|
Themata
The themes or (, , singular: , ) were the main military and administrative divisions of the middle Byzantine Empire. They were established in the mid-7th century in the aftermath of the Slavic migrations to Southeastern Europe and Muslim conquests of parts of Byzantine territory, and replaced the earlier provincial system established by Diocletian and Constantine the Great. In their origin, the first themes were created from the areas of encampment of the field armies of the East Roman army, and their names corresponded to the military units that had existed in those areas. The theme system reached its apogee in the 9th and 10th centuries, as older themes were split up and the conquest of territory resulted in the creation of new ones. The original theme system underwent significant changes in the 11th and 12th centuries, but the term remained in use as a provincial and financial circumscription until the very end of the Empire. History Background During the late 6th and earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Romanization (cultural), Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine the Great, Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I, Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subdivisions Of The Byzantine Empire
Subdivisions of the Byzantine Empire were administrative units of the Byzantine Empire, Eastern Roman or Byzantine Empire (330–1453). The Empire had a developed administrative system, which can be divided into three major periods: the late Roman/early Byzantine, which was a continuation and evolution of the system begun by the emperors Diocletian and Constantine the Great, which gradually evolved into the middle Byzantine, where the theme system predominated alongside a restructured Byzantine bureaucracy, central bureaucracy, and the late Byzantine, where the structure was more varied and decentralized and where feudal elements appeared. Early period: 4th–7th centuries The classical administrative model, as exemplified by the ''Notitia Dignitatum'', divided the late Roman Empire into Roman province, provinces, which in turn were grouped into Roman diocese, dioceses and then into praetorian prefectures. The late Roman administrative system remained intact until the 530s, when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Province
The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as Roman governor, governor. For centuries, it was the largest administrative unit of the foreign possessions of ancient Rome. With the administrative reform initiated by Diocletian, it became a third level administrative subdivision of the Roman Empire, or rather a subdivision of the Roman diocese, imperial dioceses (in turn subdivisions of the Praetorian prefecture, imperial prefectures). History A province was the basic and, until the Tetrarchy (from AD 293), the largest territorial and administrative unit of the empire's territorial possessions outside Roman Italy. During the republic and early empire, provinces were generally governed by politicians of Roman senate, senatorial rank, usually former Roman consul, consuls or former praetors. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
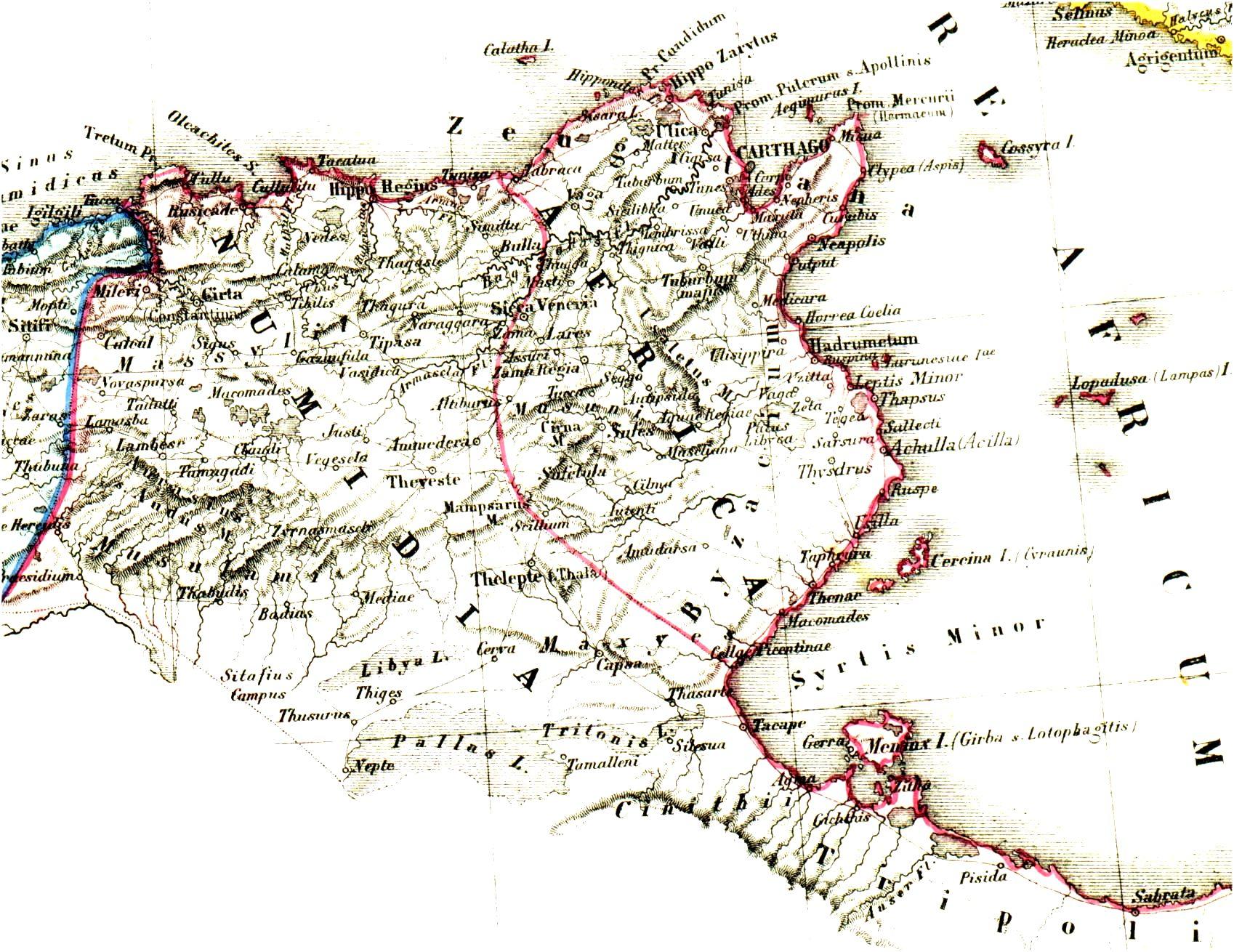
Praetorian Prefecture Of Africa
The Praetorian Prefecture of Africa () was an administrative division of the Byzantine Empire in the Maghreb. With its seat at Carthage, it was established after the reconquest of northwestern Africa from the Vandals in 533–534 by the Byzantine Emperor Justinian I. It continued to exist until 591, when it was replaced by the Exarchate of Africa. History Establishment In 533, the Eastern Roman army under Belisarius defeated and destroyed the Vandal Kingdom that had existed in the former Roman territories of Northern Africa. Immediately after the victory, in April 534, the emperor Justinian published a law concerning the administrative organization of the recovered territories. The old provinces of the Roman Diocese of Africa had been mostly preserved by the Vandals, but large parts, including almost all of Mauretania Tingitana, much of Mauretania Caesariensis and Mauretania Sitifensis and large parts of the interior of Numidia and Byzacena, had been lost to the inland Berbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maurice (emperor)
Maurice (; ; 539 – 27 November 602) was Eastern Roman emperor from 582 to 602 and the last member of the Justinian dynasty. A successful general, Maurice was chosen as heir and son-in-law by his predecessor Tiberius II. Maurice's reign was troubled by almost constant warfare. After he became emperor, he brought the Byzantine–Sasanian War of 572–591, war with Sasanian Persia to a Battle of the Blarathon, victorious conclusion. The empire's eastern border in the South Caucasus was vastly expanded and, for the first time in nearly two centuries, the Romans were no longer obliged to pay the Persians thousands of pounds of gold annually for peace. Afterward, Maurice Maurice's Balkan campaigns, campaigned extensively in the Balkans against the Pannonian Avars, Avars—pushing them back across the Danube by 599. He also conducted campaigns across the Danube, the first Roman emperor to do so in over two centuries. In the west, he established two large semi-autonomous provinces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exarch
An exarch (; from Ancient Greek ἔξαρχος ''exarchos'') was the holder of any of various historical offices, some of them being political or military and others being ecclesiastical. In the late Roman Empire and early Byzantine Empire, an ''exarch'' was a governor of a particular territory. From the end of the 3rd century or early 4th, every Roman diocese was governed by a vicarius, who was titled "exarch" in eastern parts of the Empire, where the Greek language and the use of Greek terminology dominated, even though Latin was the language of the imperial administration from the provincial level up until the 440s (Greek translations were sent out with the official Latin text). In Greek texts, the Latin title is spelled βικάριος (). The office of exarch as a governor with extended political and military authority was later created in the Byzantine Empire, with jurisdiction over a particular territory, usually a frontier region at some distance from the capital Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viceroy
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory. The term derives from the Latin prefix ''vice-'', meaning "in the place of" and the Anglo-Norman ''roy'' (Old French ''roi'', ''roy''), meaning "king". This denotes the position as one who acts on behalf of a king or monarch. A viceroy's territory may be called a viceroyalty, though this term is not always applied. The adjective form is ''viceregal'', less often ''viceroyal''. The term ''vicereine'' is sometimes used to indicate a female viceroy '' suo jure'', although ''viceroy'' can serve as a gender-neutral term. Vicereine is more commonly used to indicate a viceroy's wife, known as the ''viceregal consort''. The term has occasionally been applied to the governors-general of the Commonwealth realms, who are ''viceregal'' representatives of the monarch. The position of a viceroy is by royal appointment rather than a noble rank. An individual vicer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exarchate Of Ravenna
The Exarchate of Ravenna (; ), also known as the Exarchate of Italy, was an administrative district of the Byzantine Empire comprising, between the 6th and 8th centuries, the territories under the jurisdiction of the exarch of Italy (''exarchus Italiae'') resident in Ravenna. The term is used in historiography in a double sense: "exarchate" in the strict sense denotes the territory under the direct jurisdiction of the exarch, i.e. the area of the capital Ravenna, but the term is mainly used to designate all the Byzantine territories in continental and peninsular Italy. According to the legal sources of the time, these territories constituted the so-called ''Provincia Italiae'', on the basis of the fact that they too, until at least the end of the 7th century, fell under the jurisdiction of the exarch and were governed by ''duces'' or ''magistri militum'' under him. The exarchate was established around 584, the year in which the presence of an exarch in Ravenna is attested for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exarchate Of Africa
The Exarchate of Africa was a division of the Byzantine Empire around Carthage that encompassed its possessions on the Western Mediterranean. Ruled by an exarch (viceroy), it was established by the Emperor Maurice in 591 and survived until the Muslim conquest of the Maghreb in the late 7th century. It was, along with the Exarchate of Ravenna, one of two exarchates established following the western reconquests under Emperor Justinian I to administer the territories more effectively. History Background In the Vandalic War of 533, Byzantine forces under Belisarius reconquered the Maghreb along with Corsica and Sardinia and the Balearic Islands. Emperor Justinian I () organized the recovered territories as the Praetorian prefecture of Africa, which included the provinces of Africa Proconsularis, Byzacena, Tripolitania, Numidia, Mauretania Caesariensis and Mauretania Sitifensis, and was centered at Carthage. In the 550s, a Roman expedition succeeded in regaining parts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Droysen - Oströmisches Reich
Johann Gustav Bernhard Droysen (; ; 6 July 180819 June 1884) was a German historian. His history of Alexander the Great was the first work representing a new school of German historical thought that idealized power held by so-called "great" men. Early life and education Droysen was born at Treptow in Pomerania (now Trzebiatów in Poland) on 6 July 1808. His father, Johann Christoph Droysen, was an army chaplain who had been present at the celebrated siege of Kolberg in 1806–1807. As a child, Droysen witnessed some of the military operations during the War of Liberation, his father by then being pastor at Greifenhagen, in the immediate neighbourhood of Stettin, which was held by the French for most of 1813. These youthful impressions laid the foundation of his ardent attachment to the Kingdom of Prussia. He was educated at the gymnasium of Stettin and at the University of Berlin; from 1827 to 1829 he was the private tutor of Felix Mendelssohn, who set several of his poem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praetorian Prefecture Of Italy
The praetorian prefecture of Italy (, in its full form (until 356) ) was one of four praetorian prefectures into which the Late Roman Empire was divided since the first half of the 4th century. It comprised the Italian peninsula, the western Balkans, the upper Danube, Danubian provinces and parts of North Africa. The Prefecture's seat moved from Rome to Mediolanum, Milan and finally, Ravenna. It existed during the Later Roman Empire, and was part of the Western Roman Empire. The prefecture continued to function within Odoacer's and Ostrogothic Kingdom, Ostrogothic kingdoms, and later within the Byzantine Empire, up to 584, when it was reorganized into the Exarchate of Ravenna. Structure and history The prefecture was established in the division of the Empire after the death of Constantine the Great in 337, and was made up of Roman diocese, dioceses. Initially these were the Diocese of Africa, the Roman Italy#Diocletian re-organization, Diocese of Italy, the Diocese of Pannonia, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justinian I
Justinian I (, ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 527 to 565. His reign was marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was expressed by the partial recovery of the territories of the defunct Western Roman Empire. His general, Belisarius, swiftly conquered the Vandal Kingdom in North Africa. Subsequently, Belisarius, Narses, and other generals Gothic War (535–554), conquered the Ostrogothic Kingdom, restoring Dalmatia, Sicily, Italian peninsula, Italy, and Rome to the empire after more than half a century of rule by the Ostrogoths. The Liberius (praetorian prefect), praetorian prefect Liberius reclaimed the south of the Iberian Peninsula, establishing the province of Spania. These campaigns re-established Roman control over the western Mediterranean, increasing the Empire's annual revenue by over a million ''solidi''. During his reign, Justinian also subdued ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |