|
The Greek Myths
''The Greek Myths'' (1955) is a mythography, a compendium of Greek mythology, with comments and analyses, by the poet and writer Robert Graves. Many editions of the book separate it into two volumes. Abridged editions of the work contain only the myths and leave out Graves's commentary. Each myth is presented in the voice of a narrator writing under the Antonines, such as Plutarch or Pausanias, with citations of the classical sources. The literary quality of his retellings is generally praised. Following each retelling, Graves presents his interpretation of its origin and significance, influenced by his belief in a prehistoric Matriarchal religion, as discussed in his book ''The White Goddess'' and elsewhere. Graves's theories and etymologies are rejected by most classical scholars. Graves argued in response that classical scholars lack "the poetic capacity to forensically examine mythology". Contents Graves interpreted Bronze Age Greece as changing from a matriarchal soci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Graves
Captain Robert von Ranke Graves (24 July 1895 – 7 December 1985) was an English poet, soldier, historical novelist and critic. His father was Alfred Perceval Graves, a celebrated Irish poet and figure in the Gaelic revival; they were both Celticists and students of Irish mythology Irish mythology is the body of myths indigenous to the island of Ireland. It was originally Oral tradition, passed down orally in the Prehistoric Ireland, prehistoric era. In the History of Ireland (795–1169), early medieval era, myths were .... Robert Graves produced more than 140 works in his lifetime. His poems, his translations and innovative analysis of the Greek myths, his memoir of his early life—including his role in World War I—''Good-Bye to All That'' (1929), and his speculative study of poetic inspiration ''The White Goddess'' have never been out of print. He was also a renowned short story writer, with stories such as "The Tenement" still being popular today. He ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
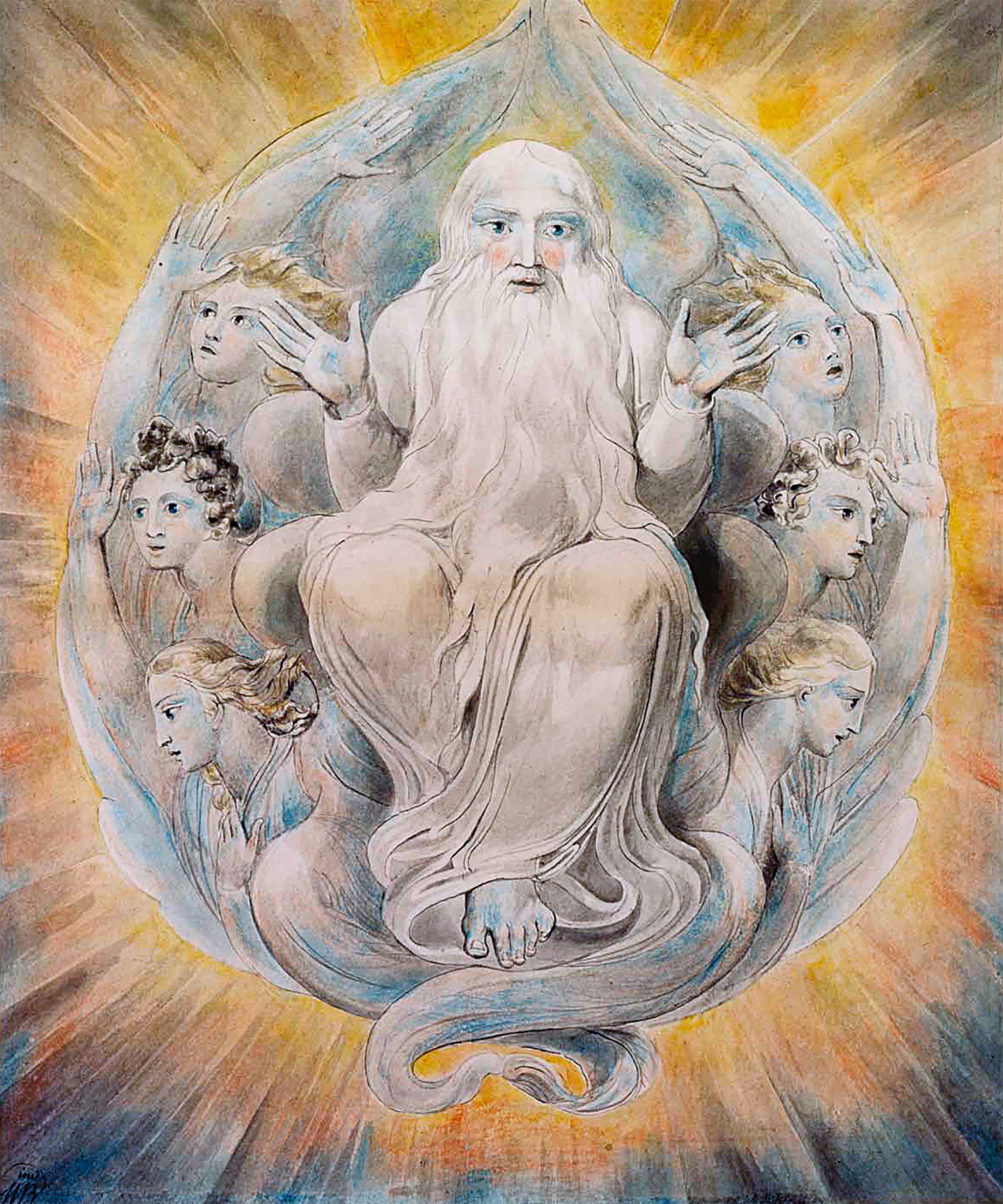
Creator Deity
A creator deity or creator god is a deity responsible for the creation of the Earth, world, and universe in human religion and mythology. In monotheism, the single God is often also the creator. A number of monolatristic traditions separate a secondary creator from a primary transcendent being, identified as a primary creator.(2004) Sacred Books of the Hindus Volume 22 Part 2: Pt. 2, p. 67, R.B. Vidyarnava, Rai Bahadur Srisa Chandra Vidyarnava Monotheism Atenism Initiated by Pharaoh Akhenaten and Queen Nefertiti around 1330 BCE, during the New Kingdom period in ancient Egyptian history. They built an entirely new capital city ( Akhetaten) for themselves and worshippers of their sole creator god in a wilderness. His father used to worship Aten alongside other gods of their polytheistic religion. Aten, for a long time before his father's time, was revered as a god among the many gods and goddesses in Egypt. Atenism was countermanded by later pharaoh Tutankhamun, as chro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoebe (Titaness)
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Phoebe ( ; ) is one of the first generation of Titan (mythology), Titans, who were one set of sons and daughters of Uranus (mythology), Uranus and Gaia, the sky and the earth.Hesiod, ''Theogony'116-138 With her brother and consort Coeus she had two daughters, Leto and Asteria. She is thus the grandmother of the Olympian gods Apollo and Artemis, as well as the witchcraft goddess Hecate. According to the myth, she was the original owner of the site of the Oracle of Delphi before gifting it to her grandson Apollo. Her name, meaning "bright", was also given to a number of lunar goddesses like Artemis and later the Roman goddesses Luna (goddess), Luna and Diana (mythology), Diana, but Phoebe herself was not actively seen as a moon goddess in her own right in ancient religion or mythology. Etymology The Greek name ''Phoíbē'' is the feminine form of ''Phoîbos'' meaning "pure, bright, radiant", an epithet given to Apollo a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperion (mythology)
In Greek mythology, Hyperion (; , 'he who goes before') was one of the twelve Titan children of Gaia (Earth) and Uranus (Sky). With his sister, the Titaness Theia, Hyperion fathered Helios (Sun), Selene (Moon) and Eos (Dawn). Hyperion was, along with his son Helios, a personification of the sun, with the two sometimes identified. John Keats's abandoned epic poem ''Hyperion'' is among the literary works that feature the figure. Etymology "Hyperion" means "he that walks on high" or simply "the god above", often joined with "Helios". There is a possible attestation of his name in Linear B (Mycenaean Greek) in the lacunose form '']pe-rjo- ' (Linear B: Knossos.html" ;"title=", found on the Knossos">KN E 842 tablet (reconstructed ''[upe-rjo-[ne]'') though it has been suggested that the name actually reads "Apollo" (''[a]-pe-rjo-[ne]''). Mythology Hyperion is one of the twelve or thirteen Titans, the children of Gaia and Uranus. In the ''Theogony'', Uranus imprisoned all the ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theia
Theia (; , also rendered Thea or Thia), also called Euryphaessa (, "wide-shining"), is one of the twelve Titans, the children of the earth goddess Gaia and the sky god Uranus in Greek mythology. She is the Greek goddess of sight and vision, and by extension the goddess who endowed gold, silver, and gems with their brilliance and intrinsic value. Her brother-consort is Hyperion, a Titan and god of the sun, and together they are the parents of Helios (the Sun), Selene (the Moon), and Eos (the Dawn). She seems to be the same figure as Aethra, who is the consort of Hyperion and mother of his children in some accounts. Like her husband, Theia features scarcely in myth, being mostly important for the children she bore, though she appears in some texts and rare traditions. Etymology The name ''Theia'' alone means simply "goddess" or "divine"; ''Theia Euryphaessa'' () brings overtones of extent (, ''eurys'', "wide", root: ) and brightness (, ''phaos'', "light", root: φαεσ-). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titan (mythology)
In Greek mythology, the Titans ( ; ) were the pre- Olympian gods. According to the ''Theogony'' of Hesiod, they were the twelve children of the primordial parents Uranus (Sky) and Gaia (Earth). The six male Titans were Oceanus, Coeus, Crius, Hyperion, Iapetus, and Cronus; the six female Titans—called the Titanides () or Titanesses—were Theia, Rhea, Themis, Mnemosyne, Phoebe, and Tethys. After Cronus mated with his older sister Rhea, she bore the first generation of Olympians: the six siblings Zeus, Hades, Poseidon, Hestia, Demeter, and Hera. Certain other descendants of the Titans, such as Prometheus, Atlas, Helios, and Leto, are sometimes also called Titans. The Titans were the former gods: the generation of gods preceding the Olympians. They were overthrown as part of the Greek succession myth, which tells how Cronus seized power from his father Uranus and ruled the cosmos with his fellow Titans before being in turn defeated and replaced as the ruling pantheon o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Olympus
Mount Olympus (, , ) is an extensive massif near the Thermaic Gulf of the Aegean Sea, located on the border between Thessaly and Macedonia (Greece), Macedonia, between the regional units of Larissa (regional unit), Larissa and Pieria (regional unit), Pieria, about southwest from Thessaloniki. Mount Olympus has 52 peaks and deep gorges. The highest peak, Mytikas ( ''Mýtikas''), meaning "nose", rises to and is the highest peak in Greece, and one of the highest peaks in Europe in terms of topographic prominence. In Greek mythology, Olympus is the home of the List of Greek deities, Greek gods, on Mytikas peak. The mountain has exceptional biodiversity and rich flora (plants), flora. It has been a National parks of Greece, National Park, the first in Greece, since 1938. It is also a Man and the Biosphere Programme, World Biosphere Reserve. Olympus remains the most popular hiking summit in Greece, as well as one of the most popular in Europe. Organized mountain refuges and var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcadia (ancient Region)
Arcadia (; ) is a region in the central Peloponnese, Greece. It takes its name from the mythological character Arcas, and in Greek mythology it was the home of the gods Hermes and Pan. In European Renaissance arts, Arcadia was celebrated as an unspoiled, harmonious wilderness; as such, it was referenced in popular culture. The modern regional unit of the same name more or less overlaps with the historical region, but is slightly larger. History Arcadia was gradually linked in a loose confederation that included all the Arcadian towns and was named League of the Arcadians. In the 7th century BC, it successfully faced the threat of Sparta and the Arcadians managed to maintain their independence. They participated in the Persian Wars alongside other Greeks by sending forces to Thermopylae and Plataea. During the Peloponnesian War, Arcadia allied with Sparta and Corinth. In the following years, during the period of the hegemony of Thebes, the Theban general Epaminondas re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
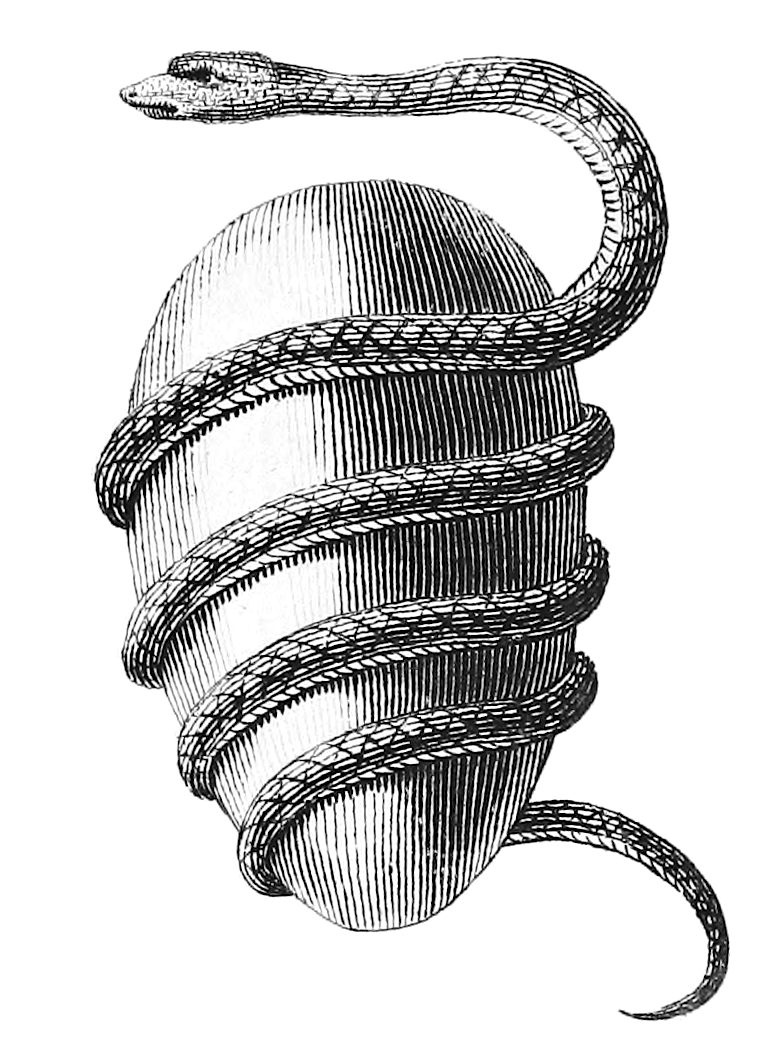
World Egg
''Cosmic Egg'' is the second studio album by Australian rock band Wolfmother, released on 23 October 2009. It is the first album by the second lineup of the band, featuring vocalist, songwriter and lead guitarist Andrew Stockdale, bassist and keyboardist Ian Peres, rhythm guitarist Aidan Nemeth and drummer Dave Atkins, formed in 2009 after original members Chris Ross and Myles Heskett left in August 2008. Upon its release, ''Cosmic Egg'' peaked at number three on the Australian ARIA Albums Chart, the same position as the band's first album. The album was the only studio release by the band to feature Atkins, who left the band in April 2010 during the ''Cosmic Egg'' promotional tour cycle. The album was recorded between April and May 2009 at Sound City Studios and Sunset Sound Studios in Los Angeles, California. The title of the album comes from a position in yoga described by frontman Stockdale as "like the fetal pose". The album's release was promoted throughout 2009 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophion
In some versions of Greek mythology, Ophion (; "serpent"; ''gen''.: Ὀφίωνος), also called Ophioneus ({{lang, grc, Ὀφιονεύς) ruled the world with Eurynome before the two of them were cast down by Cronus and Rhea. Mythology Pherecydes of Syros's ''Heptamychia'' is the first attested mention of Ophion. The story was apparently popular in Orphic poetry, of which only fragments survive. Apollonius of Rhodes in his ''Argonautica'' (1.495f) summarizes a song of Orpheus: :He sang how the earth, the heaven and the sea, once mingled together in one form, after deadly strife were separated each from the other; and how the stars and the moon and the paths of the sun ever keep their fixed place in the sky; and how the mountains rose, and how the resounding rivers with their nymphs came into being and all creeping things. And he sang how first of all Ophion and Eurynome, daughter of Oceanus, held the sway of snowy Olympus, and how through strength of arm one yielded his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spontaneous Generation
Spontaneous generation is a superseded scientific theory that held that living creatures could arise from non-living matter and that such processes were commonplace and regular. It was hypothesized that certain forms, such as fleas, could arise from inanimate matter such as dust, or that maggots could arise from dead flesh. The doctrine of spontaneous generation was coherently synthesized by the Greek philosopher and naturalist Aristotle, who compiled and expanded the work of earlier natural philosophers and the various ancient explanations for the appearance of organisms. Spontaneous generation was taken as scientific fact for two millennia. Though challenged in the 17th and 18th centuries by the experiments of the Italian biologists Francesco Redi and Lazzaro Spallanzani, it was not discredited until the work of the French chemist Louis Pasteur and the Irish physicist John Tyndall in the mid-19th century. Among biologists, rejecting spontaneous genesis is no longer con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pneuma
''Pneuma'' () is an ancient Greek word for "breathing, breath", and in a religious context for "spirit (animating force), spirit". It has various technical meanings for medical writers and philosophers of classical antiquity, particularly in regard to physiology, and is also used in Greek translations of ''ruach'' :wikt:רוח, רוח in the Hebrew Bible, and in the Novum Testamentum Graece, Greek New Testament. In classical philosophy, it is distinguishable from ''Psyche (psychology)#Etymology, psyche'' (), which originally meant "breath of life", but is regularly translated as "spirit" or most often "soul#Philosophical views, soul". Presocratics , "air in motion, breath, wind", is equivalent in the material monism of Anaximenes of Miletus, Anaximenes to (, "air") as the element from which all else originated. This usage is the earliest extant occurrence of the term in philosophy. A quotation from Anaximenes observes that "just as our soul (''psyche''), being air (), holds us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |