic *𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰𐍂𐌴𐌹𐌺𐍃 (*þiudareiks). Anglicized spellings of the name during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages include ''Theodoric'', ''Theoderic'', ''Theudoric'', ''Theuderic''. Gregory of Tours Latinized the name as ''Theodore (given name), Theodorus'', in origin the unrelated Greek name Theodore (given name), T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
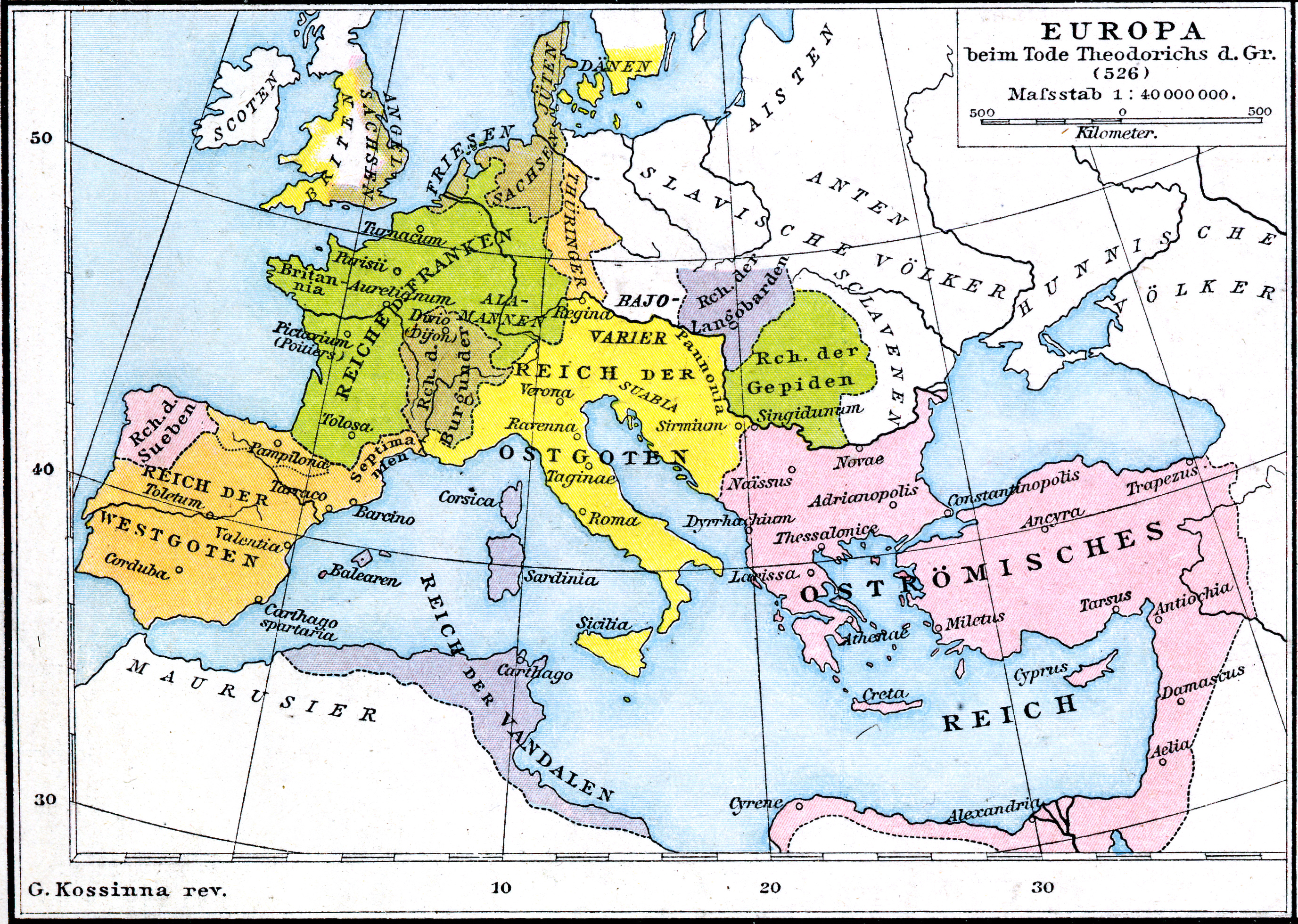
Theodoric The Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal, was king of the Ostrogoths (475–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy between 493 and 526, regent of the Visigoths (511–526), and a patrician (ancient Rome)#Late Roman and Byzantine period, patrician of the Byzantine Empire#Loss of the Western Roman Empire, Eastern Roman Empire. As ruler of the combined Gothic realms, Theodoric controlled an empire stretching from the Atlantic Ocean to the Adriatic Sea. Though Theodoric himself only used the title 'king' (''rex''), some scholars characterize him as a Roman Emperor#Later assertions to the title, Western Roman emperor in all but name, since he ruled a large part of the former Western Roman Empire described as a ''Res Publica'', had received the former Western imperial regalia from Constantinople in 497 which he used, was referred to by the imperial title ''princeps'' by the Italian aristocracy and exercised imper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tietje
Tietje is a surname and given name. Notable people with the name include: * Les Tietje (1910–1996), American baseball player * Tietje Spannenburg-Pagels (1906 – after 1933), Dutch ''kortebaan'' speed skater See also * {{given name, type=both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reich
( ; ) is a German word whose meaning is analogous to the English word " realm". The terms and are respectively used in German in reference to empires and kingdoms. In English usage, the term " Reich" often refers to Nazi Germany, also called "the Third Reich". The term (sometimes translated to "German Empire") continued to be used even after the collapse of the German Empire and the abolition of the monarchy in 1918. There was no emperor, but many Germans had imperialistic ambitions. According to historian Richard J. Evans: The term is used for historical empires in general, such as the Roman Empire (), Persian Empire (), and both the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire (, literally " Tsars' realm"). , the name used for Austria today, is composed of and which, literally translated, means "Eastern Realm". The name once referred to the eastern parts of the Holy Roman Empire. In the history of Germany specifically, it is used to refer to: * the early medieva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Celtic
The Continental Celtic languages are the now-extinct group of the Celtic languages that were spoken on the continent of Europe and in central Anatolia, as distinguished from the Insular Celtic languages of the British Isles, Ireland and Brittany. ''Continental Celtic'' is a geographic, rather than linguistic, grouping of the ancient Celtic languages. These languages were spoken by the people known to Roman and Greek writers as the ''Keltoi'', ''Celtae'', ''Galli'', and ''Galatae''. They were spoken in an area arcing from the northern half of Iberia in the west to north of Belgium, and east to the Carpathian basin and the Balkans as Noric, and in inner Anatolia (modern day Turkey) as Galatian. Even though Breton has been spoken in Continental Europe since at least the 6th century AD, it is not considered one of the Continental Celtic languages, as it is a Brittonic language, like Cornish and Welsh. A Gaulish substratum in Breton has been suggested, but that is debated. Att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Language
Gothic is an extinct language, extinct East Germanic languages, East Germanic language that was spoken by the Goths. It is known primarily from the ''Codex Argenteus'', a 6th-century copy of a 4th-century Bible translation, and is the only East Germanic language with a sizeable text corpus. All others, including Burgundian language (Germanic), Burgundian and Vandalic language, Vandalic, are known, if at all, only from proper names that survived in historical accounts, and from loanwords in other, mainly Romance languages, Romance, languages. As a Germanic language, Gothic is a part of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is the earliest Germanic language that is attested in any sizable texts, but it lacks any modern descendants. The oldest documents in Gothic date back to the fourth century. The language was in decline by the mid-sixth century, partly because of the military defeat of the Goths at the hands of the Franks, the elimination of the Goths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Germanic Language
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages. Proto-Germanic eventually developed from pre-Proto-Germanic into three Germanic branches during the fifth century BC to fifth century AD: West Germanic, East Germanic and North Germanic. North Germanic remained in contact with the other branches over a considerable time, especially with the Ingvaeonic languages (including English), which arose from West Germanic dialects, and had remained in contact with the Norse. A defining feature of Proto-Germanic is the completion of the process described by Grimm's law, a set of sound changes that occurred between its status as a dialect of Proto-Indo-European and its gradual divergence into a separate language. The end of the Common Germanic period is reached with the beginning of the Migration Period in the fourth century AD. The alternative term " Germanic parent langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latinisation Of Names
Latinisation (or Latinization) of names, also known as onomastic Latinisation (or onomastic Latinization), is the practice of rendering a ''non''-Latin name in a Neo-Latin, modern Latin style. It is commonly found with historical proper names, including personal names and toponyms, and in the standard binomial nomenclature of the life sciences. It goes further than romanisation, which is the transliteration of a word to the Latin alphabet from another script (e.g. Cyrillic). For authors writing in Latin, this change allows the name to function grammatically in a sentence through declension. In a scientific context, the main purpose of Latinisation may be to produce a name which is internationally consistent. Latinisation may be carried out by: * transforming the name into Latin sounds (e.g. for ), or * adding Latinate suffixes to the end of a name (e.g. for ''Heinrich Meibom (doctor), Meibom),'' or * translating a name with a specific meaning into Latin (e.g. for Italian ; b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths () were a Roman-era Germanic peoples, Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Goths, Gothic kingdoms within the Western Roman Empire, drawing upon the large Gothic populations who had settled in the Balkans in the 4th century. While the Visigoths had formed under the leadership of Alaric I, the new Ostrogothic political entity which came to rule Italy was formed in the Balkans under Theodoric the Great. Theoderic's family, the Amal dynasty, accumulated royal power in Roman Pannonia after the death of Attila, and collapse of his Hunnic empire. Byzantine Empire, Byzantine Zeno (emperor), Emperor Zeno played these Pannonian Goths off against the Thracian Goths to their south. However, instead the two groups united after the death of the Thracian leader Theoderic Strabo and his son Recitach. Zeno then backed Theodoric to invade Italy and replace Odoacer there, whom he had previously supported as its king. In 493, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Name
The Onomastics of the Gothic language (Gothic personal names) are an important source not only for the history of the Goths themselves, but for Germanic onomastics in general and the linguistic and cultural history of the Germanic Heroic Age of c. the 3rd to 6th centuries. Gothic names can be found in Roman records as far back as the 4th century AD. After the Muslim invasion of Hispania and the fall of the Visigothic kingdom in the early 8th century, the Gothic tradition was largely interrupted, although Gothic or pseudo-Gothic names continued to be given in the Kingdom of Asturias in the 9th and 10th centuries. (Not to be confused with names inspired by the modern-day Goth subculture.) History The names of the Goths themselves have been traced to their 3rd century settlement in Scythia. The names Tervingi and Greuthungi have been interpreted as meaning "forest-dwellers" and "steppe-dwellers", respectively. Later on, the terms Ostrogothi and Visigothi have also been under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |